Sous vide allows precise temperature control for slow, uniform marination, enhancing flavor penetration and tenderness without mechanical disruption. Ultrasonic homogenization accelerates marination by breaking down tissue structure through high-frequency sound waves, promoting faster infusion of marinades. Choosing between the two depends on whether gradual flavor development or rapid infusion is desired for the meat.
Table of Comparison
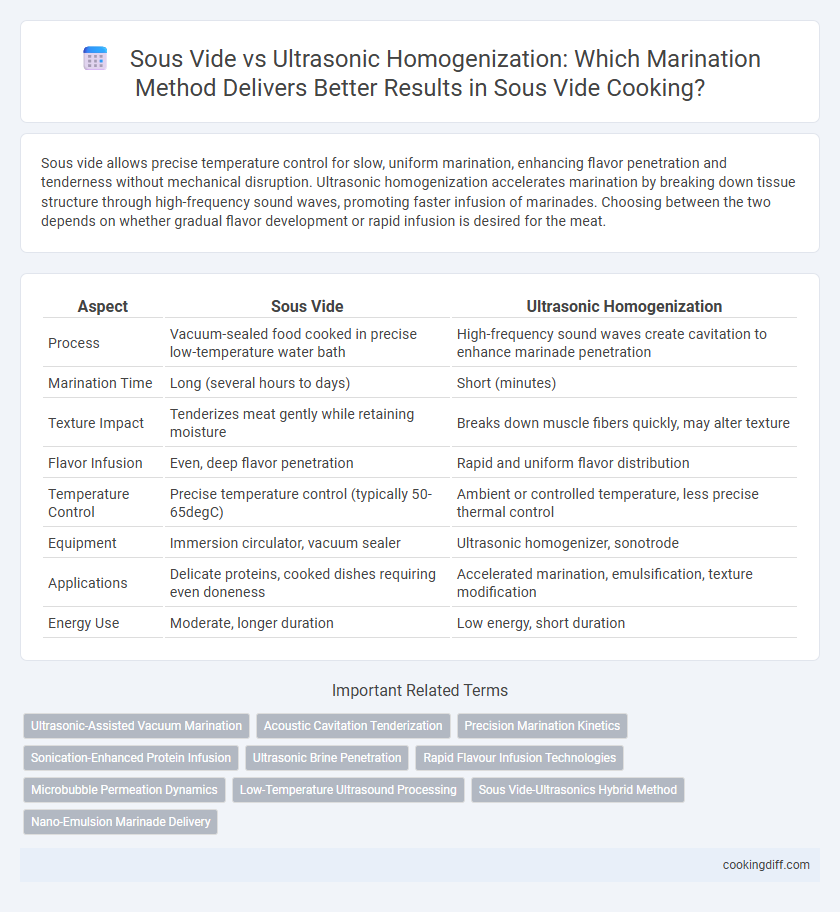
| Aspect | Sous Vide | Ultrasonic Homogenization |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Vacuum-sealed food cooked in precise low-temperature water bath | High-frequency sound waves create cavitation to enhance marinade penetration |
| Marination Time | Long (several hours to days) | Short (minutes) |
| Texture Impact | Tenderizes meat gently while retaining moisture | Breaks down muscle fibers quickly, may alter texture |
| Flavor Infusion | Even, deep flavor penetration | Rapid and uniform flavor distribution |
| Temperature Control | Precise temperature control (typically 50-65degC) | Ambient or controlled temperature, less precise thermal control |
| Equipment | Immersion circulator, vacuum sealer | Ultrasonic homogenizer, sonotrode |
| Applications | Delicate proteins, cooked dishes requiring even doneness | Accelerated marination, emulsification, texture modification |
| Energy Use | Moderate, longer duration | Low energy, short duration |
Introduction: Comparing Sous Vide and Ultrasonic Homogenization for Marination
Sous vide and ultrasonic homogenization are advanced techniques used to enhance marination by improving flavor penetration and texture. Sous vide cooks food at precise low temperatures in vacuum-sealed bags, allowing even absorption of marinades while preserving moisture. Ultrasonic homogenization employs high-frequency sound waves to create cavitation, breaking down marinade particles for faster and more uniform diffusion into the food.
Principles of Sous Vide Marination
Sous vide marination utilizes precise temperature control in a vacuum-sealed environment to enhance flavor absorption and tenderize meat through enzymatic activity. This method ensures uniform heat distribution, preserving texture and moisture while allowing marinades to penetrate deeply over extended cooking times. Unlike ultrasonic homogenization, which relies on high-frequency sound waves to mechanically disrupt tissue, sous vide maintains the integrity of food structure for consistent, flavorful results.
How Ultrasonic Homogenization Works in Marination
Ultrasonic homogenization uses high-frequency sound waves to create microscopic cavitation bubbles in the marinade, which implode and generate intense local pressure and shear forces. These forces break down muscle fibers and effectively disperse marinade molecules for deeper penetration in a shorter time compared to traditional methods.
In marination, ultrasonic waves facilitate rapid emulsification and uniform mixing, enhancing flavor absorption and texture modification. The cavitation process increases cell membrane permeability, allowing marinade ingredients to penetrate meat tissue more efficiently. This technique offers precise control over marination parameters and reduces processing time, making it a powerful alternative to sous vide for flavor infusion.
Speed and Efficiency: Sous Vide vs Ultrasonic Homogenization
Sous vide marination offers precise temperature control and uniform cooking, but typically requires several hours to achieve flavor infusion. Ultrasonic homogenization significantly accelerates this process by using high-frequency sound waves to rapidly penetrate and blend marinades into the food matrix.
The efficiency of ultrasonic homogenization reduces marination time from hours to minutes, boosting productivity for commercial kitchens. While sous vide excels in consistent texture development, ultrasonic treatment prioritizes speed and enhanced flavor absorption in a fraction of the time.
Flavor Penetration: Which Method Delivers Better Results?
| Flavor Penetration Efficiency | Sous vide uses precise temperature control and prolonged cooking times to evenly tenderize meat fibers, allowing deep and consistent marinade absorption. Ultrasonic homogenization employs high-frequency sound waves to break down marinade particles and muscle tissue, rapidly enhancing flavor infusion but may result in uneven penetration in thicker cuts. Studies indicate sous vide achieves more uniform flavor distribution in dense proteins, while ultrasonic homogenization excels in speed and surface-level infusion. |
Texture and Tenderness: Effects of Sous Vide and Ultrasonics
Sous vide cooking enhances texture and tenderness by precisely controlling temperature over extended periods, leading to uniform protein denaturation and gelatinization. Ultrasonic homogenization improves marination by disrupting muscle fibers and increasing marinade penetration, resulting in faster tenderization but sometimes less uniform texture compared to sous vide.
- Sous Vide Texture - Achieves consistent softness by gently breaking down collagen without overcooking muscle fibers.
- Ultrasonic Tenderness - Utilizes cavitation effects to mechanically fragment muscle tissues, accelerating marinade absorption.
- Comparative Outcome - Sous vide offers superior uniformity and moisture retention, while ultrasonics provide rapid but occasionally uneven tenderization.
Choice between sous vide and ultrasonic homogenization depends on desired balance between marination speed and texture quality.
Equipment and Cost Considerations
Sous vide equipment typically includes immersion circulators and vacuum sealers, offering precise temperature control for consistent marination results. Initial investment ranges from $100 to $400, making it cost-effective for both home cooks and professional kitchens.
Ultrasonic homogenization requires specialized ultrasonic processors that operate at high frequencies, with prices often exceeding $1,000, reflecting their industrial application focus. Maintenance and operational costs are higher due to the complexity of the machinery and the need for skilled handling.
Safety and Consistency in Marination Processes
Which method ensures greater safety and consistency in marination processes, sous vide or ultrasonic homogenization? Sous vide offers precise temperature control that minimizes bacterial growth, enhancing food safety during marination. Ultrasonic homogenization improves uniformity in flavor absorption but requires strict monitoring to avoid microbial risks.
Best Use Cases for Each Technique
Sous vide offers precise temperature control ideal for evenly marinating proteins over extended periods, enhancing flavor penetration without overcooking. Ultrasonic homogenization accelerates marinade absorption through cavitation, making it perfect for rapid preparation and uniform texture modification.
- Sous vide - Best for slow marination of delicate meats requiring precise doneness and subtle flavor infusion.
- Ultrasonic homogenization - Ideal for quick marination of tougher cuts where breaking down muscle fibers is desired.
- Combination use - Using ultrasonic treatment before sous vide can maximize flavor absorption while maintaining texture integrity.
Related Important Terms
Ultrasonic-Assisted Vacuum Marination
Ultrasonic-assisted vacuum marination enhances flavor infusion by using high-frequency sound waves combined with vacuum pressure to accelerate the penetration of marinades into meat fibers, resulting in more uniform and faster marination compared to traditional sous vide methods. This technique improves tenderness and juiciness while maintaining food safety, making it a cutting-edge alternative to conventional slow marination processes.
Acoustic Cavitation Tenderization
Acoustic cavitation in ultrasonic homogenization generates microbubbles that implode, producing intense shear forces and localized high temperatures, which enhance tenderization by disrupting muscle fibers more effectively than sous vide's low-temperature, long-time cooking method. This physical mechanism accelerates marinade penetration and texture modification, offering faster and potentially more uniform meat tenderization compared to the gradual enzymatic and thermal effects achieved with sous vide.
Precision Marination Kinetics
Sous vide ensures precise temperature control and uniform heat transfer, enabling consistent diffusion rates for even marinade penetration over extended cooking times. Ultrasonic homogenization accelerates marination kinetics by generating cavitation and microstreaming, enhancing mass transfer and improving flavor infusion efficiency in shorter durations.
Sonication-Enhanced Protein Infusion
Sonication-enhanced protein infusion via ultrasonic homogenization significantly improves marinade penetration by disrupting muscle fibers at a microscopic level, accelerating flavor absorption compared to sous vide alone. Ultrasonic waves increase cell membrane permeability, allowing for more efficient and uniform distribution of marinade compounds within the meat.
Ultrasonic Brine Penetration
Ultrasonic homogenization enhances brine penetration by generating cavitation bubbles that disrupt meat fibers, enabling faster and deeper marinade absorption compared to traditional sous vide methods. This ultrasonic brine penetration improves flavor infusion and tenderness in a reduced marination time, optimizing the meat preparation process.
Rapid Flavour Infusion Technologies
Sous vide and ultrasonic homogenization are rapid flavor infusion technologies used for marination, with sous vide providing precise temperature control to enhance tenderness and even flavor distribution over extended cooking times. Ultrasonic homogenization employs high-frequency sound waves to create microscopic cavitation, accelerating marinade absorption and dramatically reducing marination time while maintaining texture integrity.
Microbubble Permeation Dynamics
Sous vide enhances marination through controlled temperature and time, promoting uniform protein denaturation and improved flavor absorption, while ultrasonic homogenization accelerates microbubble permeation dynamics by generating cavitation effects that create intense microjets, increasing marinade diffusion into the meat matrix. The synergistic impact of ultrasonic-induced microbubbles leads to faster and deeper marinade penetration compared to traditional sous vide marination techniques.
Low-Temperature Ultrasound Processing
Low-temperature ultrasound processing in sous vide marination enhances flavor infusion and meat tenderness by creating microchannels for marinade penetration without compromising texture. This technique offers precise control over temperature and ultrasonic intensity, resulting in uniform marinade absorption and improved meat quality compared to traditional ultrasonic homogenization.
Sous Vide-Ultrasonics Hybrid Method
The Sous Vide-Ultrasonics hybrid method combines precise temperature control with ultrasonic cavitation to enhance marination efficiency, resulting in improved flavor penetration and texture uniformity. This synergy accelerates marinade absorption while preserving meat integrity, outperforming traditional Sous Vide or ultrasonic homogenization used independently.
Sous vide vs ultrasonic homogenization for marination. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com