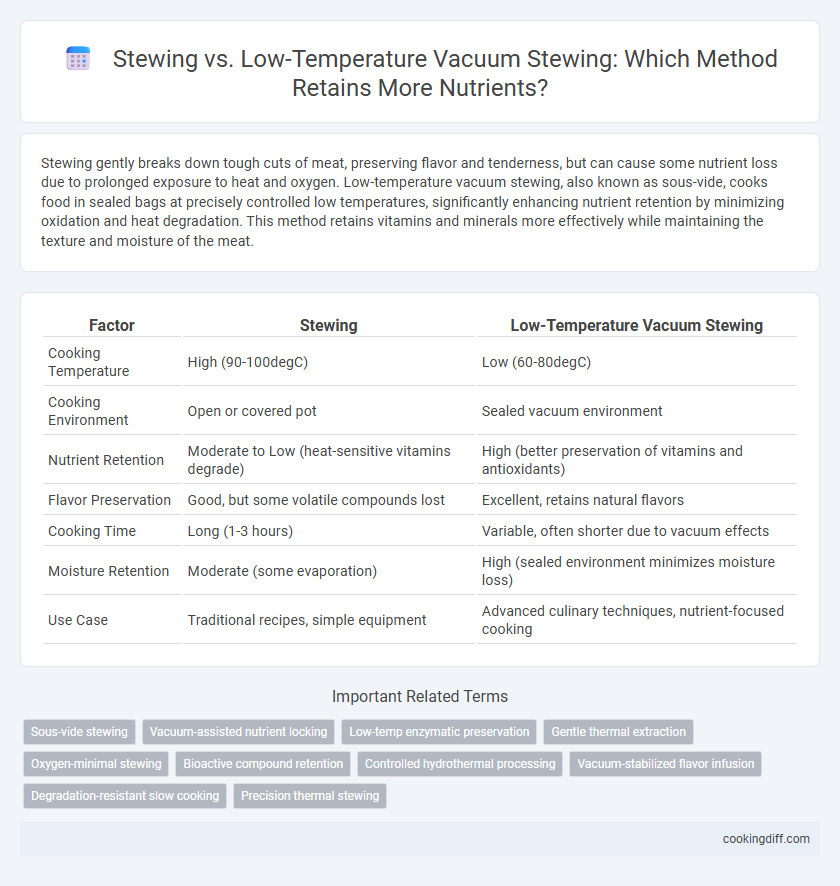
Stewing gently breaks down tough cuts of meat, preserving flavor and tenderness, but can cause some nutrient loss due to prolonged exposure to heat and oxygen. Low-temperature vacuum stewing, also known as sous-vide, cooks food in sealed bags at precisely controlled low temperatures, significantly enhancing nutrient retention by minimizing oxidation and heat degradation. This method retains vitamins and minerals more effectively while maintaining the texture and moisture of the meat.
Table of Comparison
| Factor | Stewing | Low-Temperature Vacuum Stewing |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Temperature | High (90-100degC) | Low (60-80degC) |
| Cooking Environment | Open or covered pot | Sealed vacuum environment |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate to Low (heat-sensitive vitamins degrade) | High (better preservation of vitamins and antioxidants) |
| Flavor Preservation | Good, but some volatile compounds lost | Excellent, retains natural flavors |
| Cooking Time | Long (1-3 hours) | Variable, often shorter due to vacuum effects |
| Moisture Retention | Moderate (some evaporation) | High (sealed environment minimizes moisture loss) |
| Use Case | Traditional recipes, simple equipment | Advanced culinary techniques, nutrient-focused cooking |
Introduction to Stewing and Low-Temperature Vacuum Stewing
Stewing is a traditional cooking method involving slow simmering of ingredients in liquid, which helps break down fibers and meld flavors while preserving some nutrients. Low-temperature vacuum stewing uses sealed bags and precise temperature control below boiling point, significantly reducing nutrient loss by minimizing oxidation and moisture evaporation. Studies show that vacuum stewing better retains vitamins and antioxidants compared to conventional stewing due to its controlled environment and reduced exposure to heat and air.
Understanding Traditional Stewing Methods
How does traditional stewing compare to low-temperature vacuum stewing in preserving nutrients? Traditional stewing involves cooking food slowly in liquid at moderate heat, which can lead to nutrient loss due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures and oxygen. Low-temperature vacuum stewing reduces oxidation and heat damage by cooking food sealed in a vacuum at lower temperatures, enhancing nutrient retention and flavor intensity.
What is Low-Temperature Vacuum Stewing?
| Low-Temperature Vacuum Stewing is a cooking technique that uses controlled low heat and vacuum-sealed conditions to enhance nutrient retention. |
| This method minimizes oxidation and nutrient loss by cooking foods in a sealed environment at temperatures typically below 85degC (185degF). |
| Compared to traditional stewing, it preserves vitamins such as vitamin C and antioxidants more effectively, resulting in healthier, nutrient-rich meals. |
Key Differences in Cooking Temperatures
Stewing typically involves cooking at temperatures around 85-95degC, which can lead to nutrient loss due to prolonged exposure to heat. Low-temperature vacuum stewing operates at lower temperatures, usually between 60-70degC, preserving more vitamins and minerals by reducing oxidation and heat degradation.
- Stewing Temperature Range - Traditional stewing uses higher heat (85-95degC) to break down fibers and tenderize food.
- Vacuum Stewing Temperature Range - Low-temperature vacuum stewing maintains 60-70degC to protect sensitive nutrients.
- Nutrient Retention - Lower temperatures in vacuum stewing minimize nutrient loss compared to conventional stewing.
Effects on Nutrient Retention: Stewing vs Vacuum Stewing
Stewing at traditional temperatures often leads to significant nutrient loss, especially water-soluble vitamins such as vitamin C and B-complex vitamins. Low-temperature vacuum stewing preserves nutrients more effectively by reducing oxidation and preventing nutrient degradation through minimal exposure to air and lower cooking temperatures. Research shows vacuum stewing retains up to 30% more antioxidants and essential vitamins compared to conventional stewing methods.
Moisture and Texture: Comparing Outcomes
Low-temperature vacuum stewing significantly preserves moisture content compared to traditional stewing, resulting in juicier dishes. Texture retention is superior in vacuum stewing, maintaining tenderness and structural integrity without overcooking.
- Moisture preservation - Vacuum stewing limits water loss by cooking in a sealed environment, enhancing juiciness.
- Texture maintenance - Slow, controlled heat prevents fiber breakdown, keeping meat tender and intact.
- Comparative outcome - Traditional stewing allows more moisture evaporation, often leading to drier textures.
Impact on Vitamins and Minerals
Stewing typically leads to significant nutrient loss, especially water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex due to prolonged heat exposure. Low-temperature vacuum stewing preserves more vitamins and minerals by reducing oxidation and thermal degradation.
- Vitamin Retention in Stewing - Vitamins C and B are highly sensitive to heat and prolonged cooking times, resulting in decreased nutrient levels during traditional stewing.
- Mineral Stability - Minerals such as potassium and magnesium remain more stable during low-temperature vacuum stewing because the cooking environment limits leaching into cooking liquids.
- Oxidation Reduction - Vacuum conditions reduce oxygen exposure, minimizing oxidative damage to sensitive vitamins, enhancing overall nutrient preservation.
Low-temperature vacuum stewing is scientifically proven to optimize nutrient retention compared to conventional stewing methods.
Flavor Development in Both Techniques
Stewing at higher temperatures intensifies flavor through Maillard reactions and caramelization, creating richer and more robust taste profiles. Low-temperature vacuum stewing, however, preserves subtle flavors by gently breaking down collagen without overcooking delicate ingredients.
Vacuum stewing enhances umami and tenderness by maintaining consistent heat and moisture, which prevents nutrient loss and flavor degradation. Traditional stewing can sometimes cause volatile flavor compounds to evaporate, reducing aromatic complexity. Both methods develop flavor effectively but differ in how they balance intensity and subtlety based on temperature and cooking environment.
Practical Considerations: Equipment and Time
Traditional stewing requires basic cookware such as heavy pots or slow cookers, which are widely accessible and easy to use, but it often involves longer cooking times that can lead to nutrient loss. Low-temperature vacuum stewing demands specialized equipment like vacuum sealers and immersion circulators, making it less accessible but more efficient in preserving vitamins and minerals.
Time management also differs significantly; conventional stewing can take several hours, relying on sustained heat exposure, whereas low-temperature vacuum stewing shortens cooking duration with precise temperature control. The investment in advanced equipment balances with improved nutrient retention and consistent cooking quality, making it practical for health-conscious users.
Related Important Terms
Sous-vide stewing
Sous-vide stewing employs precise low-temperature vacuum cooking that significantly preserves vitamins and minerals compared to traditional stewing methods, which often degrade heat-sensitive nutrients. This technique maintains optimal moisture and nutrient retention by sealing food in airtight bags, minimizing oxidation and nutrient loss during prolonged cooking.
Vacuum-assisted nutrient locking
Low-temperature vacuum stewing preserves nutrients by minimizing oxygen exposure and reducing oxidative degradation, which is a common issue in traditional stewing methods. Vacuum-assisted nutrient locking enhances the retention of vitamins and minerals, resulting in more nutrient-dense, flavorful dishes compared to conventional high-heat stewing.
Low-temp enzymatic preservation
Low-temperature vacuum stewing preserves nutrients more effectively by maintaining enzymatic activity that prevents nutrient degradation, unlike traditional stewing methods where high heat denatures enzymes and reduces nutrient bioavailability. This gentle cooking process enhances the retention of vitamins, antioxidants, and proteins, optimizing the nutritional value of stewed foods.
Gentle thermal extraction
Stewing uses higher temperatures that can degrade heat-sensitive nutrients, whereas low-temperature vacuum stewing employs gentle thermal extraction, preserving vitamins and antioxidants more effectively. This method minimizes nutrient loss by maintaining a controlled, low-oxygen environment that reduces oxidation and thermal damage.
Oxygen-minimal stewing
Oxygen-minimal stewing reduces oxidation, preserving heat-sensitive vitamins such as vitamin C and B-complex more effectively than traditional stewing methods. Low-temperature vacuum stewing further enhances nutrient retention by creating an anaerobic environment that limits nutrient degradation and maintains the natural flavors and textures of ingredients.
Bioactive compound retention
Stewing preserves a moderate amount of bioactive compounds, but low-temperature vacuum stewing significantly enhances nutrient retention by minimizing heat exposure and oxygen contact. This method protects sensitive antioxidants, vitamins, and polyphenols, ensuring higher bioactive compound stability compared to traditional stewing.
Controlled hydrothermal processing
Controlled hydrothermal processing during low-temperature vacuum stewing significantly enhances nutrient retention by minimizing thermal degradation and preserving water-soluble vitamins compared to traditional stewing methods. This technique maintains optimal moisture levels and reduces oxidation, resulting in higher bioavailability of essential nutrients such as vitamin C, B-complex vitamins, and antioxidants.
Vacuum-stabilized flavor infusion
Low-temperature vacuum stewing enhances nutrient retention by minimizing oxidation and preserving heat-sensitive vitamins better than traditional stewing methods. Vacuum-stabilized flavor infusion intensifies taste profiles by sealing in aromas and promoting deeper ingredient absorption during the slow cooking process.
Degradation-resistant slow cooking
Stewing preserves nutrients by slowly cooking ingredients in liquid at moderate temperatures, but low-temperature vacuum stewing significantly enhances nutrient retention through a sealed, oxygen-free environment that minimizes oxidative degradation. This degradation-resistant slow cooking method maintains higher levels of vitamins and antioxidants compared to traditional stewing by preventing nutrient loss caused by heat and exposure to air.
Stewing vs Low-temperature vacuum stewing for nutrient retention. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com