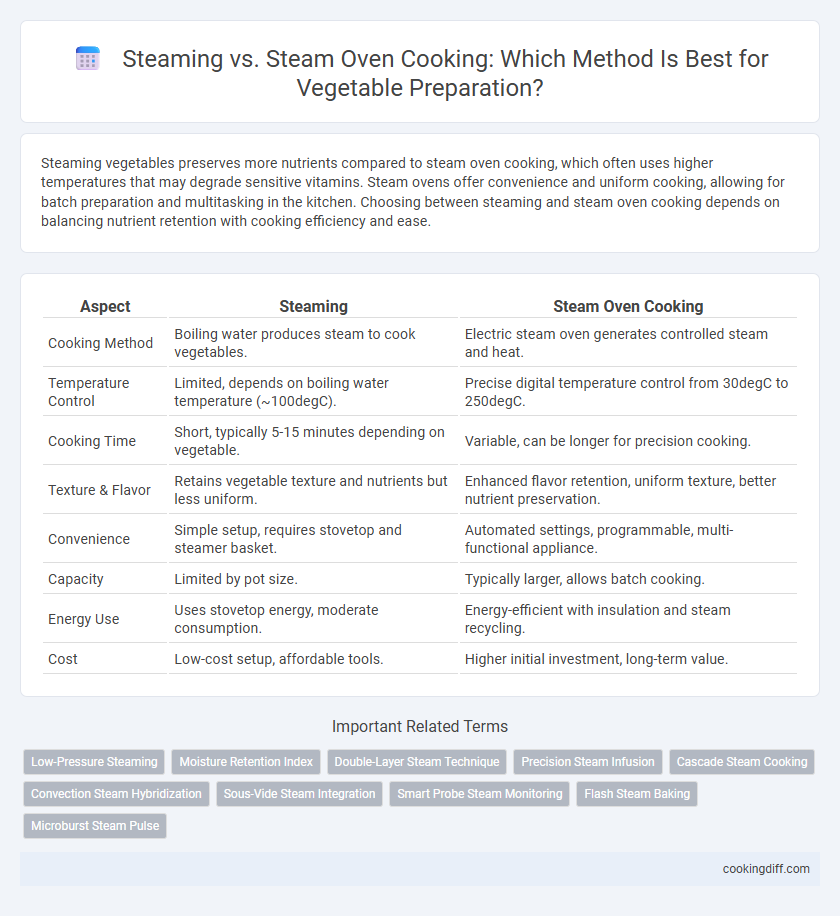
Steaming vegetables preserves more nutrients compared to steam oven cooking, which often uses higher temperatures that may degrade sensitive vitamins. Steam ovens offer convenience and uniform cooking, allowing for batch preparation and multitasking in the kitchen. Choosing between steaming and steam oven cooking depends on balancing nutrient retention with cooking efficiency and ease.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Steaming | Steam Oven Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Boiling water produces steam to cook vegetables. | Electric steam oven generates controlled steam and heat. |
| Temperature Control | Limited, depends on boiling water temperature (~100degC). | Precise digital temperature control from 30degC to 250degC. |
| Cooking Time | Short, typically 5-15 minutes depending on vegetable. | Variable, can be longer for precision cooking. |
| Texture & Flavor | Retains vegetable texture and nutrients but less uniform. | Enhanced flavor retention, uniform texture, better nutrient preservation. |
| Convenience | Simple setup, requires stovetop and steamer basket. | Automated settings, programmable, multi-functional appliance. |
| Capacity | Limited by pot size. | Typically larger, allows batch cooking. |
| Energy Use | Uses stovetop energy, moderate consumption. | Energy-efficient with insulation and steam recycling. |
| Cost | Low-cost setup, affordable tools. | Higher initial investment, long-term value. |
Introduction to Steaming and Steam Oven Cooking
Steaming is a traditional cooking method that uses boiling water vapor to cook vegetables gently, preserving their nutrients and natural flavors. This technique helps maintain the vibrant color and crisp texture of vegetables while avoiding the use of added fats.
Steam oven cooking integrates steam with convection heat, offering precise temperature control and even cooking for vegetables. Steam ovens enhance moisture retention and reduce cooking time compared to conventional steaming methods, making them an efficient choice for preparing nutrient-rich vegetables.
How Traditional Steaming Works for Vegetables
Traditional steaming cooks vegetables by exposing them to steam generated from boiling water, which gently transfers heat without direct contact. This method preserves nutrients, color, and texture by minimizing nutrient loss often caused by boiling. Steam penetrates the cell walls slowly, allowing for even cooking and retaining the vegetables' natural flavors and crispness.
Understanding Steam Oven Cooking Technology
Steam oven cooking technology uses a precise combination of steam and convection heat to cook vegetables evenly while preserving nutrients and natural flavors. Unlike traditional steaming, steam ovens maintain consistent moisture levels, preventing vegetable dryness and enhancing texture.
Advanced steam ovens feature customizable steam settings and rapid heat-up times, allowing tailored cooking processes for various vegetables. This technology reduces cooking time compared to conventional steaming, ensuring vitamins and antioxidants remain intact during preparation.
Nutrient Retention: Steaming vs Steam Ovens
Steaming vegetables preserves water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex by minimizing nutrient loss during cooking. Steam ovens offer precise temperature control, reducing overcooking and enhancing nutrient retention compared to traditional steaming methods.
- Steaming retains up to 80% of vitamin C - gentle heat prevents nutrient degradation during cooking.
- Steam ovens maintain consistent temperatures - this accuracy minimizes nutrient loss and improves texture.
- Traditional steaming risks uneven heat distribution - which can lead to variable nutrient retention.
Flavor and Texture Comparison: Steamed vs Steam Oven Vegetables
Steaming vegetables on the stovetop preserves natural flavors and nutrients by using direct steam contact, resulting in vibrant color and a slightly firmer texture. Steam oven cooking, however, ensures even heat distribution and precise temperature control, enhancing tenderness without overcooking.
Steam oven vegetables often exhibit deeper flavor infusion due to consistent humidity and uniform heat, which helps maintain moisture levels better than traditional steaming. The texture from a steam oven is typically softer yet not mushy, providing a balanced bite ideal for delicate vegetables like asparagus or broccoli. Both methods excel in nutrient retention compared to boiling but differ in texture nuances based on cooking environment.
Cooking Time Differences Between Steaming Methods
How does cooking time compare between traditional steaming and steam oven cooking for vegetables? Traditional steaming typically cooks vegetables faster due to direct contact with boiling water vapor, while steam ovens use controlled humidity and temperature, resulting in slightly longer but more even cooking. Steam ovens optimize flavor retention and texture despite the increased cooking time.
Energy Efficiency: Steaming vs Steam Oven Cooking
Steaming vegetables using a stovetop method typically consumes less energy due to shorter preheating times compared to steam oven cooking. Steam ovens, while offering precise temperature control, generally use more electricity over longer cooking cycles.
- Stovetop Steaming Efficiency - Utilizes direct heat with minimal energy loss, making it faster and more energy-efficient for small vegetable batches.
- Steam Oven Energy Use - Requires electrical power and extended preheating, increasing overall energy consumption during vegetable preparation.
- Temperature Control Advantage - Steam ovens provide consistent temperatures that can optimize cooking quality but at the expense of higher energy usage.
Versatility and Capacity in Vegetable Preparation
Steaming offers flexibility for small, quick batches of vegetables, allowing for easy adjustment of cooking times and textures. Steam ovens provide larger capacity and consistent heat distribution, making them ideal for preparing multiple vegetable varieties simultaneously. Their versatility in cooking modes also enhances the ability to tailor temperature and humidity settings for optimal vegetable flavor and nutrient retention.
Ease of Use and Cleaning: Steamer vs Steam Oven
Steaming vegetables using a traditional steamer offers straightforward setup and minimal cleaning, making it accessible for everyday use. Steam ovens provide a more automated process but may require more time for maintenance due to larger surfaces and components.
- Steamer simplicity - Compact design allows easy handling and quick assembly before cooking.
- Steam oven automation - Programmable settings deliver consistent results with reduced manual intervention.
- Cleaning differences - Steamers usually have fewer parts, facilitating faster washing compared to steam ovens.
Choosing between a steamer and a steam oven depends on balancing ease of use with cleaning preferences for efficient vegetable preparation.
Related Important Terms
Low-Pressure Steaming
Low-pressure steaming preserves more nutrients and vitamins in vegetables compared to steam oven cooking by maintaining a gentler heat environment below 100degC. This method ensures tender texture and vibrant color while reducing nutrient loss caused by high temperatures and prolonged exposure in steam ovens.
Moisture Retention Index
Steaming vegetables preserves a higher Moisture Retention Index compared to steam oven cooking, resulting in crisper texture and enhanced nutrient retention. Steam ovens, while convenient, often expose vegetables to longer heat cycles, causing slight moisture loss and softer consistency.
Double-Layer Steam Technique
The double-layer steam technique in steaming ensures even heat distribution and retains maximum nutrients by simultaneously cooking multiple vegetable layers without flavor mixing. Steam oven cooking offers precise temperature control and automated timing, but traditional double-layer steaming excels in preserving texture and vibrant color through natural convection steam flow.
Precision Steam Infusion
Precision Steam Infusion in steaming delivers consistent heat and moisture, preserving the nutrients and vibrant colors of vegetables more effectively than traditional steam oven cooking. This method ensures uniform cooking by penetrating the vegetable fibers evenly, enhancing texture and flavor without overcooking or nutrient loss.
Cascade Steam Cooking
Cascade Steam Cooking enhances vegetable preparation by evenly distributing steam to preserve nutrients, texture, and color compared to traditional steaming methods. Steam ovens provide precise temperature control and uniform heat, resulting in consistent and flavorful vegetable dishes with minimal nutrient loss.
Convection Steam Hybridization
Convection steam hybridization combines the moist heat of steaming with the even circulation of hot air, enhancing vegetable preparation by preserving nutrients and providing a crisp texture. This method surpasses traditional steaming by reducing cooking time and achieving uniform doneness while maintaining vibrant color and flavor.
Sous-Vide Steam Integration
Sous-vide steam integration combines precise temperature control with moist heat, enhancing vegetable texture and nutrient retention compared to traditional steaming methods. Steam ovens equipped with sous-vide functions ensure even cooking and improved flavor infusion by maintaining consistent vapor pressure and temperature throughout the cooking cycle.
Smart Probe Steam Monitoring
Smart Probe Steam Monitoring in steam ovens enhances vegetable cooking by precisely controlling internal moisture and temperature, resulting in optimal texture and nutrient retention. Unlike traditional steaming, this technology ensures consistent heat distribution and prevents overcooking, maximizing flavor and health benefits.
Flash Steam Baking
Flash steam baking combines the speed of high-pressure steam with precise heat, preserving vegetable nutrients and texture better than traditional steaming or steam oven cooking. This method reduces cooking time significantly while enhancing flavor retention and maintaining vibrant vegetable colors.
Steaming vs Steam Oven Cooking for vegetable preparation. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com