Steaming enhances flavor by gently cooking food with hot vapor, preserving natural tastes and nutrients without dilution. Steam infusion intensifies flavor by injecting steam directly into the food, promoting faster heat transfer and deeper flavor absorption. Both methods improve taste, but steam infusion offers more rapid cooking and enhanced flavor penetration for certain dishes.
Table of Comparison
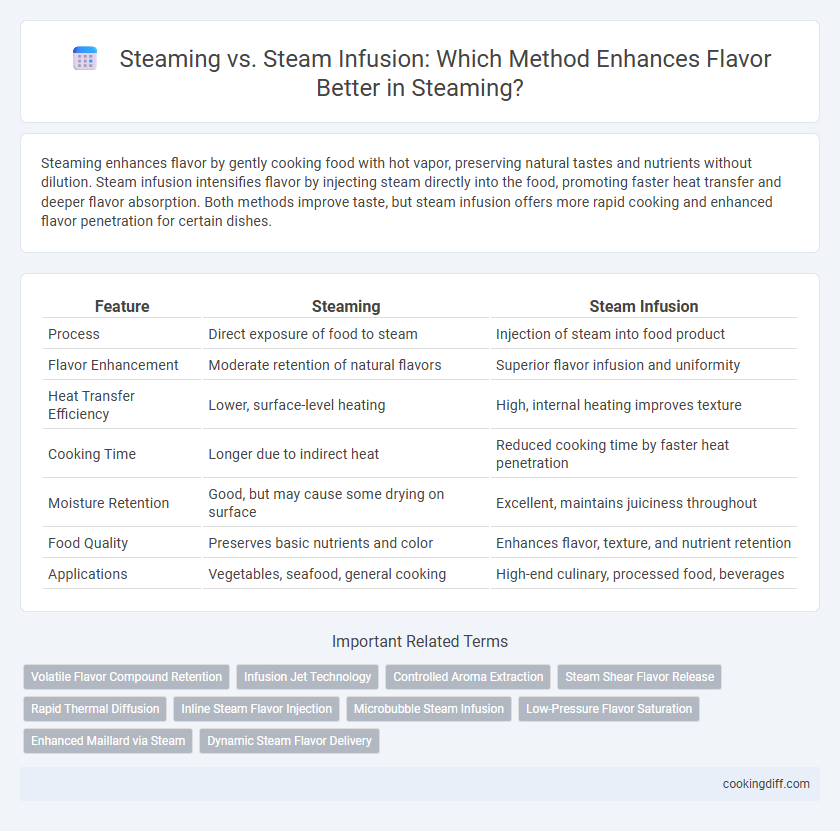
| Feature | Steaming | Steam Infusion |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Direct exposure of food to steam | Injection of steam into food product |
| Flavor Enhancement | Moderate retention of natural flavors | Superior flavor infusion and uniformity |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | Lower, surface-level heating | High, internal heating improves texture |
| Cooking Time | Longer due to indirect heat | Reduced cooking time by faster heat penetration |
| Moisture Retention | Good, but may cause some drying on surface | Excellent, maintains juiciness throughout |
| Food Quality | Preserves basic nutrients and color | Enhances flavor, texture, and nutrient retention |
| Applications | Vegetables, seafood, general cooking | High-end culinary, processed food, beverages |
Introduction to Steaming and Steam Infusion
Steaming is a cooking method that uses hot steam to gently cook food, preserving nutrients and natural flavors. Steam infusion involves injecting steam directly into liquids or semi-solid foods to rapidly enhance flavor and texture. Both techniques optimize moisture retention but differ in their application and intensity of flavor enhancement.
Understanding Traditional Steaming Techniques
Traditional steaming techniques utilize direct exposure to steam to cook food, preserving natural flavors and nutrients effectively. This method ensures even heat distribution, preventing drying and maintaining food texture.
Unlike steam infusion, which injects steam directly into the food for intensified flavor absorption, traditional steaming relies on ambient steam surrounding the food to enhance taste subtly. It is widely used for vegetables, seafood, and delicate proteins, offering a gentle cooking environment. Understanding these techniques helps optimize flavor retention while maintaining nutritional integrity during cooking.
What Is Steam Infusion Cooking?
Steam infusion cooking uses high-velocity steam injected directly into food, allowing rapid and uniform heating that preserves flavor and nutrients. Unlike traditional steaming, which surrounds food with steam, steam infusion delivers targeted steam, enhancing taste intensity and texture. This method improves cooking efficiency while maintaining moisture and minimizing nutrient loss, making it ideal for flavor enhancement.
Key Differences: Steaming vs Steam Infusion
What are the key differences between steaming and steam infusion for flavor enhancement? Steaming uses direct steam contact to cook food quickly while preserving moisture, enhancing natural flavors through heat. Steam infusion injects steam into liquid mixtures, intensifying flavors by evenly distributing heat and accelerating extraction of aromatic compounds.
Mechanisms of Flavor Enhancement in Steaming
| Steaming enhances flavor by gently cooking food with hot vapor, preserving natural moisture and intensifying taste compounds without dilution. Steam infusion introduces flavors through vaporized aromatics directly into the steam, enabling deeper and more uniform flavor penetration. The key mechanism in steaming relies on moisture retention and heat transfer, whereas steam infusion uses vaporized flavor carriers for enhanced aromatic impact. |
Flavor Retention with Steam Infusion Technology
Steam infusion technology enhances flavor retention by enveloping food in fine steam droplets, minimizing nutrient loss and preserving aromatic compounds better than traditional steaming methods. This technique ensures even heat distribution, reducing overcooking and maintaining the natural taste profile of ingredients.
Compared to conventional steaming, steam infusion allows for faster cooking times and improved moisture retention, which intensifies the flavors and textures of the food. The precision of steam infusion technology offers chefs greater control over cooking processes, resulting in consistently flavorful dishes.
Texture and Nutrient Preservation: A Comparison
Steaming preserves the natural texture of foods by using moist heat that gently cooks without direct contact, maintaining firmness and preventing sogginess. Steam infusion enhances flavor infusion while preserving nutrients through rapid steam condensation, resulting in a more uniform texture and intensified taste.
- Texture Retention - Steaming maintains a firmer texture by avoiding direct immersion, which prevents food from becoming waterlogged.
- Nutrient Preservation - Both methods retain vitamins and minerals, but steam infusion often preserves more heat-sensitive nutrients due to shorter cooking times.
- Flavor Enhancement - Steam infusion delivers deeper flavor penetration from infused steam, enhancing the sensory profile without compromising texture.
Choosing between steaming and steam infusion depends on the desired balance between texture integrity and flavor intensity while maximizing nutrient preservation.
Culinary Applications: When to Use Each Method
Steaming utilizes direct steam to cook food, preserving natural flavors and nutrients, making it ideal for delicate vegetables and seafood. It offers a gentle method that prevents overcooking while maintaining texture and moisture.
Steam infusion combines steam with flavor elements, such as herbs or spices, enhancing dishes with infused aromas and tastes during cooking. This technique is preferred when a subtle yet distinct flavor boost is desired, especially in complex sauces and infusions.
Advantages and Limitations of Steaming and Steam Infusion
Steaming preserves natural flavors through gentle heat, while steam infusion enhances flavor by directly injecting steam into food. Both methods improve texture but differ in speed and efficiency of flavor absorption.
- Advantages of Steaming - Retains nutrients and natural color without direct contact with water.
- Limitations of Steaming - Slower process and limited flavor penetration in dense foods.
- Advantages of Steam Infusion - Rapid flavor enhancement and uniform heat distribution for quicker cooking.
Related Important Terms
Volatile Flavor Compound Retention
Steaming preserves volatile flavor compounds effectively by using direct contact with steam, minimizing compound loss through rapid heating. Steam infusion enhances flavor retention further by enveloping food in saturated steam, reducing oxidation and improving the intensity and retention of delicate aromas.
Infusion Jet Technology
Steam infusion utilizes advanced Infusion Jet Technology to deliver precise steam penetration, enhancing flavor extraction more efficiently than traditional steaming methods. This technology mixes steam and product in a vacuum chamber, promoting uniform heat transfer and intensified aromatic development.
Controlled Aroma Extraction
Steaming offers consistent heat application for controlled aroma extraction by slowly releasing essential oils and flavors from ingredients. Steam infusion accelerates this process by directly injecting steam, intensifying aroma release while preserving delicate flavor compounds in culinary applications.
Steam Shear Flavor Release
Steam shear flavor release uses high-velocity steam to rapidly rupture food cells, intensifying aroma and taste more efficiently than traditional steaming methods. Steam infusion combines steam with immersion, but steam shear maximizes flavor extraction by creating a dynamic pressure differential that enhances volatile compound release.
Rapid Thermal Diffusion
Steam infusion delivers rapid thermal diffusion by directly injecting steam into food, enabling faster heat transfer and flavor absorption than conventional steaming, which relies on surrounding steam to cook from the outside in. This method maximizes flavor enhancement by preserving volatile compounds and reducing cooking time, resulting in more intense and evenly distributed tastes.
Inline Steam Flavor Injection
Inline steam flavor injection delivers rapid and uniform flavor enhancement by directly infusing steam into the product, preserving volatile aromatic compounds better than traditional steaming methods. This technique improves flavor intensity and consistency while reducing processing time and energy consumption in food production.
Microbubble Steam Infusion
Microbubble steam infusion enhances flavor by using ultra-fine steam bubbles to rapidly and evenly infuse food with moisture and aromas, improving taste intensity and texture compared to traditional steaming. This method significantly reduces cooking time and energy consumption while preserving essential nutrients and volatile compounds.
Low-Pressure Flavor Saturation
Low-pressure flavor saturation through steaming gently infuses ingredients with aromatic compounds, preserving delicate flavors without overwhelming the palate. Steam infusion, by contrast, utilizes higher pressure to rapidly penetrate food, intensifying flavor extraction but risking loss of subtle nuances.
Enhanced Maillard via Steam
Steam infusion enhances flavor by promoting the Maillard reaction more efficiently than traditional steaming, resulting in intensified browning and richer taste profiles. The high-temperature steam contact during steam infusion accelerates complex flavor compound development, amplifying savory and caramelized notes in foods.
Steaming vs Steam Infusion for flavor enhancement. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com