Stewing involves cooking ingredients slowly in liquid over low heat, allowing flavors to meld and meats to become tender, while bag stewing uses sealed bags to trap moisture and heat, enhancing flavor retention and preventing nutrient loss. Traditional stewing offers a more rustic approach with direct contact between food and liquid, whereas bag stewing provides a controlled environment that can intensify taste and texture. Choosing between the two methods depends on desired flavor depth and cooking convenience.
Table of Comparison
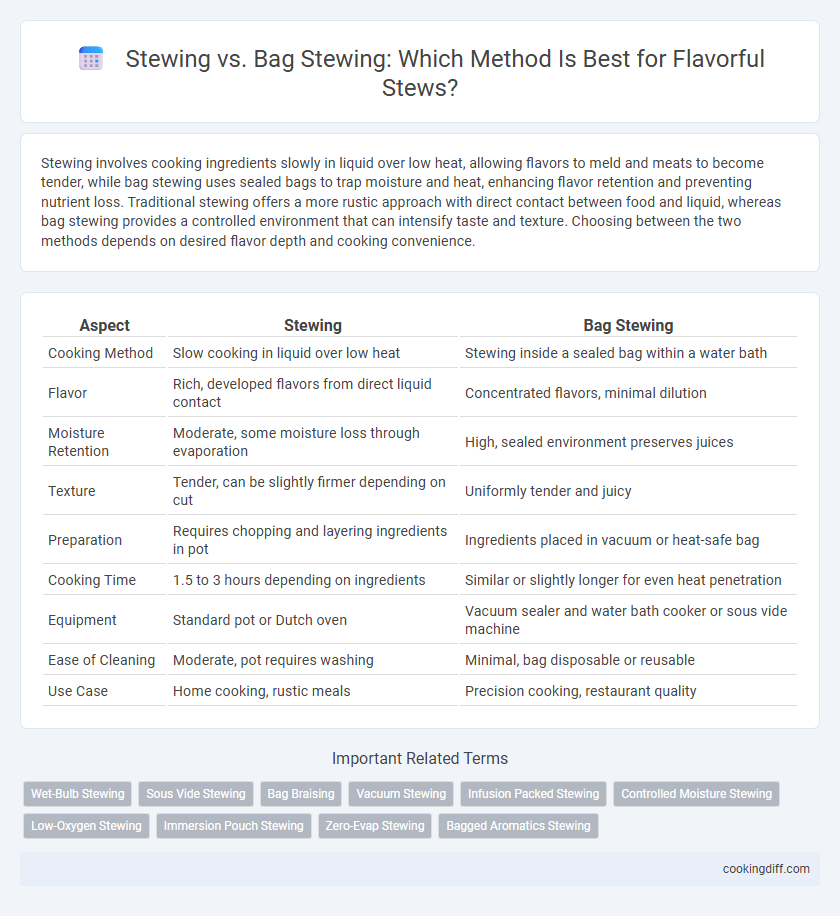
| Aspect | Stewing | Bag Stewing |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Slow cooking in liquid over low heat | Stewing inside a sealed bag within a water bath |
| Flavor | Rich, developed flavors from direct liquid contact | Concentrated flavors, minimal dilution |
| Moisture Retention | Moderate, some moisture loss through evaporation | High, sealed environment preserves juices |
| Texture | Tender, can be slightly firmer depending on cut | Uniformly tender and juicy |
| Preparation | Requires chopping and layering ingredients in pot | Ingredients placed in vacuum or heat-safe bag |
| Cooking Time | 1.5 to 3 hours depending on ingredients | Similar or slightly longer for even heat penetration |
| Equipment | Standard pot or Dutch oven | Vacuum sealer and water bath cooker or sous vide machine |
| Ease of Cleaning | Moderate, pot requires washing | Minimal, bag disposable or reusable |
| Use Case | Home cooking, rustic meals | Precision cooking, restaurant quality |
Introduction to Stewing and Bag Stewing
Stewing is a slow-cooking method where ingredients are simmered in liquid over low heat to tenderize and develop flavor. Bag stewing involves placing ingredients in a sealed bag to cook in liquid, preserving moisture and intensifying taste.
- Stewing - Traditional slow-cooking technique using an open pot with ingredients submerged in broth or sauce.
- Bag Stewing - Cooking method that encloses ingredients in a sealed bag, often vacuum-sealed, before simmering.
- Flavor and Texture - Bag stewing enhances moisture retention and flavor concentration compared to conventional stewing.
What is Traditional Stewing?
What is traditional stewing in cooking? Traditional stewing involves slowly cooking food, usually meat and vegetables, in a covered pot with a small amount of liquid over low heat for several hours. This method allows flavors to meld and results in tender, flavorful dishes due to the gradual breakdown of connective tissues.
Understanding the Bag Stewing Method
Bag stewing involves cooking ingredients sealed in a heat-resistant bag, preserving moisture and enhancing flavor concentration compared to traditional stewing. This method reduces nutrient loss and allows precise flavor infusion during the slow cooking process.
- Moisture Retention - The sealed environment in bag stewing traps steam, preventing evaporation and maintaining juiciness in the food.
- Flavor Enhancement - Ingredients cook in their own juices, intensifying the overall taste profile without dilution.
- Efficient Heat Transfer - The bag directly transfers heat gently and evenly, resulting in consistent texture and tenderization.
Key Differences Between Stewing and Bag Stewing
Stewing involves slow cooking food in a pot with liquid, allowing flavors to meld naturally, while bag stewing uses sealed bags to retain moisture and intensify flavors. The key difference lies in the cooking environment, where traditional stewing exposes ingredients directly to heat and liquid, whereas bag stewing isolates them for a more controlled process.
In traditional stewing, ingredients simmer in an open pot, promoting evaporation and a thicker sauce, whereas bag stewing maintains a sealed, moist environment, preventing evaporation and preserving juices. Bag stewing often results in more tender meat and enhanced flavor concentration due to the sealed environment. Both methods benefit from low, slow heat, but bag stewing provides precision in moisture retention and a cleaner cooking process.
Flavor Development: Stewing vs Bag Stewing
Traditional stewing allows flavors to meld slowly as ingredients cook together in a single pot, enhancing depth and complexity through prolonged heat exposure. Bag stewing isolates ingredients in sealed pouches, preserving individual flavors but limiting the interaction that develops richer taste profiles.
Stewing promotes the breakdown of connective tissues and infuses the dish with robust, well-rounded flavors due to the direct contact between ingredients and cooking liquid. Bag stewing retains more distinct, fresh flavors but may result in a less integrated and nuanced overall taste experience.
Texture and Moisture Retention Comparison
Stewing involves slow cooking food submerged in liquid, resulting in tender textures but with a higher chance of moisture loss due to evaporation. Bag stewing, or sous vide, seals ingredients in vacuum bags, preserving moisture and enhancing tenderness by cooking in their own juices. Texture in bag stewing is consistently smooth and juicy, while traditional stewing may yield slightly drier results depending on cooking time and liquid level.
Convenience and Ease of Preparation
Stewing offers a straightforward cooking process that requires minimal preparation, making it ideal for home cooks seeking convenience. Bag stewing enhances ease by allowing ingredients to be pre-measured and sealed, reducing cleanup and simplifying portion control. Both methods provide flexibility, but bag stewing streamlines preparation, saving time and effort in busy kitchens.
Equipment and Ingredients Required
Stewing requires a heavy-bottomed pot or Dutch oven to ensure even heat distribution, while bag stewing utilizes heat-resistant bags and a simpler water bath setup. Traditional stewing demands a variety of fresh vegetables and tougher cuts of meat, whereas bag stewing focuses on vacuum-sealed ingredients for enhanced flavor infusion and tenderness.
- Stewing equipment - Heavy pots retain heat uniformly for slow cooking.
- Bag stewing equipment - Heat-resistant, vacuum-seal bags optimize moisture and flavor retention.
- Ingredient selection - Stewing uses chunks of meat with aromatic vegetables like onions and carrots.
Choosing between stewing and bag stewing depends on the desired texture and convenience in preparation.
Health and Nutrition Considerations
Stewing often preserves more nutrients as it involves slow cooking in a closed pot, preventing vitamin loss and retaining mineral content. Bag stewing, while convenient, may lead to slight nutrient degradation due to heat exposure and less control over cooking time.
Health benefits of stewing include enhanced flavor without added fats, supporting a balanced diet rich in vegetables and lean proteins. Bag stewing can reduce the use of oil and salts, appealing to those aiming for lower-calorie meals but may sacrifice some nutritional depth.
Related Important Terms
Wet-Bulb Stewing
Wet-bulb stewing maintains precise moisture and temperature control by using the wet-bulb temperature to optimize cooking conditions, resulting in tender, evenly cooked ingredients. This method outperforms traditional bag stewing by preventing overcooking and preserving nutrients through a regulated steam environment.
Sous Vide Stewing
Sous vide stewing offers precise temperature control that enhances flavor infusion and tenderizes meat evenly, unlike traditional bag stewing which can result in uneven cooking and flavor loss. This method maintains nutrient retention and moisture, producing consistently succulent dishes with minimal supervision.
Bag Braising
Bag braising offers a controlled environment that evenly distributes heat and retains moisture, enhancing flavor depth and tenderness compared to traditional stewing methods. This technique minimizes nutrient loss and reduces cooking time, making it a superior choice for slow-cooked dishes requiring consistent texture and succulent results.
Vacuum Stewing
Vacuum stewing preserves more nutrients and intensifies flavors by cooking food in a sealed, low-oxygen environment that prevents oxidation and moisture loss. Unlike traditional bag stewing, vacuum stewing ensures tender textures and rich taste while reducing cooking time and energy consumption.
Infusion Packed Stewing
Infusion Packed Stewing enhances flavor extraction by sealing ingredients in a vacuum or infusion bag, promoting deeper nutrient retention and concentrated taste compared to traditional open pot stewing. This method reduces cooking time while preserving texture and aroma, resulting in richer and more vibrant dishes.
Controlled Moisture Stewing
Controlled Moisture Stewing enhances flavor retention and texture by precisely regulating liquid levels and cooking temperatures, unlike traditional bag stewing that often traps excess moisture leading to diluted taste and uneven cooking. This method optimizes nutrient preservation while ensuring consistent heat distribution, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes with minimal nutrient loss.
Low-Oxygen Stewing
Low-oxygen stewing preserves food nutrients by minimizing oxidation during cooking, resulting in richer flavors and enhanced texture compared to bag stewing, which traps moisture but can sometimes lead to a less vibrant taste. The controlled environment in low-oxygen stewing allows for better retention of vitamins and antioxidants, making it a superior method for slow-cooking meats and vegetables.
Immersion Pouch Stewing
Immersion pouch stewing enhances flavor infusion by sealing ingredients in a perforated bag, allowing even heat distribution and preventing nutrient loss during cooking. Unlike traditional stewing, this method minimizes liquid dilution and retains natural juices, resulting in richer, more concentrated dishes.
Zero-Evap Stewing
Zero-evap stewing preserves all the natural moisture and nutrients by sealing the pot completely, unlike bag stewing which relies on steam from a sealed bag inside the pot. This method enhances flavor concentration and maintains the original texture of ingredients without dilution from evaporated liquids.
Stewing vs Bag Stewing for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com