Steaming dumplings uses direct hot steam to cook, preserving their texture and allowing for even heat distribution, while micro-steaming employs gentle, controlled steam bursts that prevent sogginess and maintain delicate wrappers. Micro-steaming offers a precise cooking environment ideal for fragile dumplings needing careful handling, whereas traditional steaming works well for sturdier varieties. Choosing between the two methods depends on desired texture and the dumpling's thickness, with micro-steaming enhancing softness and moisture retention.
Table of Comparison
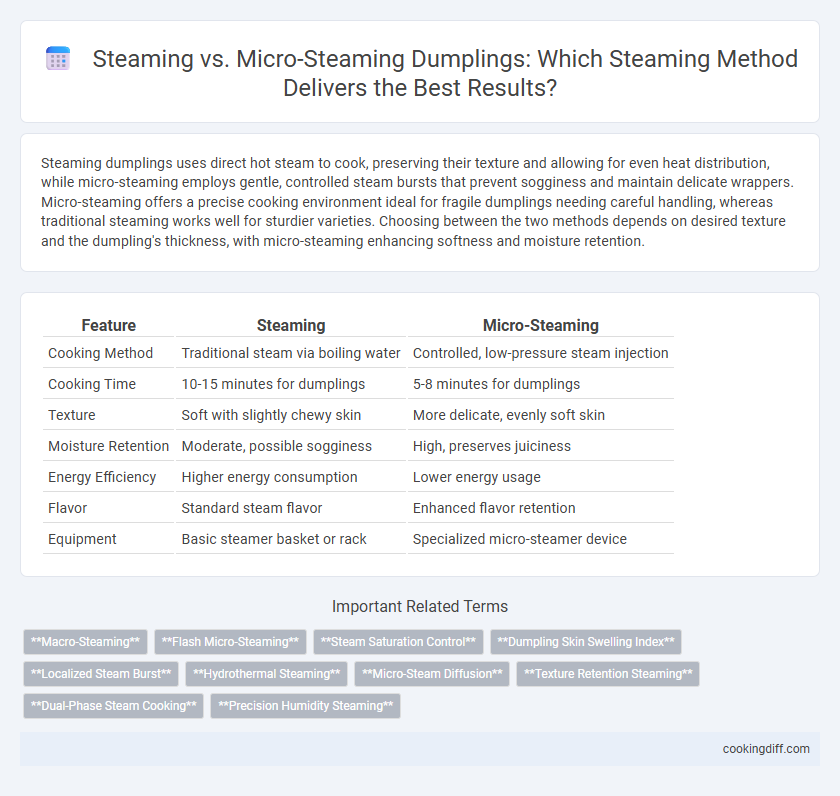
| Feature | Steaming | Micro-Steaming |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Traditional steam via boiling water | Controlled, low-pressure steam injection |
| Cooking Time | 10-15 minutes for dumplings | 5-8 minutes for dumplings |
| Texture | Soft with slightly chewy skin | More delicate, evenly soft skin |
| Moisture Retention | Moderate, possible sogginess | High, preserves juiciness |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher energy consumption | Lower energy usage |
| Flavor | Standard steam flavor | Enhanced flavor retention |
| Equipment | Basic steamer basket or rack | Specialized micro-steamer device |
Introduction to Steaming and Micro-Steaming Dumplings
Steaming dumplings involves cooking them with moist heat, preserving their delicate texture and enhancing flavor without drying. Micro-steaming uses smaller, controlled bursts of steam to cook dumplings more evenly and quickly while retaining moisture. Both methods offer unique benefits, with traditional steaming providing a classic tender bite and micro-steaming optimizing texture and juiciness.
What is Traditional Steaming?
Traditional steaming involves cooking dumplings by surrounding them with hot steam in a closed environment, typically using a bamboo or metal steamer basket. This method ensures even heat distribution and preserves the dumplings' moisture and texture.
- Preserves Flavor - Steaming retains the natural taste and juiciness of the dumpling filling without drying it out.
- Gentle Cooking - Uses indirect heat, preventing the dumplings from becoming tough or overcooked.
- Simple Equipment - Requires only a pot and a steamer basket, making it accessible and easy to use.
Traditional steaming remains a popular method for preparing delicate and flavorful dumplings.
What is Micro-Steaming?
Micro-steaming is a precise cooking method that uses minimal steam to gently cook dumplings, preserving their delicate texture and flavors. This technique maintains better moisture control compared to traditional steaming, resulting in a tender yet firm dumpling skin.
Unlike conventional steaming which employs continuous high steam, micro-steaming applies low-intensity steam in short bursts to prevent overcooking. Chefs often prefer micro-steaming for premium dumplings to achieve optimal taste and presentation.
Key Equipment for Each Method
| Steaming Method | Traditional bamboo steamers are essential, providing even heat distribution and moisture retention for dumplings. Stainless steel steamers offer durability and quick heating, often used over a boiling water pot. Heat-resistant glass lids help monitor cooking without releasing steam, preserving the dumplings' texture. |
|---|---|
| Micro-Steaming Method | Specialized microwave steamers with vented lids are designed to trap steam effectively while preventing sogginess. These containers require microwave-safe, BPA-free materials to ensure food safety and optimal heat retention. Built-in moisture control vents facilitate rapid steam circulation, enhancing quick cooking efficiency. |
Time and Temperature Differences
Traditional steaming for dumplings typically uses temperatures around 212degF (100degC) and requires 10 to 15 minutes to fully cook, ensuring even heat distribution. Micro-steaming operates at slightly lower temperatures near 180degF (82degC) but compensates with increased steam pressure, reducing cooking time to approximately 7 to 10 minutes.
Steaming maintains a consistent environment that gently cooks dumplings, preserving texture and moisture over a longer period. Micro-steaming delivers faster results by intensifying steam penetration, which can impact the delicate dough and filling differently compared to conventional steaming.
Texture Comparison: Steaming vs Micro-Steaming
Steaming dumplings produces a soft, tender texture with a slightly chewy wrapper, while micro-steaming creates a notably delicate and uniform consistency. The fine control of steam in micro-steaming helps preserve moisture inside the dumplings, enhancing juiciness.
- Steaming - Uses direct steam heat that results in a firmer but less uniform dumpling skin texture.
- Micro-steaming - Employs gentle, low-pressure steam for a consistently smooth and tender wrapper.
- Texture impact - Micro-steaming maintains moisture levels more effectively, preventing dryness and improving overall mouthfeel.
Flavor Retention in Both Methods
Steaming dumplings preserves their natural flavors by cooking them gently with moist heat, allowing the fillings to remain juicy and aromatic. Flavor retention is high as the steam envelops the dumplings without diluting their taste.
Micro-steaming uses finer, more controlled steam particles, which can enhance flavor retention by preventing overcooking and retaining more moisture within the dumplings. This method reduces flavor loss compared to traditional steaming, maintaining the original freshness of ingredients. As a result, micro-steamed dumplings often have a richer, more concentrated taste profile.
Nutritional Impact of Each Technique
How does the nutritional impact of traditional steaming compare to micro-steaming for dumplings? Traditional steaming preserves most vitamins and minerals by using gentle heat, maintaining the dumplings' nutritional integrity. Micro-steaming, with its precise temperature control, reduces nutrient loss even further, especially retaining delicate antioxidants and water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex.
Convenience and Practicality for Home Cooks
Steaming dumplings using a traditional bamboo steamer offers a hands-free cooking method that evenly cooks multiple dumplings at once, perfect for batch preparation. Micro-steaming involves using a specialized microwave-safe container that drastically reduces cooking time but may cook unevenly or alter texture. Home cooks prioritize traditional steaming for its reliability and superior texture, while micro-steaming appeals for quick meals when convenience and speed outweigh culinary precision.
Related Important Terms
Macro-Steaming
Macro-steaming involves cooking dumplings using a larger volume of steam over an extended period, ensuring even heat distribution and thorough cooking. This method preserves the dumplings' texture and enhances their flavor by allowing moisture to penetrate deeply without sogginess.
Flash Micro-Steaming
Flash Micro-Steaming uses high-frequency bursts of steam to rapidly cook dumplings, preserving texture and enhancing flavor compared to traditional steaming methods. This technique reduces cooking time by up to 50% while maintaining moisture balance, preventing sogginess and ensuring a tender, yet crisp dumpling skin.
Steam Saturation Control
Steam saturation control in traditional steaming ensures consistent temperature and moisture levels, resulting in evenly cooked dumplings with a tender texture. Micro-steaming utilizes precise steam saturation management to prevent over-saturation, maintaining dumplings' delicate firmness and enhancing flavor retention.
Dumpling Skin Swelling Index
The Dumpling Skin Swelling Index measures the water absorption and expansion of dumpling wrappers during cooking, with steaming typically resulting in moderate swelling that preserves texture, while micro-steaming produces a higher swelling index due to finer steam particles penetrating the dough more effectively. Enhanced swelling in micro-steaming improves dough elasticity and chewiness, offering a softer yet resilient dumpling skin compared to traditional steaming methods.
Localized Steam Burst
Localized steam burst in micro-steaming delivers intense, targeted heat that enhances dumpling texture by creating a crisp outer layer while preserving juicy fillings. Traditional steaming provides even, gentle heat, resulting in uniformly soft dumplings but lacks the precision and texture contrast achieved with micro-steaming technology.
Hydrothermal Steaming
Hydrothermal steaming uses precise temperature and humidity control to cook dumplings evenly, preserving texture and flavor by preventing moisture loss. Compared to micro-steaming, hydrothermal steaming ensures thorough heat penetration, resulting in consistently tender and juicy dumplings.
Micro-Steam Diffusion
Micro-steam diffusion enhances dumpling cooking by creating uniform moisture distribution at a microscopic level, resulting in tender, evenly steamed dumplings without sogginess. This technique optimizes heat transfer and prevents over-saturation, preserving the texture and flavor that traditional steaming methods often fail to achieve.
Texture Retention Steaming
Steaming preserves the delicate texture of dumplings by maintaining consistent moisture and gentle heat, preventing sogginess and ensuring a tender bite. Micro-steaming enhances texture retention further by using precise, controlled steam flow to evenly cook dumplings while preserving their elasticity and structural integrity.
Dual-Phase Steam Cooking
Dual-phase steam cooking combines traditional steaming and micro-steaming techniques to optimize dumpling texture by first using high-temperature steam for thorough cooking, followed by gentle micro-steaming to preserve moisture and delicate flavors. This method enhances the overall eating experience by maintaining dumpling integrity while ensuring even heat distribution and preventing sogginess.
Steaming vs Micro-Steaming for dumplings. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com