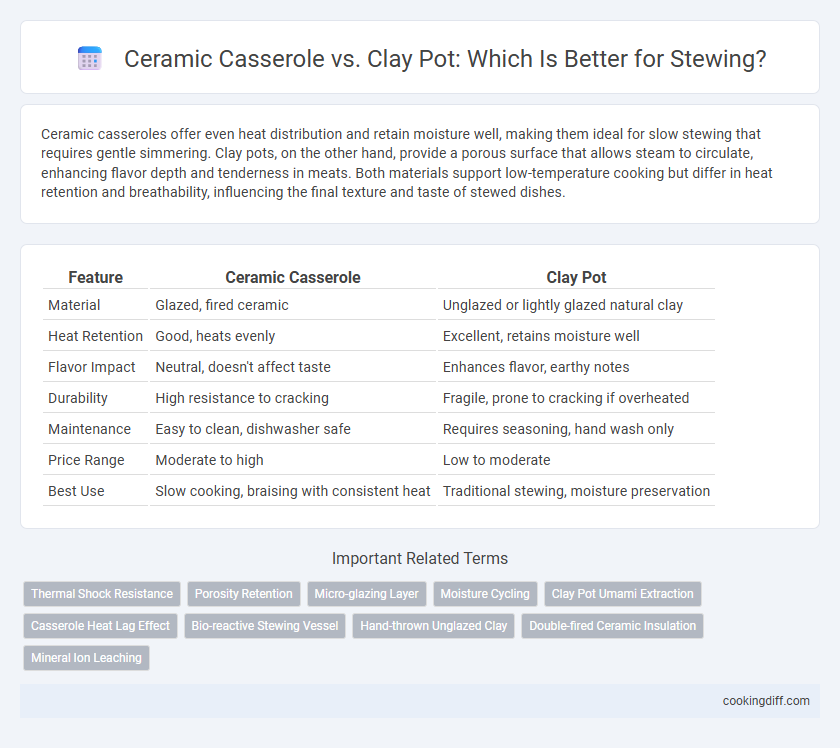
Ceramic casseroles offer even heat distribution and retain moisture well, making them ideal for slow stewing that requires gentle simmering. Clay pots, on the other hand, provide a porous surface that allows steam to circulate, enhancing flavor depth and tenderness in meats. Both materials support low-temperature cooking but differ in heat retention and breathability, influencing the final texture and taste of stewed dishes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Casserole | Clay Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Glazed, fired ceramic | Unglazed or lightly glazed natural clay |
| Heat Retention | Good, heats evenly | Excellent, retains moisture well |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral, doesn't affect taste | Enhances flavor, earthy notes |
| Durability | High resistance to cracking | Fragile, prone to cracking if overheated |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Requires seasoning, hand wash only |
| Price Range | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Best Use | Slow cooking, braising with consistent heat | Traditional stewing, moisture preservation |
Introduction to Stewing: Ceramic Casserole vs Clay Pot
Stewing is a slow-cooking method that tenderizes tougher cuts of meat by simmering them in liquid over low heat. Both ceramic casseroles and clay pots are popular vessels for stewing, each offering unique heat retention and moisture distribution properties.
- Ceramic Casserole - Provides even heat distribution and retains heat well, ideal for consistent simmering.
- Clay Pot - Porous material allows moisture to circulate naturally, enhancing flavor and tenderness.
- Durability and Care - Ceramic casseroles are typically more durable and easier to clean than delicate clay pots which require careful seasoning and maintenance.
Material Properties: Ceramic Casserole vs Clay Pot
Ceramic casseroles are made from refined clay fired at high temperatures, creating a dense and non-porous surface that retains heat evenly and resists staining. Clay pots, often unglazed and porous, allow for slight moisture absorption and gradual evaporation, which enhances flavor concentration during stewing.
The thermal conductivity of ceramic casseroles provides consistent and controlled heating, reducing the risk of hot spots that can burn the stew. Clay pots excel in moisture retention due to their porous nature, enabling slow, gentle cooking that preserves nutrient content. Both materials require careful handling to avoid cracking under thermal shock, but their distinct properties offer unique benefits suited to different stewing techniques.
Heat Retention and Distribution
Ceramic casseroles offer excellent heat retention, maintaining steady temperatures ideal for slow stewing. Clay pots provide superior heat distribution, ensuring even cooking and enhanced flavor development throughout the dish. Both materials excel in slow-cooked recipes but differ in their thermal properties, influencing cooking time and texture.
Cooking Performance and Flavor Development
| Ceramic Casserole | Provides consistent heat distribution, allowing for even cooking and preventing hotspots, which enhances the tenderness of stewed ingredients. |
| Clay Pot | Offers porous properties that retain moisture and release steam gradually, intensifying flavor development and preserving the natural aroma of the stew. |
| Flavor Profile | Ceramic casseroles maintain subtle, clean flavors ideal for delicate ingredients; clay pots contribute earthy undertones and a richer, deeper taste due to slow evaporation. |
Durability and Lifespan
Ceramic casseroles offer excellent durability with a glazed surface that resists chipping and cracking under regular indoor use. They typically have a longer lifespan when properly cared for, maintaining their structural integrity through numerous stewing cycles.
Clay pots, while prized for natural heat retention and flavor enhancement, are more fragile and prone to cracking if exposed to sudden temperature changes or mishandling. Their lifespan tends to be shorter compared to ceramic casseroles, requiring careful maintenance to avoid damage during stewing.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Ceramic casseroles offer smoother surfaces that resist food sticking, making them easier to clean after stewing. Clay pots, while traditional, can absorb flavors and require more careful seasoning and maintenance to prevent cracking and odors.
- Ceramic casserole - Its non-porous glaze simplifies cleaning by preventing food residue from adhering strongly.
- Clay pot - Porous material demands soaking and gentle scrubbing to avoid damage and maintain seasoning.
- Maintenance - Clay pots need occasional oiling and drying to preserve integrity, whereas ceramic casseroles primarily benefit from straightforward washing.
Versatility in the Kitchen
Ceramic casseroles offer exceptional versatility in the kitchen, easily transitioning from stovetop to oven and retaining heat evenly for consistent stewing results. Their smooth, non-porous surface resists staining and odors, making them ideal for cooking a wide range of dishes beyond stews, including casseroles and baked goods.
Clay pots excel in enhancing flavor profiles due to their porous nature, which allows slow evaporation and moisture circulation during long stews. While more delicate and requiring careful seasoning, clay pots bring authenticity to traditional recipes and can be used for both cooking and serving, adding rustic charm to the dining experience.
Safety and Health Considerations
Ceramic casseroles are often glazed to prevent porosity, reducing the risk of bacteria growth and making them safer for prolonged use in stewing. Clay pots, if unglazed, may absorb liquids and harbor harmful bacteria, but high-quality, properly fired clay pots are non-toxic and can enhance flavor without leaching chemicals. Both options require careful cleaning and maintenance to ensure food safety and avoid health hazards during stewing.
Price Comparison and Value
Which offers better value for stewing, a ceramic casserole or a clay pot? Ceramic casseroles tend to be more affordable upfront while providing excellent heat retention and durability. Clay pots, though often pricier, deliver unique flavor enhancement and moisture retention that may justify the higher cost for specialty cooking.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Shock Resistance
Ceramic casseroles offer moderate thermal shock resistance, making them suitable for steady temperature changes during stewing. Clay pots generally provide superior thermal shock resistance, allowing rapid transitions from stovetop to oven without risk of cracking.
Porosity Retention
Ceramic casseroles offer lower porosity, ensuring better heat retention and even cooking for stews, while clay pots have higher porosity that allows moisture evaporation, enhancing flavor concentration but requiring more careful heat management. The semi-porous nature of clay pots helps to naturally retain steam, resulting in tender, richly flavored stews compared to the more sealed environment of ceramic casserole dishes.
Micro-glazing Layer
Ceramic casseroles feature a micro-glazing layer that provides a non-porous surface, enhancing heat retention and preventing flavor absorption during stewing. Clay pots, lacking this micro-glazing, allow slow evaporation and subtle mineral exchange, imparting a distinct earthy taste to stews.
Moisture Cycling
Ceramic casseroles excel in moisture cycling by evenly distributing heat and retaining steam, which enhances the tenderness of stewed ingredients. Clay pots naturally absorb and release moisture during cooking, creating a self-basting effect that intensifies flavors and preserves juiciness in slow-cooked dishes.
Clay Pot Umami Extraction
Clay pots excel in stewing due to their porous nature, which enables gradual moisture retention and even heat distribution, enhancing umami extraction from ingredients. This slow, consistent cooking process intensifies flavors and preserves nutrients better than ceramic casseroles.
Casserole Heat Lag Effect
Ceramic casseroles exhibit a heat lag effect due to their dense material, allowing for slow, even heat distribution ideal for stewing tender meats and vegetables without burning. In contrast, clay pots absorb and release heat more gradually, enhancing moisture retention but requiring careful temperature control to prevent hotspots during prolonged cooking.
Bio-reactive Stewing Vessel
Ceramic casserole dishes offer excellent heat retention and even cooking, making them ideal for slow stewing processes that enhance flavor extraction and nutrient preservation. Bio-reactive clay pots go further by interacting with ingredients at a molecular level, releasing beneficial minerals and regulating moisture to create richer, more aromatic stews.
Hand-thrown Unglazed Clay
Hand-thrown unglazed clay pots excel in stewing by providing superior heat retention and gradual moisture evaporation, enhancing flavor concentration in slow-cooked dishes. Unlike ceramic casseroles that often feature glazes affecting heat distribution, these natural clay vessels allow for even cooking and a unique earthy taste, making them ideal for traditional stews.
Double-fired Ceramic Insulation
Double-fired ceramic casserole dishes provide superior heat retention and even temperature distribution during stewing, enhancing flavor development by maintaining a consistent simmer. In contrast, clay pots offer porous insulation but lack the durability and precise heat control afforded by double-fired ceramics, making the latter ideal for long, slow cooking processes.
Ceramic casserole vs Clay pot for stewing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com