Stewing requires low, slow cooking to tenderize meats and develop rich flavors, typically taking several hours, while Instant Pot pressure cooking dramatically reduces cooking time by using high pressure and heat to achieve similar results in under an hour. The Instant Pot is ideal for busy individuals seeking time-saving convenience without sacrificing the depth of taste stewing offers. Despite the faster cook time, stewing allows for more gradual flavor melding that some cooks may prefer for traditional dishes.
Table of Comparison
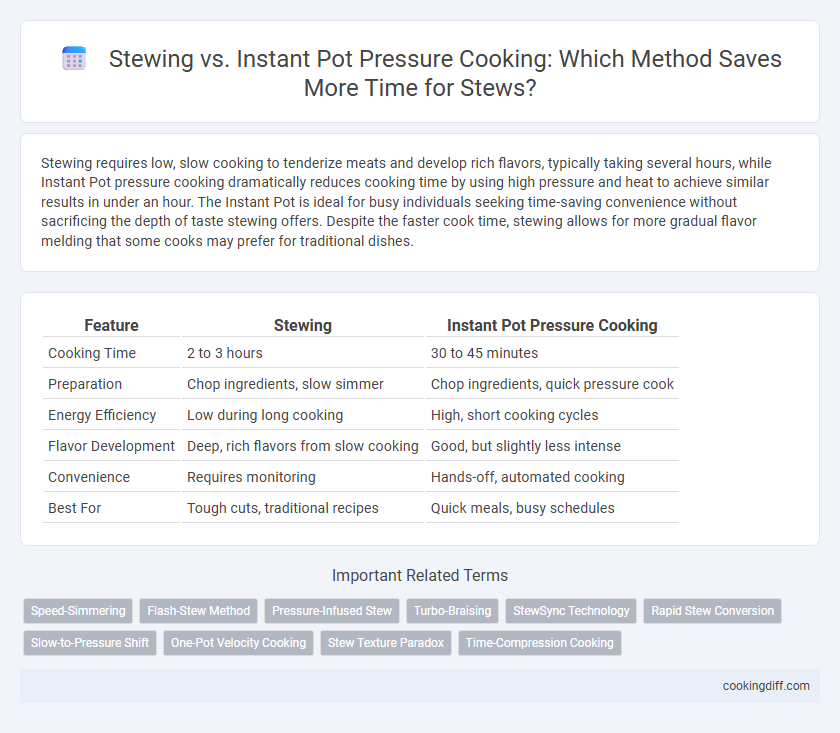
| Feature | Stewing | Instant Pot Pressure Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Time | 2 to 3 hours | 30 to 45 minutes |
| Preparation | Chop ingredients, slow simmer | Chop ingredients, quick pressure cook |
| Energy Efficiency | Low during long cooking | High, short cooking cycles |
| Flavor Development | Deep, rich flavors from slow cooking | Good, but slightly less intense |
| Convenience | Requires monitoring | Hands-off, automated cooking |
| Best For | Tough cuts, traditional recipes | Quick meals, busy schedules |
Introduction to Stewing and Instant Pot Pressure Cooking
Stewing is a slow-cooking method that involves simmering ingredients in liquid at low temperatures for extended periods, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes. Instant Pot pressure cooking uses high-pressure steam to cook foods rapidly, significantly reducing cooking time compared to traditional stewing. Comparing these techniques highlights stewing's depth of flavor development versus the Instant Pot's efficiency in time-saving meal preparation.
How Stewing Works: Traditional Techniques
Stewing involves slow cooking ingredients submerged in liquid over low heat for several hours, allowing flavors to meld and tough cuts of meat to become tender. Traditional stewing techniques rely on consistent, gentle heat from a stovetop or oven, which preserves texture and develops depth in the dish. While stewing is time-intensive, it enhances the complexity of flavors that faster methods like Instant Pot pressure cooking may not fully replicate.
What Is Instant Pot Pressure Cooking?
| Instant Pot pressure cooking uses sealed high-pressure steam to accelerate cooking times drastically. It typically reduces stewing from hours to under an hour by increasing the boiling point of water inside the pot. This method retains moisture and intensifies flavors rapidly compared to traditional stewing. |
Cooking Time Comparison: Stewing vs Instant Pot
Stewing requires several hours of slow cooking to break down tough fibers and develop deep flavors, while Instant Pot pressure cooking drastically reduces this process to under an hour. The significant difference in cooking times makes the Instant Pot a more efficient method for time-saving without sacrificing taste.
- Stewing cooking time - Typically ranges from 2 to 4 hours depending on the recipe and cut of meat.
- Instant Pot pressure cooking time - Usually completes the same dishes in 30 to 45 minutes.
- Time-saving advantage - Instant Pot cooking shortens preparation by up to 75%, ideal for busy schedules.
Using an Instant Pot for stewing delivers tender, flavorful meals with a fraction of the traditional cooking time.
Flavor Development in Both Methods
Stewing allows slow, gentle simmering that enhances flavor development by breaking down collagen and infusing ingredients over several hours. The Instant Pot pressure cooker significantly reduces cooking time while still tenderizing meat and blending flavors efficiently through high-pressure steam.
While stewing promotes deep, complex flavor profiles due to prolonged cooking, the Instant Pot preserves essential aromas and nutrients by sealing in steam and preventing oxidation. Both methods achieve rich, savory results, but the Instant Pot is ideal for fast, flavorful meals without sacrificing taste quality.
Nutrient Retention: Slow vs Pressure Cooking
Stewing retains nutrients by cooking food slowly at low temperatures, preserving vitamins sensitive to heat degradation. Instant Pot pressure cooking uses high pressure and temperature to reduce cooking time, which can sometimes cause slight nutrient loss.
Nutrient retention in stewing is higher for heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and some B vitamins due to the gentle cooking process. Pressure cooking, while faster and efficient in breaking down fibers, may lead to greater nutrient depletion because of intense heat exposure. Choosing between these methods depends on the balance of time-saving and desired nutrient preservation for specific meals.
Texture Differences: Stewed vs Instant Pot Dishes
Stewing slowly breaks down connective tissues, resulting in tender, melt-in-the-mouth textures with rich, developed flavors ideal for hearty dishes. Instant Pot pressure cooking significantly reduces cooking time but can produce a firmer texture that lacks the depth achieved through prolonged simmering.
Stewed dishes typically have a thicker, more cohesive sauce due to gradual reduction, enhancing the dish's overall mouthfeel and complexity. Pressure-cooked meals may retain more liquid, yielding a lighter, less concentrated sauce with a different palate experience.
Convenience and Ease of Use
Is stewing or Instant Pot pressure cooking more convenient and easier to use for time-saving? Stewing requires longer cooking times and more active monitoring, making it less convenient for busy schedules. The Instant Pot offers preset functions and faster pressure cooking, simplifying meal preparation and maximizing ease of use.
Energy and Cost Efficiency
Stewing involves long, slow cooking times that typically consume more energy due to prolonged heat use, while Instant Pot pressure cooking significantly reduces cooking duration, leading to lower energy consumption. The energy efficiency of an Instant Pot translates into cost savings over time, especially for frequent meal preparation.
- Energy Consumption - Instant Pots use sealed, high-pressure environments that cook food faster and more efficiently, reducing electricity usage compared to traditional stewing.
- Cost Efficiency - Reduced cooking time in pressure cooking lowers utility bills, offering greater savings in energy costs relative to slow, continuous heating in stewing.
- Time and Resource Management - Pressure cooking minimizes active cooking time and energy waste, making it an economically and environmentally smarter choice for home cooks prioritizing efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Speed-Simmering
Stewing involves slow cooking over low heat for several hours, resulting in tender, deeply flavored dishes, whereas Instant Pot pressure cooking dramatically reduces cooking time through high-pressure steam, achieving similar tenderness in under an hour. Speed-simmering in an Instant Pot balances rapid cooking with flavor infusion, making it a superior time-saving method for stewing without sacrificing taste or texture.
Flash-Stew Method
The Flash-Stew Method significantly reduces cooking time compared to traditional stewing by combining high heat with short cooking periods, preserving flavors and textures effectively. Unlike Instant Pot pressure cooking, which relies on sealed pressure to cook quickly, flash-stewing uses intense direct heat for rapid flavor development without the risk of overcooking.
Pressure-Infused Stew
Pressure-infused stew created with an Instant Pot significantly reduces cooking time compared to traditional stewing methods by utilizing high-pressure steam to tenderize meat and blend flavors in under an hour. This method maintains the rich, slow-cooked taste while optimizing efficiency, making it ideal for quick meal preparation without sacrificing depth of flavor.
Turbo-Braising
Turbo-braising in stewing accelerates collagen breakdown and flavor infusion by maintaining low, consistent heat over extended periods, enhancing texture and depth compared to Instant Pot pressure cooking. While Instant Pot reduces overall cooking time significantly through high-pressure steam, turbo-braising preserves the nuanced development of flavors essential for traditional stews.
StewSync Technology
StewSync Technology enhances stewing by precisely regulating temperature and cooking duration to optimize flavor and tenderness, often reducing total cooking time compared to traditional methods. Unlike Instant Pot pressure cooking, which uses high pressure to speed up cooking, StewSync maintains ideal simmering conditions that preserve texture and depth in long-simmered dishes while still offering a time-saving advantage.
Rapid Stew Conversion
Stewing requires several hours of slow simmering to fully tenderize ingredients, whereas Instant Pot pressure cooking dramatically reduces this time by using high pressure and temperature to rapidly convert tough cuts into rich, flavorful stews in under an hour. This time-saving method preserves depth of flavor while offering convenient, efficient meal preparation ideal for busy schedules.
Slow-to-Pressure Shift
Stewing requires several hours of gentle simmering to tenderize ingredients, whereas Instant Pot pressure cooking dramatically reduces cooking time by reaching high pressure quickly. The slow-to-pressure shift in Instant Pot models preserves the rich flavors and textures of traditional stewing while delivering meals in a fraction of the time.
One-Pot Velocity Cooking
Stewing typically requires hours of slow simmering, whereas Instant Pot pressure cooking significantly reduces cooking time by rapidly tenderizing ingredients under high pressure. One-Pot Velocity Cooking in an Instant Pot combines speed and convenience, making it the ideal method for time-conscious home cooks seeking hearty, flavorful meals without the long wait.
Stew Texture Paradox
Stewing slowly breaks down collagen and connective tissues, resulting in a rich, tender texture that is difficult to replicate with Instant Pot pressure cooking, which often produces a softer, less complex mouthfeel despite significantly reducing cooking time. The Stew Texture Paradox highlights that while pressure cooking saves time, it may sacrifice the depth and consistency of traditional stew textures achieved through prolonged simmering.
Stewing vs Instant Pot Pressure Cooking for time-saving Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com