Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control for evenly cooked, tender meat by sealing food in a vacuum bag and immersing it in a water bath for extended periods. Ultrasonic tenderization uses high-frequency sound waves to break down muscle fibers quickly, enhancing meat tenderness but without the temperature precision that sous vide offers. Combining both methods can optimize texture and flavor, with ultrasonic tenderization improving tenderness before the sous vide process locks in juiciness and uniform doneness.
Table of Comparison
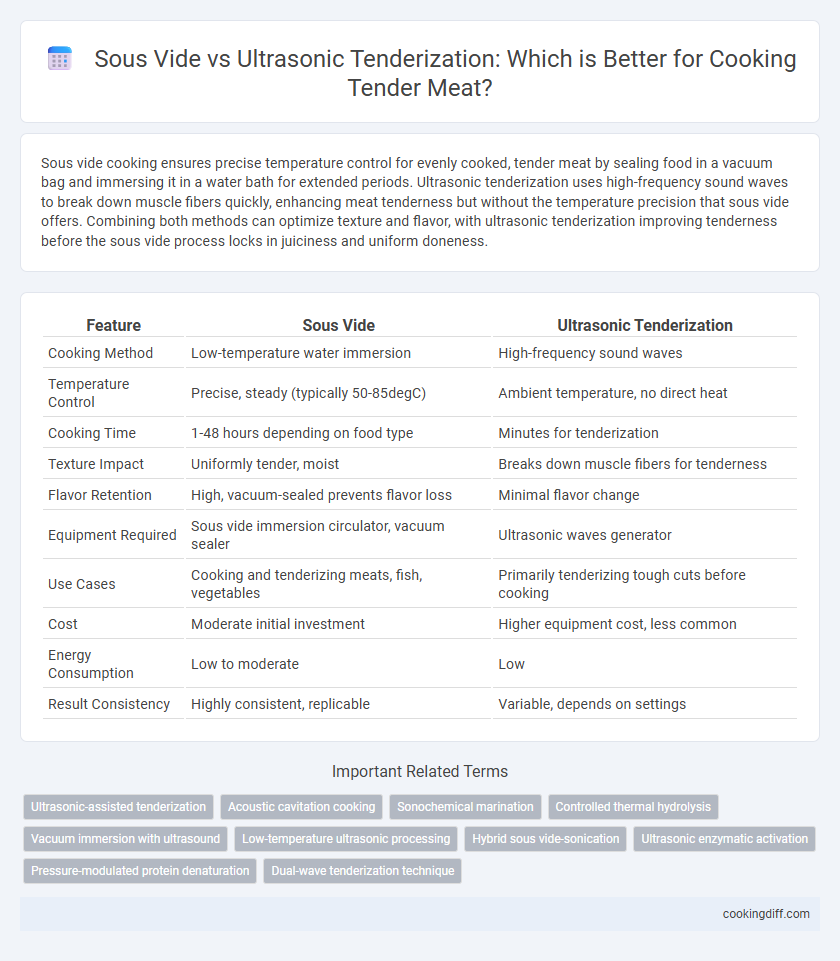
| Feature | Sous Vide | Ultrasonic Tenderization |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Low-temperature water immersion | High-frequency sound waves |
| Temperature Control | Precise, steady (typically 50-85degC) | Ambient temperature, no direct heat |
| Cooking Time | 1-48 hours depending on food type | Minutes for tenderization |
| Texture Impact | Uniformly tender, moist | Breaks down muscle fibers for tenderness |
| Flavor Retention | High, vacuum-sealed prevents flavor loss | Minimal flavor change |
| Equipment Required | Sous vide immersion circulator, vacuum sealer | Ultrasonic waves generator |
| Use Cases | Cooking and tenderizing meats, fish, vegetables | Primarily tenderizing tough cuts before cooking |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher equipment cost, less common |
| Energy Consumption | Low to moderate | Low |
| Result Consistency | Highly consistent, replicable | Variable, depends on settings |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Ultrasonic Tenderization
Sous vide is a precise cooking technique that involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a water bath at controlled temperatures for extended periods. Ultrasonic tenderization uses high-frequency sound waves to disrupt muscle fibers, enhancing meat texture before cooking.
- Sous vide method - Employs temperature control to ensure even cooking and retain moisture and flavor.
- Ultrasonic tenderization - Breaks down connective tissues through cavitation without altering the food's temperature.
- Cooking outcomes - Sous vide ensures consistent doneness while ultrasonic tenderization improves tenderness before cooking.
Both techniques offer innovative ways to elevate meat quality but differ fundamentally in their approach to texture and cooking precision.
Principles Behind Sous Vide Cooking
Sous vide cooking relies on precise temperature control in a water bath to evenly cook food over extended periods, preserving moisture and texture. This method contrasts with ultrasonic tenderization, which uses high-frequency sound waves to break down muscle fibers quickly, enhancing tenderness but not cooking the food.
- Temperature Precision - Sous vide maintains a consistent temperature, typically between 50degC to 85degC, ensuring uniform doneness throughout the food.
- Moisture Retention - Vacuum sealing in sous vide cooking prevents moisture loss, resulting in juicier and more flavorful dishes.
- Time-Dependent Cooking - Extended cooking times allow collagen to break down slowly, tenderizing tough cuts without overcooking.
How Ultrasonic Tenderization Works
| Ultrasonic tenderization uses high-frequency sound waves to create microscopic cavitation bubbles in meat, disrupting muscle fibers and connective tissues to enhance tenderness. This non-thermal technique accelerates enzyme activity and improves marinade absorption without compromising the meat's structural integrity. Combining ultrasonic tenderization with sous vide cooking can optimize texture and flavor by ensuring uniform tenderization and precise temperature control. |
Temperature Control: Sous Vide vs Ultrasonic Methods
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control by maintaining water at a consistent level, typically within +-0.1degC, ensuring even cooking and optimal texture. Ultrasonic tenderization, while effective for breaking down muscle fibers, lacks the ability to regulate cooking temperatures throughout the process.
The precise temperature control in sous vide allows for gradual protein denaturation, preventing overcooking and preserving juiciness. Ultrasonic methods focus on mechanical tenderization without regulated thermal input, often requiring subsequent cooking to achieve desired doneness. Therefore, sous vide provides superior control over both temperature and texture compared to ultrasonic tenderization techniques.
Impact on Meat Texture and Tenderness
Sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control to break down collagen gradually, resulting in consistent tenderness while maintaining the meat's natural juices. Ultrasonic tenderization employs high-frequency sound waves to disrupt muscle fibers, enhancing tenderness but with a quicker, less uniform effect.
Meat treated sous vide shows a uniform texture due to prolonged exposure to low temperatures, preserving flavor and moisture. Ultrasonic methods can create localized softening but may lead to uneven texture and potential loss of juiciness in comparison.
Flavor Retention and Enhancement
How does flavor retention compare between sous vide and ultrasonic tenderization in cooking? Sous vide preserves natural juices and enhances the meat's intrinsic flavors by cooking evenly at precise temperatures. Ultrasonic tenderization improves texture but may cause slight flavor loss due to cell disruption during the process.
Cooking Times: Efficiency Comparison
Sous vide cooking typically requires longer cooking times, ranging from 1 to 48 hours depending on the type and thickness of the food, to achieve precise temperature control and even doneness. Ultrasonic tenderization significantly reduces cooking times by breaking down muscle fibers prior to cooking, allowing faster heat penetration and shorter overall preparation. The efficiency comparison highlights ultrasonic tenderization as a time-saving technique, while sous vide excels in consistent texture and flavor development through extended low-temperature cooking.
Nutrient Preservation in Both Techniques
Sous vide cooking maintains nutrient retention by precisely controlling temperature and cooking time, which minimizes nutrient loss through oxidation and heat degradation. Ultrasonic tenderization uses high-frequency sound waves to break down muscle fibers without significantly impacting water-soluble vitamins and minerals.
Both techniques preserve essential nutrients better than traditional high-heat cooking methods, with sous vide excelling in preventing vitamin C and B-vitamin loss due to low-temperature cooking. Ultrasonic tenderization enhances texture without altering nutrient composition, supporting overall food quality and nutritional value.
Equipment Required for Sous Vide and Ultrasonic Tenderization
Sous vide cooking requires precise temperature control equipment, such as immersion circulators and vacuum sealers, to ensure even cooking. Ultrasonic tenderization demands specialized ultrasonic devices to generate high-frequency sound waves that break down meat fibers.
- Immersion Circulator - Maintains water bath temperature within +-0.1degC for consistent sous vide cooking.
- Vacuum Sealer - Removes air from packaging to enhance heat transfer and food preservation in sous vide.
- Ultrasonic Tenderizer - Utilizes high-frequency sound waves (20 kHz to 40 kHz) to disrupt muscle fibers and improve meat tenderness.
Related Important Terms
Ultrasonic-assisted tenderization
Ultrasonic-assisted tenderization uses high-frequency sound waves to break down muscle fibers and connective tissues, enhancing meat texture and reducing cooking time compared to traditional sous vide methods. This technology improves marinade absorption and uniform tenderization, making it a valuable complement to precise temperature control in sous vide cooking.
Acoustic cavitation cooking
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control for even doneness, while ultrasonic tenderization leverages acoustic cavitation to break down muscle fibers, enhancing meat tenderness without altering cooking temperature. Acoustic cavitation induces microbubbles that implode, creating mechanical effects that speed up marination and improve texture, complementing traditional sous vide methods.
Sonochemical marination
Sonochemical marination in ultrasonic tenderization enhances flavor penetration and accelerates meat tenderizing by creating cavitation bubbles that disrupt muscle fibers, achieving uniform texture. Sous vide cooking provides precise temperature control for consistent doneness but lacks the intense mechanical effects of ultrasound, making ultrasonic sonochemical marination a complementary method to improve marinade absorption before sous vide cooking.
Controlled thermal hydrolysis
Sous vide utilizes precise temperature control to achieve controlled thermal hydrolysis, breaking down collagen and proteins slowly for enhanced tenderness and flavor retention. Ultrasonic tenderization relies on high-frequency waves to disrupt muscle fibers but lacks the uniform thermal environment essential for optimal hydrolytic enzyme activation seen in sous vide cooking.
Vacuum immersion with ultrasound
Vacuum immersion with ultrasound combines sous vide's precise temperature control and ultrasonic waves to enhance tenderization and marination by accelerating enzyme activity and improving flavor penetration. This hybrid method results in more uniform texture and reduced cooking time compared to traditional sous vide or ultrasonic tenderization alone.
Low-temperature ultrasonic processing
Low-temperature ultrasonic processing enhances sous vide cooking by improving meat tenderness through precise cavitation effects without compromising the controlled temperature environment essential for sous vide. Combining ultrasonic tenderization with sous vide results in accelerated marination, reduced cooking time, and superior texture consistency due to enhanced protein breakdown at low temperatures.
Hybrid sous vide-sonication
Hybrid sous vide-sonication combines precise temperature control with ultrasonic waves to enhance meat tenderness, significantly reducing cooking time compared to traditional sous vide methods. This innovative technique disrupts muscle fibers while maintaining juiciness and flavor, offering a superior texture and consistent results for premium culinary applications.
Ultrasonic enzymatic activation
Ultrasonic enzymatic activation in tenderization uses high-frequency sound waves to accelerate enzyme activity, breaking down muscle fibers more efficiently than traditional sous vide cooking. This method enhances meat texture by promoting protein degradation at a molecular level, resulting in faster and more uniform tenderization compared to solely temperature-controlled sous vide techniques.
Pressure-modulated protein denaturation
Sous vide cooking utilizes precise temperature control to induce pressure-modulated protein denaturation, resulting in evenly cooked, tender meats through gradual collagen breakdown. In contrast, ultrasonic tenderization accelerates protein denaturation by applying high-frequency vibrations that disrupt muscle fibers and improve tenderness rapidly but may lack the uniform texture achieved by sous vide.
Sous vide vs ultrasonic tenderization for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com