Electric steamers offer precise temperature control and consistent steam output, making them ideal for evenly cooking pet food without the risk of burning. Stovetop steamers provide a more traditional method but require careful monitoring to maintain water levels and prevent overheating, which can be challenging during long cooking sessions. Choosing an electric steamer ensures convenience and safety, especially for pet owners seeking efficiency and reliable results.
Table of Comparison
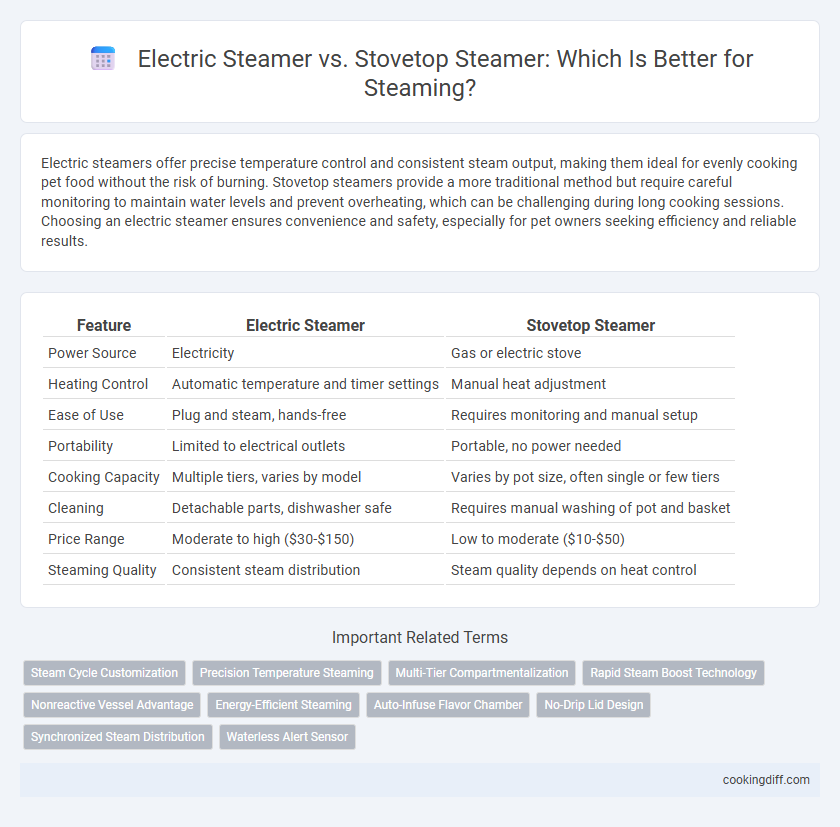
| Feature | Electric Steamer | Stovetop Steamer |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Electricity | Gas or electric stove |
| Heating Control | Automatic temperature and timer settings | Manual heat adjustment |
| Ease of Use | Plug and steam, hands-free | Requires monitoring and manual setup |
| Portability | Limited to electrical outlets | Portable, no power needed |
| Cooking Capacity | Multiple tiers, varies by model | Varies by pot size, often single or few tiers |
| Cleaning | Detachable parts, dishwasher safe | Requires manual washing of pot and basket |
| Price Range | Moderate to high ($30-$150) | Low to moderate ($10-$50) |
| Steaming Quality | Consistent steam distribution | Steam quality depends on heat control |
Introduction to Electric vs Stovetop Steamers
| Electric Steamer | Plug-in device with built-in timers and temperature settings for consistent steaming results. |
| Stovetop Steamer | Requires placing a pot with boiling water on a stove, using steam baskets to cook food naturally. |
| Efficiency | Electric steamers offer precise control and hands-free operation, while stovetop steamers depend on manual heat adjustments. |
| Portability | Stovetop steamers are more versatile for different heat sources; electric steamers need a power outlet. |
How Electric Steamers Work
Electric steamers use built-in heating elements to boil water, producing consistent steam for cooking. This method offers precise temperature control compared to stovetop steamers, which rely on the stove's heat source.
- Integrated Heating Element - Electric steamers contain a heating element that directly heats water, ensuring rapid and even steam generation.
- Temperature Regulation - These devices often include thermostats or timers to maintain optimal steaming temperature and cooking time.
- Energy Efficiency - Electric steamers typically use less energy by maintaining steady heat without frequent stove adjustments.
How Stovetop Steamers Work
Stovetop steamers operate by placing a pot of boiling water beneath a perforated basket that holds the food, allowing steam to rise and cook the ingredients evenly. The heat source from the stove maintains consistent boiling, generating continuous steam for efficient cooking.
These steamers rely on direct contact with the heat stove, which requires careful temperature monitoring to prevent water from evaporating completely. Their design uses simple materials, making them an affordable and versatile option for steaming vegetables, seafood, and dumplings.
Steaming Performance Comparison
Electric steamers provide consistent temperature control and automated timing, ensuring even cooking results. Stovetop steamers rely on manual monitoring and heat adjustment, which can lead to variability in steaming performance.
- Temperature Consistency - Electric steamers maintain steady heat, optimizing nutrient retention and texture.
- Ease of Use - Stovetop steamers require more attention to prevent overheating or undercooking.
- Cooking Efficiency - Electric steamers often feature multi-tier compartments, enhancing simultaneous food preparation.
Versatility: What Can You Steam?
What foods can you steam using an electric steamer compared to a stovetop steamer? Electric steamers offer multiple tiers allowing simultaneous steaming of vegetables, fish, and rice, enhancing meal versatility. Stovetop steamers provide flexible temperature control for steaming delicate items like dumplings and seafood, making them suitable for a variety of dishes.
Energy Efficiency and Power Consumption
Electric steamers generally offer superior energy efficiency due to their precise temperature controls and insulated cooking chambers that minimize heat loss. Stovetop steamers rely on external heat sources, which can lead to higher power consumption and longer cooking times. Studies show electric models can reduce energy use by up to 30% compared to traditional stovetop methods.
Ease of Use: Setup and Controls
Electric steamers offer a straightforward setup with preset controls that simplify the steaming process, making them user-friendly for beginners. Stovetop steamers require manual temperature adjustments and closer attention to water levels, demanding more hands-on operation.
- Electric steamers have digital timers and automatic shut-off - This enhances convenience by reducing the need for constant monitoring during steaming.
- Stovetop steamers need manual heat regulation - Users must adjust the flame to maintain consistent steam, which can be less intuitive.
- Electric steamers often come with stackable compartments - Allowing easy addition or removal of food layers without interrupting the process.
For those seeking simplicity and minimal supervision, electric steamers provide a more hassle-free steaming experience compared to stovetop models.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Electric steamers often feature detachable components and dishwasher-safe parts, making cleaning straightforward and time-efficient. Stovetop steamers, typically made of metal or bamboo, require manual scrubbing and careful drying to prevent rust or mold buildup. Regular descaling is essential for electric steamers to maintain optimal performance, while stovetop steamers benefit from thorough drying to extend their lifespan.
Cost Comparison: Upfront and Long-Term
Electric steamers typically have a higher upfront cost ranging from $40 to $150, while stovetop steamers are more affordable, often priced between $10 and $50. However, electric models offer energy efficiency that can reduce long-term electricity costs compared to using a stovetop burner.
Stovetop steamers rely on gas or electric stove energy, which may vary in cost depending on local utility rates and usage frequency. Over time, electric steamers may provide savings through quicker cooking times and automated temperature control, minimizing wasted energy.
Related Important Terms
Steam Cycle Customization
Electric steamers offer precise steam cycle customization with programmable timers and temperature controls, allowing consistent and tailored cooking for various foods. Stovetop steamers rely on manual heat adjustment, making it harder to maintain consistent steam cycles and potentially leading to less precise cooking results.
Precision Temperature Steaming
Electric steamers offer precise temperature control through built-in thermostats, ensuring consistent and optimal steaming conditions that preserve nutrients and texture. Stovetop steamers rely on manual heat adjustment, making it challenging to maintain exact temperatures, which can result in uneven cooking or nutrient loss.
Multi-Tier Compartmentalization
Electric steamers typically offer multi-tier compartmentalization with separate, stackable trays that allow simultaneous cooking of different foods without flavor mixing, enhancing efficiency and meal variety. Stovetop steamers generally feature a single or dual-tier design, limiting capacity and requiring more attention to water levels and heat control for even steaming.
Rapid Steam Boost Technology
Electric steamers with Rapid Steam Boost Technology offer faster steam generation and more consistent heat distribution compared to stovetop steamers, resulting in quicker cooking times and better nutrient retention. This technology enhances efficiency by producing higher pressure steam rapidly, ensuring even cooking and superior texture in steamed foods.
Nonreactive Vessel Advantage
Electric steamers offer a nonreactive cooking environment, preventing acidic or alkaline foods from interacting with the vessel, which preserves the flavor and nutritional content during steaming. In contrast, stovetop steamers made from reactive metals like aluminum can alter the taste and degrade sensitive nutrients due to chemical reactions.
Energy-Efficient Steaming
Electric steamers use precise temperature controls and insulated chambers to minimize energy loss, making them significantly more energy-efficient than traditional stovetop steamers that rely on continuous boiling. Stovetop steamers often consume more fuel due to longer heating times and less effective heat retention, resulting in higher overall energy usage.
Auto-Infuse Flavor Chamber
Electric steamers with Auto-Infuse Flavor Chambers enhance steaming by circulating infused herbs and spices, delivering consistent and intensified flavors directly into the food. Stovetop steamers lack this technology, relying solely on basic steam vapor, which often results in less pronounced aromatic infusion.
No-Drip Lid Design
Electric steamers often feature a no-drip lid design that prevents condensation from dripping back onto food, preserving texture and flavor, whereas stovetop steamers typically lack this specialized feature, making them more prone to moisture accumulation. The no-drip lid enhances cooking efficiency by maintaining consistent steam circulation and reducing cleanup efforts in electric steamers.
Synchronized Steam Distribution
Electric steamers provide synchronized steam distribution through built-in timers and heating elements that ensure consistent temperature and moisture levels, enhancing even cooking. Stovetop steamers rely on manual heat control, which can result in uneven steam output and less precise synchronization during the steaming process.
Electric steamer vs stovetop steamer for steaming. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com