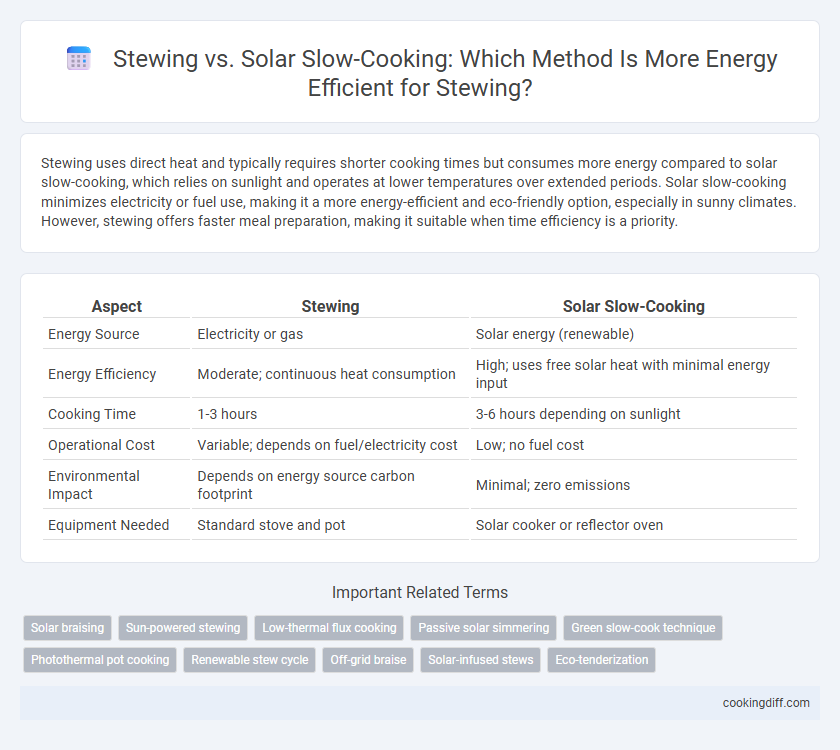
Stewing uses direct heat and typically requires shorter cooking times but consumes more energy compared to solar slow-cooking, which relies on sunlight and operates at lower temperatures over extended periods. Solar slow-cooking minimizes electricity or fuel use, making it a more energy-efficient and eco-friendly option, especially in sunny climates. However, stewing offers faster meal preparation, making it suitable when time efficiency is a priority.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stewing | Solar Slow-Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Electricity or gas | Solar energy (renewable) |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate; continuous heat consumption | High; uses free solar heat with minimal energy input |
| Cooking Time | 1-3 hours | 3-6 hours depending on sunlight |
| Operational Cost | Variable; depends on fuel/electricity cost | Low; no fuel cost |
| Environmental Impact | Depends on energy source carbon footprint | Minimal; zero emissions |
| Equipment Needed | Standard stove and pot | Solar cooker or reflector oven |
Introduction to Stewing and Solar Slow-Cooking
Stewing is a traditional slow-cooking method that uses low heat and moisture to tenderize food over time, preserving nutrients and flavors. Solar slow-cooking employs solar energy to heat food gradually, reducing reliance on conventional energy sources and enhancing sustainability. Both techniques emphasize energy efficiency by utilizing prolonged cooking at low temperatures for optimal taste and resource conservation.
How Traditional Stewing Consumes Energy
Traditional stewing relies on consistent heat application over an extended period, typically using gas or electric stovetops that consume significant amounts of energy. The continuous energy demand maintains the liquid at a simmer, leading to considerable fuel usage throughout the cooking process.
In contrast, solar slow-cooking harnesses renewable solar energy, minimizing electricity or gas consumption. This method traps heat efficiently, allowing food to cook slowly without the constant energy input required by conventional stoves.
The Science Behind Solar Slow-Cooking
Solar slow-cooking harnesses concentrated solar energy to maintain consistent low temperatures, optimizing the slow-cooking process with minimal energy loss. This method utilizes the greenhouse effect and thermal insulation to trap heat, making it significantly more energy-efficient than traditional stewing on stovetops or in ovens.
- Concentrated Solar Heat - Solar slow-cookers use reflective panels to focus sunlight, generating steady temperatures ideal for slow cooking.
- Greenhouse Effect - The design traps infrared radiation within an insulated chamber, reducing heat dissipation and conserving energy.
- Reduced Fuel Consumption - By relying on renewable solar energy, this method eliminates the need for electricity or gas, boosting overall energy efficiency.
Comparing Energy Inputs: Stewing vs Solar Slow-Cooking
Stewing typically requires continuous energy input from a stove or electric source, making it more energy-intensive during the cooking process. Solar slow-cooking harnesses solar energy, significantly reducing conventional energy consumption by utilizing natural heat over extended periods.
- Energy Consumption in Stewing - Stewing demands a consistent fuel source, usually gas or electricity, leading to higher operational energy usage.
- Solar Slow-Cooking Efficiency - Solar slow-cooking captures free solar energy, minimizing reliance on non-renewable energy resources.
- Environmental Impact - Solar slow-cooking reduces carbon emissions compared to stewing, contributing to greener cooking methods.
Choosing solar slow-cooking over traditional stewing enhances overall energy efficiency and sustainability in meal preparation.
Cookware and Equipment for Optimal Efficiency
Choosing the right cookware significantly impacts energy efficiency in stewing and solar slow-cooking methods. Properly insulated, dark-bottomed pots retain heat longer, reducing energy consumption regardless of the heat source.
- Material Matters - Cast iron and enameled steel pots offer superior heat retention essential for slow, consistent cooking.
- Insulation is Key - Double-walled or insulated cookware maintains temperature better, minimizing heat loss during the cooking process.
- Size and Fit - Using cookware sized appropriately for the heat source ensures maximum heat transfer and less wasted energy.
Environmental Impact of Both Methods
Stewing on a conventional stove typically consumes more fossil fuel energy, leading to higher greenhouse gas emissions compared to solar slow-cooking, which harnesses renewable solar energy and produces zero direct emissions. Solar slow-cooking significantly reduces the carbon footprint by eliminating the need for electricity or gas, making it a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious cooking. The decreased reliance on non-renewable energy sources in solar slow-cooking contributes to long-term environmental benefits, including reduced air pollution and conservation of natural resources.
Heat Retention and Cooking Duration
Stewing typically involves slow cooking on a stovetop, where heat retention is limited by the pot's material and ambient temperature, often resulting in longer cooking durations. Solar slow-cooking utilizes insulated solar cookers that maintain consistent heat through natural energy, significantly enhancing heat retention during the cooking process.
This optimized heat retention in solar slow-cooking reduces overall cooking times compared to traditional stewing, leveraging renewable energy for enhanced efficiency. Consequently, solar slow-cooking offers a sustainable alternative with lower energy consumption and comparable or faster stewing results.
Flavor and Texture Differences
| Method | Flavor | Texture | Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stewing | Allows deep flavor infusion as ingredients simmer together, enhancing richness and complexity. | Produces tender, well-cooked meat and soft vegetables due to consistent low heat. | Uses moderate stovetop heat; less energy efficient than solar slow-cooking but faster results. |
| Solar Slow-Cooking | Develops subtle, nuanced flavors over extended cooking times, preserving delicate herbs and spices. | Results in extremely tender, melt-in-mouth texture with fibers breaking down slowly. | Highly energy efficient by harnessing renewable solar energy, ideal for sustainable cooking. |
Cost Savings Over Time
Stewing uses consistent low heat on a stovetop, consuming more energy compared to solar slow-cooking, which harnesses renewable solar power and significantly reduces electricity or gas bills. Over time, solar slow-cooking offers substantial cost savings by eliminating fuel expenses associated with conventional stewing methods.
Solar slow-cooking's reliance on natural sunlight cuts monthly energy costs, especially in sunny regions, making it an eco-friendly alternative with long-term financial benefits. Although initial setup costs for solar cookers may be higher, the payback period is short due to zero operational fuel costs. In contrast, traditional stewing continuously draws power from utility sources, increasing cumulative expenses over time.
Related Important Terms
Solar braising
Solar braising utilizes concentrated solar energy to maintain steady low temperatures ideal for stewing, significantly reducing reliance on conventional fuels and cutting cooking energy costs by up to 70%. This method enhances thermal retention and nutrient preservation while promoting sustainable, eco-friendly slow-cooking compared to traditional stewing techniques.
Sun-powered stewing
Sun-powered stewing harnesses solar energy through specialized slow cookers, reducing reliance on electricity and lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional stewing methods. This sustainable approach maximizes energy efficiency by utilizing consistent, renewable heat, making it an eco-friendly alternative for long-duration cooking.
Low-thermal flux cooking
Stewing utilizes low-thermal flux cooking by gently simmering food at consistent, moderate temperatures, minimizing energy waste and preserving nutrients. Solar slow-cooking harnesses renewable solar energy to maintain similar low-thermal flux conditions, offering an eco-friendly alternative with significantly reduced reliance on conventional power sources.
Passive solar simmering
Passive solar simmering harnesses natural sunlight through insulated, reflective solar cookers that trap heat for slow-cooking stews, reducing reliance on electricity or fuel. This method achieves high energy efficiency by maintaining steady, low temperatures ideal for simmering, minimizing heat loss compared to conventional stewing on stovetops.
Green slow-cook technique
Stewing utilizes simmering in a pot to tenderize food but requires continuous heat, leading to higher energy consumption compared to solar slow-cooking, which harnesses renewable solar energy for a sustainable, low-impact cooking process. Green slow-cook techniques like solar cooking reduce carbon emissions and lower utility costs, making them ideal for eco-conscious kitchens focused on energy efficiency and environmental preservation.
Photothermal pot cooking
Photothermal pot cooking uses solar energy to generate consistent heat for stewing, significantly reducing reliance on conventional fuels and lowering carbon emissions. This method offers superior energy efficiency compared to traditional slow-cooking by harnessing renewable solar power through specialized photothermal materials that maximize heat retention and minimize energy loss.
Renewable stew cycle
Stewing with a renewable stew cycle harnesses solar slow-cooking energy to reduce fuel consumption and carbon emissions compared to conventional stewing methods that rely on fossil fuels. Solar slow-cooking optimizes thermal retention and utilizes renewable solar energy, enhancing energy efficiency and supporting sustainable cooking practices.
Off-grid braise
Stewing relies on continuous heat from a stove or open fire, consuming more fuel compared to solar slow-cooking, which harnesses free solar energy to maintain low temperatures ideal for off-grid braising. Solar slow-cooking reduces carbon emissions and fuel dependency, making it the most sustainable option for energy-efficient off-grid cooking methods.
Solar-infused stews
Solar-infused stews leverage solar slow-cooking methods that reduce energy consumption by using the sun's natural heat to gently cook ingredients over several hours, preserving nutrients and enhancing flavors without relying on electricity or gas. This sustainable technique offers significant energy savings compared to traditional stewing, making it an eco-friendly choice for long, low-temperature cooking processes.
Stewing vs Solar slow-cooking for energy efficiency. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com