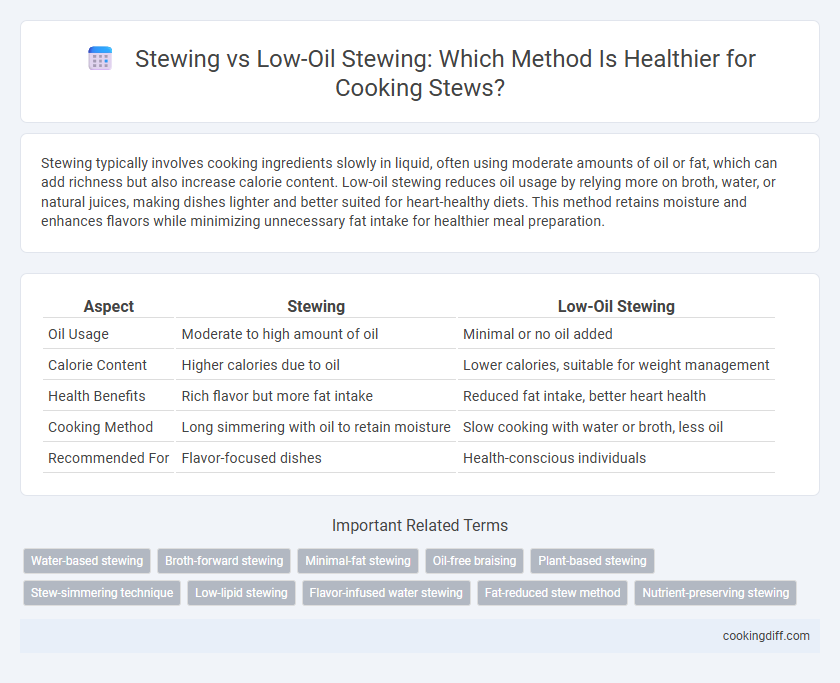
Stewing typically involves cooking ingredients slowly in liquid, often using moderate amounts of oil or fat, which can add richness but also increase calorie content. Low-oil stewing reduces oil usage by relying more on broth, water, or natural juices, making dishes lighter and better suited for heart-healthy diets. This method retains moisture and enhances flavors while minimizing unnecessary fat intake for healthier meal preparation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stewing | Low-Oil Stewing |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Usage | Moderate to high amount of oil | Minimal or no oil added |
| Calorie Content | Higher calories due to oil | Lower calories, suitable for weight management |
| Health Benefits | Rich flavor but more fat intake | Reduced fat intake, better heart health |
| Cooking Method | Long simmering with oil to retain moisture | Slow cooking with water or broth, less oil |
| Recommended For | Flavor-focused dishes | Health-conscious individuals |
Introduction to Stewing: Classic Comfort Cooking
Stewing is a traditional cooking method that involves slow-cooking ingredients in liquid to develop deep flavors and tender textures. Low-oil stewing reduces the amount of added fats, making it a healthier alternative without sacrificing taste.
- Classic Stewing - Uses moderate to high amounts of oil to enhance flavor and promote browning of ingredients before simmering.
- Low-Oil Stewing - Minimizes oil usage, focusing on the natural moisture in ingredients for a lighter, heart-friendly meal.
- Health Benefits - Low-oil stewing reduces calorie intake and saturated fat, supporting cardiovascular health while maintaining nutrient retention.
What Is Low-Oil Stewing?
Low-oil stewing is a cooking method that uses minimal oil, preserving nutrients while reducing calorie intake. It emphasizes slow cooking with liquids like broth or water, enhancing flavor without added fats.
- Healthier Preparation - Low-oil stewing minimizes fat content, making meals heart-friendly and suitable for weight management.
- Nutrient Retention - Cooking with less oil helps retain vitamins and minerals often lost in high-fat stewing processes.
- Flavor Enhancement - Using natural liquids and spices during low-oil stewing intensifies the taste without relying on oil-based flavors.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Low-Oil Stewing
Traditional stewing typically involves cooking ingredients slowly in a moderate amount of liquid with added oils, enhancing flavor but increasing fat content. Low-oil stewing minimizes or eliminates added fats, relying on natural moisture from vegetables and meats to create a lighter, healthier dish. This method preserves nutrients better and reduces calorie intake, making it a preferred choice for health-conscious cooking.
Nutrition Profile: Stewing vs Low-Oil Stewing
Stewing typically uses a moderate amount of oil which enhances flavor but increases calorie content and fat levels. Low-oil stewing reduces added fats, leading to a lower calorie dish while retaining essential nutrients like vitamins and minerals.
The nutrition profile of low-oil stewing prioritizes heart-healthy benefits by limiting saturated fat intake and promoting lean protein absorption. Both methods preserve the hydration and fiber content from vegetables, but low-oil stewing better supports weight management goals.
Oil’s Role in Flavor and Texture
Stewing typically involves using moderate amounts of oil to enhance flavor and tenderize ingredients by promoting Maillard reactions, which develop rich, complex tastes and appealing textures. Oil also helps distribute heat evenly, preventing sticking and ensuring consistent cooking.
Low-oil stewing reduces fat content, making dishes healthier but can result in less intense flavor and a slightly different texture due to reduced browning and moisture retention. To compensate, alternative techniques like using flavorful broths, herbs, and spices are employed to maintain taste while minimizing oil usage.
Health Benefits of Low-Oil Stewing
Low-oil stewing significantly reduces calorie intake and minimizes saturated fat consumption, promoting heart health and weight management. This method retains essential nutrients and flavors by gently cooking ingredients without the excess of unhealthy oils.
Compared to traditional stewing, low-oil stewing lowers the risk of cardiovascular diseases due to decreased bad cholesterol levels. It enhances the absorption of antioxidants from vegetables, supporting immune function and overall well-being. Furthermore, reducing oil usage contributes to better digestion and decreased inflammation, making meals more beneficial for long-term health.
Techniques to Reduce Oil Without Sacrificing Taste
Stewing with minimal oil retains the rich flavors and tender textures characteristic of traditional methods while promoting healthier eating. Techniques such as using non-stick cookware, incorporating moisture-rich ingredients, and carefully controlling cooking temperatures enhance taste without excess fat.
- Non-stick Cookware Usage - Enables cooking with less oil by preventing food from sticking and burning.
- Incorporation of Moist Ingredients - Adds natural juices that reduce the need for added fats during the stewing process.
- Temperature Control - Maintains gentle simmering to efficiently infuse flavors without requiring additional oil.
These techniques make low-oil stewing a practical and flavorful option for health-conscious cooking.
Best Ingredients for Low-Oil Stewing
What are the best ingredients for low-oil stewing to maximize health benefits? Choosing lean proteins like skinless chicken or turkey breast reduces fat content while maintaining rich flavor. Incorporating vegetables such as carrots, onions, and tomatoes enhances nutrient density and natural sweetness without added oils.
Stewing Recipes: Classic vs Low-Oil Versions
| Stewing Method | Health Benefits | Recipe Variations |
| Traditional Stewing | Retains rich flavors and nutrients but may include higher fat content due to oil usage. | Classic beef stew with vegetables, enriched with herbs and broth for depth. |
| Low-Oil Stewing | Reduces fat intake while preserving essential nutrients and moisture in ingredients. | Modified beef stew using minimal oil, enhanced with spices and low-sodium broth. |
Related Important Terms
Water-based stewing
Water-based stewing uses minimal or no oil, preserving nutrients while reducing calorie intake compared to traditional low-oil stewing methods that still incorporate some fat. This technique enhances the natural flavors and tenderness of ingredients through slow cooking in water, promoting a healthier and lighter dish without sacrificing taste.
Broth-forward stewing
Broth-forward stewing enhances nutrient retention and flavor while reducing added fats, making it a healthier alternative to traditional low-oil stewing methods. Utilizing a rich, flavorful broth as the cooking base maximizes moisture and tenderizes ingredients without relying on excessive oil.
Minimal-fat stewing
Minimal-fat stewing eliminates excess oil by using natural juices and water-based liquids to tenderize ingredients, preserving nutrients and reducing calorie intake. This approach enhances flavors through prolonged simmering at low temperatures, offering a healthier alternative to traditional stewing methods that often rely on higher-fat content.
Oil-free braising
Stewing traditionally involves cooking ingredients slowly in liquid, often with added oil or fat to enhance flavor and texture, whereas oil-free braising, a low-oil stewing technique, uses only natural juices and broth, resulting in a healthier dish with reduced calorie content and lower fat levels. This oil-free method preserves nutrients while maintaining tenderness and depth of flavor, making it ideal for health-conscious cooking and weight management.
Plant-based stewing
Stewing plant-based ingredients using low-oil methods reduces calorie intake while preserving essential nutrients and enhancing natural flavors. This approach promotes heart health and supports weight management by minimizing unhealthy fat consumption during prolonged cooking.
Stew-simmering technique
Stewing relies on slow simmering in ample liquid, which tenderizes ingredients and enhances flavor absorption, while low-oil stewing reduces fat without sacrificing the moist heat method essential for nutrient retention. The stew-simmering technique promotes deeper integration of herbs and spices, offering a healthier alternative by minimizing oil use and maximizing savory richness through prolonged, gentle cooking.
Low-lipid stewing
Low-lipid stewing significantly reduces fat content by minimizing oil use while maintaining moisture and enhancing flavor through slow, even cooking; this method preserves nutrients and supports heart-healthy diets. Compared to traditional stewing, low-oil stewing prevents excess calorie intake and reduces saturated fat exposure, promoting overall better health outcomes.
Flavor-infused water stewing
Flavor-infused water stewing preserves nutrient integrity and enhances natural food flavors without added fats, making it a healthier alternative to traditional low-oil stewing. This method delivers tender, richly flavored dishes through slow simmering in seasoned water, reducing calorie intake while maintaining moisture and depth of taste.
Fat-reduced stew method
Stewing with low-oil techniques significantly reduces fat content by substituting excessive fat with water, broth, or natural juices, enhancing nutrient retention while maintaining flavor and tenderness. This fat-reduced stew method benefits heart health and weight management by minimizing saturated fat intake without sacrificing the dish's rich texture.
Stewing vs Low-Oil Stewing for healthier preparation Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com