Stewing involves slow-cooking meat and vegetables to develop rich flavors and tender textures, typically using animal-based ingredients like beef or chicken. Plant-based stewing emphasizes vegetables, legumes, and meat alternatives, prioritizing nutrient-dense, fiber-rich options such as lentils, mushrooms, and tofu to create hearty, flavorful dishes without animal products. Ingredient selection in plant-based stewing focuses on maximizing umami and texture contrasts to replicate the depth found in traditional stews.
Table of Comparison
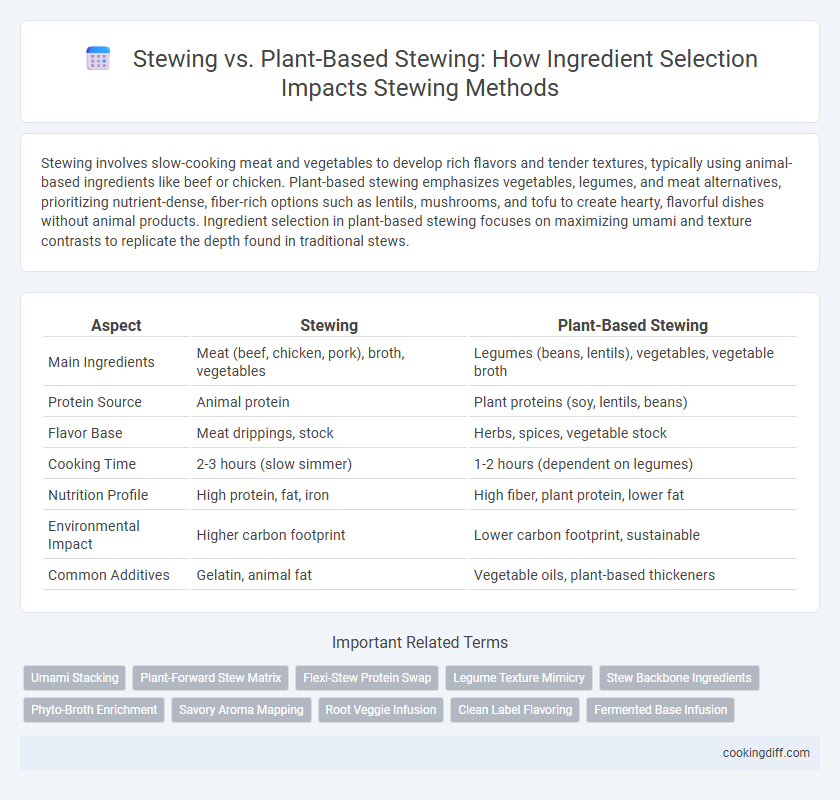
| Aspect | Stewing | Plant-Based Stewing |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredients | Meat (beef, chicken, pork), broth, vegetables | Legumes (beans, lentils), vegetables, vegetable broth |
| Protein Source | Animal protein | Plant proteins (soy, lentils, beans) |
| Flavor Base | Meat drippings, stock | Herbs, spices, vegetable stock |
| Cooking Time | 2-3 hours (slow simmer) | 1-2 hours (dependent on legumes) |
| Nutrition Profile | High protein, fat, iron | High fiber, plant protein, lower fat |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint | Lower carbon footprint, sustainable |
| Common Additives | Gelatin, animal fat | Vegetable oils, plant-based thickeners |
Understanding Stewing: Traditional vs. Plant-Based Approaches
What are the key differences between traditional stewing and plant-based stewing in ingredient selection? Traditional stewing relies on animal proteins like beef, pork, or chicken combined with root vegetables and broth to develop rich flavors. Plant-based stewing emphasizes legumes, mushrooms, and vegetable broths to create depth and texture while maintaining a nutrient-rich profile.
Key Differences in Ingredient Selection
Stewing traditionally relies on animal-based proteins such as beef or chicken, while plant-based stewing uses legumes, tofu, and vegetables as the primary ingredients. The choice of herbs, spices, and liquids in each approach is tailored to enhance the distinct flavors of animal or plant components.
- Protein Source Selection - Traditional stewing emphasizes meat cuts that become tender over long cooking times, whereas plant-based stewing selects hearty beans, lentils, and mushrooms for texture and nutrition.
- Flavor Enhancers - Animal-based stewing often uses meat stocks, while plant-based recipes utilize vegetable broths and umami-rich ingredients like soy sauce and nutritional yeast.
- Cooking Fat Used - Traditional stews typically incorporate animal fats or butter, whereas plant-based stews prefer oils such as olive or coconut oil to maintain vegan standards.
Ingredient selection directly influences the nutritional profile and taste complexity in stewing methods.
Protein Choices: Meat Cuts vs. Plant-Based Alternatives
Stewing traditionally relies on tougher meat cuts like chuck or brisket, which become tender through slow cooking. Plant-based stewing uses protein alternatives such as lentils, beans, and textured vegetable protein that mimic meat's texture while offering fiber and essential nutrients.
- Meat cuts in stewing - Tougher cuts with higher collagen content break down into tender, flavorful pieces during long cooking times.
- Plant-based protein alternatives - Ingredients like legumes provide protein and absorb flavors, creating hearty and nutritious stews without animal products.
- Nutrition and sustainability - Plant-based proteins typically offer lower saturated fat and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional meat cuts.
Essential Vegetables for Stewing and Plant-Based Stews
Essential vegetables for traditional stewing include carrots, onions, celery, and potatoes, which provide rich flavors and hearty textures. These ingredients create a balanced base that enhances the depth of meat or vegetable broths.
Plant-based stewing emphasizes nutrient-dense vegetables like butternut squash, mushrooms, bell peppers, and kale to deliver robust flavors and plant-derived nutrients. Selecting a variety of these vegetables ensures a vibrant, wholesome stew rich in vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants.
Broths and Liquids: Animal-Based vs. Vegetable-Based Options
Animal-based broths, such as beef or chicken stock, provide a rich umami flavor and gelatin that enhance the body and mouthfeel of traditional stews. These broths are often simmered for hours to extract collagen and deep flavors from bones and connective tissues.
Vegetable-based broths rely on a blend of herbs, vegetables, and sometimes seaweed to create a savory, nutrient-rich liquid that supports plant-based stews. These broths offer lighter profiles with versatile flavor adaptability, making them ideal for various dietary preferences and enhancing the freshness of the ingredients.
Herbs and Spices: Flavor Builders in Both Methods
Herbs and spices are essential flavor builders in both traditional stewing and plant-based stewing, enhancing depth and complexity. The choice of herbs can vary based on the protein or vegetables used, tailoring the taste profile effectively.
- Rosemary and Thyme - Commonly used in meat-based stewing for their robust, earthy flavors that complement rich proteins.
- Cumin and Coriander - Popular in plant-based stews to add warmth and a slightly citrusy note, enriching vegetable dishes.
- Bay Leaves and Garlic - Universal flavor enhancers in both methods, providing aromatic depth and savory undertones.
Fats and Oils: Animal Fats Compared to Plant Oils
Animal fats such as lard and tallow offer rich flavors and higher smoke points ideal for traditional stewing methods, enhancing texture and depth. Plant oils like olive, avocado, and coconut provide heart-healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, contributing to lighter, plant-based stews with diverse nutrient profiles. Selecting fats depends on dietary preferences and desired flavor intensity, with animal fats enriching savory profiles and plant oils supporting vegan and cholesterol-conscious options.
Cooking Times: Adjusting for Different Ingredients
| Stewing traditional meats like beef or lamb requires longer cooking times, typically 2 to 3 hours, to tenderize tougher cuts and develop rich flavors. |
| Plant-based stewing ingredients such as legumes, root vegetables, and mushrooms usually need shorter cooking times, around 45 minutes to 1.5 hours, to soften without becoming mushy. |
| Adjusting liquid levels and heat during stewing is crucial to accommodate varying ingredient absorbency and prevent overcooking, ensuring optimal texture in both meat and plant-based dishes. |
Texture and Mouthfeel: Comparing Stewing Techniques
Stewing with traditional ingredients often results in a rich, tender texture due to the breakdown of collagen in meats, creating a succulent mouthfeel. Plant-based stewing relies on legumes, vegetables, and textured proteins that maintain a firmer, sometimes slightly grainy texture, offering a different but satisfying chew. Both techniques require careful selection of ingredients to balance softness and structure for optimal mouthfeel in the final dish.
Related Important Terms
Umami Stacking
Stewing with traditional meats enriches dishes through deep umami compounds like glutamates and inosinate found in animal proteins, intensifying flavor complexity. Plant-based stewing relies on umami stacking by combining ingredients such as mushrooms, tomatoes, seaweed, and fermented soy products to replicate these savory profiles naturally.
Plant-Forward Stew Matrix
The Plant-Forward Stew Matrix emphasizes nutrient-dense vegetables, legumes, and whole grains as primary ingredients, enhancing flavor complexity and maximizing health benefits compared to traditional stewing methods reliant on animal proteins. Incorporating diverse plant-based components supports sustainability and offers a versatile base for creating hearty, fiber-rich stews without compromising taste or texture.
Flexi-Stew Protein Swap
Flexi-Stew protein swap emphasizes versatile ingredient selection, enabling easy substitution of animal proteins with plant-based options like lentils, chickpeas, and mushrooms to create nutrient-rich stews. This approach enhances flavor complexity and dietary flexibility while reducing environmental impact and accommodating diverse dietary preferences.
Legume Texture Mimicry
Stewing with traditional meats offers a hearty, fibrous texture that legumes alone often lack, but plant-based stewing leverages specific legumes like chickpeas and lentils, combined with strategic soaking and cooking times to emulate the dense, chewy consistency of meat. Techniques such as pressure cooking and the use of texturizing agents like vital wheat gluten enhance legume texture mimicry, providing a satisfying mouthfeel comparable to conventional stewed proteins.
Stew Backbone Ingredients
Traditional stewing relies heavily on backbone ingredients such as beef chuck, lamb shanks, or pork shoulder, which provide rich collagen and umami depth crucial for thick, flavorful broths. Plant-based stewing substitutes these proteins with hearty vegetables like mushrooms, lentils, and legumes, along with umami boosters such as miso or soy sauce, creating a complex, nutrient-rich backbone that supports savory and satisfying flavors.
Phyto-Broth Enrichment
Stewing with traditional ingredients often relies on animal-based broths rich in collagen and amino acids, whereas plant-based stewing emphasizes phytonutrient-dense vegetable broths that enhance phyto-broth enrichment by providing antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Utilizing ingredients such as mushrooms, seaweed, and root vegetables in plant-based stews maximizes the extraction of bioactive compounds, promoting a nutrient-rich and flavorful broth alternative.
Savory Aroma Mapping
Stewing traditional meats releases complex Maillard reaction compounds, enhancing savory aroma profiles rich in umami and roasted notes. Plant-based stewing ingredients, such as mushrooms, legumes, and soy, contribute distinct glutamate and nucleotide-based flavors, creating a layered savory aroma map with earthy, smoky, and slightly sweet characteristics.
Root Veggie Infusion
Root veggie infusion enhances stewing by intensifying natural flavors and adding rich nutrients through slow cooking of carrots, parsnips, and turnips. Plant-based stewing leverages this infusion to create vibrant, hearty dishes with improved fiber content and essential vitamins.
Clean Label Flavoring
Stewing traditionally relies on rich animal-based broths and slow-cooked herbs for deep, savory flavors, while plant-based stewing leverages natural vegetable extracts, mushrooms, and fermented ingredients to achieve clean label flavoring without artificial additives. Selecting fresh, minimally processed whole foods and spices enhances umami and mouthfeel in plant-based stews, meeting consumer demand for transparency and natural ingredients.
Stewing vs Plant-Based Stewing for ingredient selection. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com