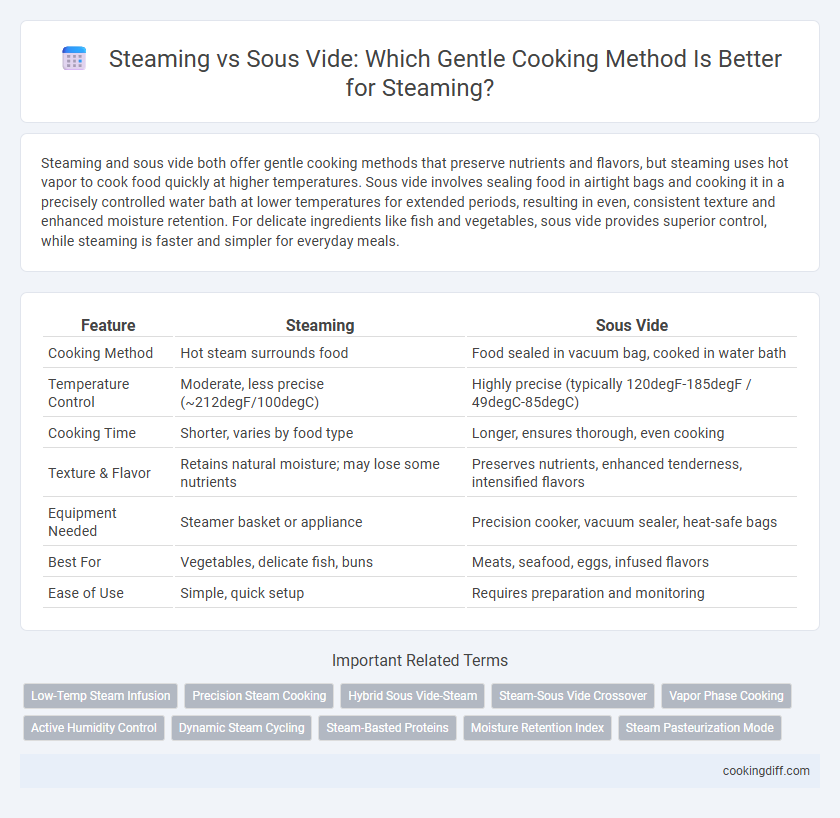
Steaming and sous vide both offer gentle cooking methods that preserve nutrients and flavors, but steaming uses hot vapor to cook food quickly at higher temperatures. Sous vide involves sealing food in airtight bags and cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath at lower temperatures for extended periods, resulting in even, consistent texture and enhanced moisture retention. For delicate ingredients like fish and vegetables, sous vide provides superior control, while steaming is faster and simpler for everyday meals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Steaming | Sous Vide |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Hot steam surrounds food | Food sealed in vacuum bag, cooked in water bath |
| Temperature Control | Moderate, less precise (~212degF/100degC) | Highly precise (typically 120degF-185degF / 49degC-85degC) |
| Cooking Time | Shorter, varies by food type | Longer, ensures thorough, even cooking |
| Texture & Flavor | Retains natural moisture; may lose some nutrients | Preserves nutrients, enhanced tenderness, intensified flavors |
| Equipment Needed | Steamer basket or appliance | Precision cooker, vacuum sealer, heat-safe bags |
| Best For | Vegetables, delicate fish, buns | Meats, seafood, eggs, infused flavors |
| Ease of Use | Simple, quick setup | Requires preparation and monitoring |
Understanding Gentle Cooking: Steaming and Sous Vide Defined
Steaming cooks food by surrounding it with hot vapor, preserving nutrients and texture through gentle heat transfer. The method ensures even cooking without direct contact with water, ideal for delicate vegetables and fish.
Sous vide involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a water bath at precise, low temperatures for extended periods. This controlled environment maintains moisture and flavor, offering unparalleled tenderness and consistency in gentle cooking.
Steaming vs Sous Vide: Key Differences in Technique
Steaming cooks food by surrounding it with hot vapor, preserving nutrients and maintaining moisture without direct contact with water. Sous vide involves sealing food in a vacuum bag and cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath, ensuring even temperature and texture throughout. Steaming offers quicker cooking times and a gentler heat, while sous vide provides unmatched precision and consistency for delicate dishes.
Temperature Control: Precision in Steaming and Sous Vide
| Steaming offers a temperature range typically between 212degF (100degC) and slightly lower, relying on the boiling point of water, which provides consistent yet less precise heat compared to sous vide. Sous vide cooking allows for exact temperature control, often within +-0.1degF, facilitating gentle cooking at precise temperatures from 104degF (40degC) to 194degF (90degC). This precision in sous vide ensures uniform doneness and retention of moisture, whereas steaming provides gentler heat but with less fine temperature regulation. |
Flavor and Nutrient Retention: Which Method Wins?
Steaming preserves the natural flavors and nutrients of foods by cooking them with gentle, moist heat, minimizing nutrient loss. Sous vide enhances flavor infusion through precise temperature control, retaining vitamins and minerals effectively.
- Flavor Retention - Sous vide locks in flavor by sealing foods in vacuum bags, preventing evaporation and flavor loss.
- Nutrient Preservation - Steaming preserves water-soluble vitamins by reducing direct contact with water compared to boiling.
- Cooking Precision - Sous vide maintains consistent low temperatures, ensuring uniform nutrient and flavor retention throughout cooking.
Cooking Times: Steaming Compared to Sous Vide
Steaming cooks food more quickly than sous vide, typically requiring 10 to 20 minutes depending on the ingredient. Sous vide uses lower temperatures over longer periods, often ranging from 1 to 4 hours for gentle, precise cooking.
- Steaming is faster - Steam transfers heat rapidly, reducing overall cooking time compared to sous vide.
- Sous vide offers precise control - Lower temperatures ensure even cooking and optimal texture without overcooking.
- Cooking times vary by food type - Delicate proteins may require only a few minutes steaming but several hours sous vide for tenderness.
Texture and Moisture: Results from Each Method
Steaming preserves food's natural moisture by cooking with gentle, consistent steam heat, resulting in tender textures without drying out ingredients. Sous vide uses precise temperature control by immersing food in a water bath, which locks in juices and creates evenly cooked, ultra-tender textures. Both methods excel in maintaining moisture, but sous vide offers superior control over texture through exact timing and temperature settings.
Equipment Needed: Steaming vs Sous Vide Essentials
What equipment is essential for steaming compared to sous vide cooking? Steaming requires a simple setup including a pot with a steaming basket or an electric steamer, focusing on maintaining high-temperature steam environment. Sous vide cooking demands a precision immersion circulator and a vacuum-sealed bag system to ensure accurate temperature control and even cooking.
Versatility: What Foods Suit Steaming or Sous Vide?
Steaming excels at gently cooking vegetables, seafood, and delicate poultry without added fats, preserving nutrients and natural flavors. Sous vide offers precise temperature control for meats, eggs, and custards, ensuring even cooking and tender textures.
- Steaming suits vegetables and fish - It retains moisture and nutrients while preventing overcooking through indirect heat.
- Sous vide is ideal for meats - Slow, controlled cooking enhances tenderness and allows for consistent doneness.
- Both methods support delicate proteins - Steaming and sous vide avoid harsh cooking, preserving texture and flavor.
Choosing between steaming and sous vide depends on the target food and desired texture precision.
Energy Efficiency and Convenience
Steaming uses less energy than sous vide because it rapidly heats water to generate steam, making it more efficient for quick cooking. Sous vide requires maintaining a precise temperature for extended periods, consuming more electricity overall.
Steaming offers greater convenience through minimal setup and faster cooking times, ideal for everyday meals. Sous vide demands specialized equipment and longer cooking schedules, which can be less practical for spontaneous use.
Related Important Terms
Low-Temp Steam Infusion
Low-temp steam infusion delivers gentle cooking by maintaining precise temperatures that preserve nutrients and texture better than traditional steaming or sous vide. Unlike sous vide, this method infuses moisture directly into food at low temperatures, enhancing flavor without overcooking or water immersion risks.
Precision Steam Cooking
Precision steam cooking offers controlled temperature and humidity, ensuring even heat distribution that preserves nutrients and texture without overcooking. Unlike sous vide, which relies on vacuum sealing and water immersion, precision steam cooking provides a gentler, low-temperature environment ideal for delicate proteins and vegetables.
Hybrid Sous Vide-Steam
Hybrid Sous Vide-Steam cooking combines precise temperature control of sous vide with the gentle moisture retention of steaming, ensuring perfectly tender and evenly cooked results. This method enhances texture and flavor by maintaining consistent heat while preserving delicate food structures, making it ideal for seafood, vegetables, and poultry.
Steam-Sous Vide Crossover
Steaming and sous vide both offer gentle cooking methods that preserve moisture and nutrients, but the steam-sous vide crossover combines precise temperature control with steam's ability to infuse flavors and maintain food texture. This hybrid approach enhances delicate proteins and vegetables by balancing even heat distribution and humidity, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes with consistent doneness.
Vapor Phase Cooking
Steaming utilizes vapor phase cooking by surrounding food with hot steam at temperatures typically between 100degC and 110degC, preserving delicate textures and nutrients through gentle heat transfer. Sous vide, in contrast, uses precise water bath temperatures submerged in a sealed bag, offering consistent cooking but lacking the direct vapor interaction that enhances moisture retention and flavor in steaming.
Active Humidity Control
Active humidity control in steaming ensures precise moisture levels that prevent food from drying out, preserving texture and nutrients more effectively than sous vide's water-bath method. This controlled environment allows for gentle cooking with consistent heat distribution, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes without overcooking.
Dynamic Steam Cycling
Dynamic Steam Cycling in steaming offers precise temperature control and rapid humidity adjustments, promoting gentle cooking that preserves texture and nutrients better than traditional sous vide methods. This technique creates an optimal environment by intermittently injecting steam, which enhances heat transfer efficiency and prevents overcooking delicate foods.
Steam-Basted Proteins
Steam-basted proteins cooked using steaming techniques retain moisture and delicate textures by continuously surrounding the food with hot steam, preventing drying and promoting even heat distribution. Unlike sous vide, which uses precise temperature water baths for slow cooking, steaming offers a faster, nutrient-preserving method ideal for tenderizing proteins without the need for vacuum sealing.
Moisture Retention Index
Steaming preserves a high Moisture Retention Index by enveloping food in humid heat, minimizing water loss during cooking. Sous vide further enhances moisture retention through precise temperature control in vacuum-sealed bags, preventing evaporation and ensuring juicier, tender results.
Steaming vs Sous Vide for gentle cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com