Stewing maximizes flavor by slowly cooking ingredients, but zero-waste root-to-stem stews enhance sustainability by using every part of vegetables and meats, reducing food waste significantly. This approach not only conserves resources but also creates nutrient-rich, diverse dishes that honor the whole ingredient. Embracing root-to-stem stewing supports environmentally friendly cooking practices while delivering complex, satisfying meals.
Table of Comparison
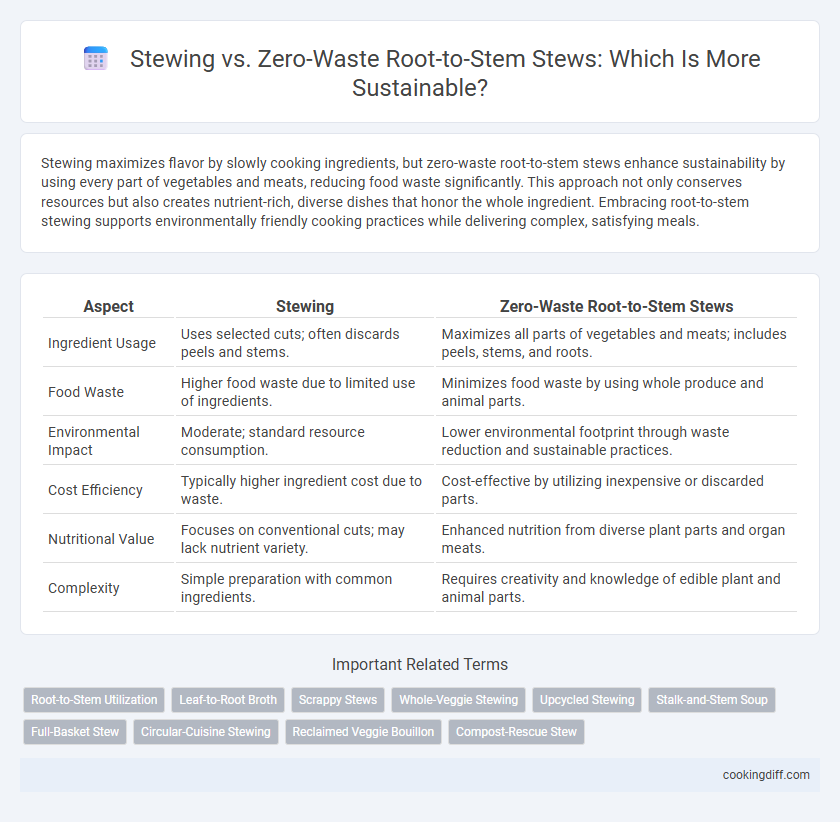
| Aspect | Stewing | Zero-Waste Root-to-Stem Stews |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient Usage | Uses selected cuts; often discards peels and stems. | Maximizes all parts of vegetables and meats; includes peels, stems, and roots. |
| Food Waste | Higher food waste due to limited use of ingredients. | Minimizes food waste by using whole produce and animal parts. |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate; standard resource consumption. | Lower environmental footprint through waste reduction and sustainable practices. |
| Cost Efficiency | Typically higher ingredient cost due to waste. | Cost-effective by utilizing inexpensive or discarded parts. |
| Nutritional Value | Focuses on conventional cuts; may lack nutrient variety. | Enhanced nutrition from diverse plant parts and organ meats. |
| Complexity | Simple preparation with common ingredients. | Requires creativity and knowledge of edible plant and animal parts. |
Understanding Stewing: Traditional Techniques and Benefits
How does traditional stewing contribute to sustainability through culinary techniques? Stewing involves slow-cooking tougher cuts of meat and root vegetables, maximizing flavor and nutrient extraction while minimizing waste. This method supports zero-waste practices by enabling root-to-stem usage of ingredients, reducing food discard and promoting resource efficiency in the kitchen.
What is Zero-Waste Root-to-Stem Cooking?
| Zero-Waste Root-to-Stem Cooking | Zero-waste root-to-stem cooking involves using every part of vegetables and fruits, including stems, roots, leaves, and peels, to minimize food waste and maximize nutritional value. This sustainable practice reduces the environmental impact of food production and promotes resource efficiency. In contrast to traditional stewing methods that often discard non-central parts, root-to-stem stews creatively incorporate all edible components into flavorful, nutrient-dense meals. |
Comparing Classic Stewing vs Root-to-Stem Stews
Classic stewing typically uses select cuts of meat and trimmed vegetables, leading to more food waste, whereas zero-waste root-to-stem stews incorporate whole ingredients, including peels and stems, maximizing nutrition and sustainability. Root-to-stem stews reduce environmental impact by minimizing discarded food and emphasizing seasonal, local produce.
- Ingredient Utilization - Classic stewing often discards vegetable scraps and less tender meat parts, while root-to-stem methods utilize all edible parts to decrease waste.
- Environmental Impact - Zero-waste stews lower carbon footprint by reducing food waste and supporting sustainable sourcing practices, enhancing eco-friendliness.
- Nutritional Value - Root-to-stem stewing preserves more vitamins and minerals found in peels and stems, providing a richer, more nutrient-dense meal.
Environmental Impact: Stewing vs Zero-Waste Approaches
Traditional stewing often leads to food waste by discarding peels and stems, increasing the environmental footprint through unnecessary resource use. Zero-waste root-to-stem stews maximize ingredient usage, significantly reducing biodegradable waste and lowering carbon emissions associated with food production and disposal.
- Resource Efficiency - Zero-waste stews use entire vegetables and meat cuts, minimizing waste and reducing the demand for new agricultural resources.
- Carbon Footprint - Utilizing all parts of ingredients in stewing decreases methane emissions from decomposing organic waste in landfills.
- Water Conservation - Root-to-stem cooking reduces water usage by making full use of harvested crops, avoiding the waste of water invested in discarded parts.
Adopting zero-waste stewing practices enhances sustainability by optimizing ingredient use and mitigating environmental harm.
Maximizing Nutrition: Whole Vegetable Utilization
Stewing enhances nutrient absorption by breaking down fibrous textures, making vitamins and minerals from whole vegetables more bioavailable. Zero-waste root-to-stem stews maximize nutrition by incorporating skins, stems, and leaves, which are rich in fiber, antioxidants, and micronutrients typically discarded. Using entire vegetables reduces food waste while delivering diverse nutrients to support sustainable and health-conscious diets.
Flavor Profiles: Conventional Stews vs Root-to-Stem Innovations
Conventional stewing methods often rely on prime cuts of meat and select vegetables, resulting in rich but sometimes predictable flavor profiles dominated by savory and umami notes. Root-to-stem stews innovate by incorporating vegetable stems, peels, and less-used meat cuts, enhancing complexity through earthy, bitter, and aromatic undertones that deepen the dish's overall sensory appeal.
The inclusion of diverse, zero-waste ingredients not only elevates flavor layers but also supports sustainability by minimizing food waste and maximizing nutrient extraction. These sustainable stewing approaches promote dynamic taste experiences that highlight the natural qualities of all plant and animal parts, pushing culinary boundaries beyond traditional stews.
Reducing Food Waste Through Root-to-Stem Stews
Stewing techniques that embrace root-to-stem cooking significantly reduce food waste by utilizing entire vegetables and meat components often discarded. This zero-waste approach not only maximizes nutritional value but also lowers environmental impact by minimizing organic discard. Seasonal produce like beet greens, carrot tops, and meat bones infuse stews with flavor and nutrients, promoting sustainable eating habits.
Practical Tips for Zero-Waste Stewing at Home
Utilize every part of your vegetables, including stems and leaves, to create nutrient-rich broths and stews, minimizing food waste. Store vegetable scraps in a freezer bag and use them to enhance flavors in your zero-waste stew recipes.
Choose seasonal, local produce to reduce your carbon footprint and support sustainable farming practices. Incorporate whole grains and legumes to boost nutritional value and stretch ingredients further. Experiment with slow cooking methods to extract maximum flavor while conserving energy in your kitchen.
Popular Root-to-Stem Ingredients in Sustainable Stews
Root-to-stem stewing maximizes the use of entire vegetables, reducing food waste and enhancing sustainability. Popular ingredients like carrot tops, beet greens, and broccoli stems add unique flavors and nutrients not typically utilized in traditional stews.
- Carrot Tops - Rich in vitamins and antioxidants, carrot tops provide a fresh, slightly bitter flavor ideal for hearty stews.
- Beet Greens - These nutrient-dense leaves offer iron and calcium, contributing both color and taste to sustainable root-to-stem recipes.
- Broccoli Stems - Often discarded, broccoli stems have a mild, sweet flavor and fibrous texture perfect for slow cooking in stews.
Related Important Terms
Root-to-Stem Utilization
Stewing methods that emphasize root-to-stem utilization maximize the use of entire vegetables, including stems, leaves, and roots, significantly reducing food waste and enhancing nutritional value. This zero-waste approach supports sustainability by minimizing discard rates and conserving resources through comprehensive ingredient usage in stews.
Leaf-to-Root Broth
Leaf-to-Root Broth maximizes sustainability by using entire vegetables, including stems, leaves, and roots, minimizing food waste in stewing. This zero-waste approach extracts intense flavors and nutrients, promoting efficient resource use while enriching the stew's complexity and health benefits.
Scrappy Stews
Scrappy stews maximize sustainability by utilizing zero-waste, root-to-stem ingredients often discarded in traditional stewing, reducing food waste significantly. Emphasizing creative use of vegetable scraps, tougher cuts, and leftover bits, scrappy stews transform seemingly negligible components into nutrient-rich, flavorful meals that support eco-friendly cooking practices.
Whole-Veggie Stewing
Whole-veggie stewing maximizes sustainability by utilizing all parts of vegetables, including peels, stems, and leaves, reducing food waste while enhancing nutrient density. This zero-waste approach conserves resources and lowers carbon footprint compared to traditional stewing methods that often discard edible vegetable components.
Upcycled Stewing
Upcycled stewing transforms food waste by incorporating imperfect or surplus ingredients like peels, stems, and leaves into nutrient-rich stews, promoting zero-waste cooking and enhancing sustainability. This method reduces landfill contributions while maximizing flavor and nutritional value from root-to-stem produce, championing eco-friendly culinary practices.
Stalk-and-Stem Soup
Stalk-and-Stem Soup maximizes sustainability by utilizing typically discarded vegetable parts, reducing food waste in stewing practices. This zero-waste approach not only enhances nutrient retention but also promotes environmental responsibility through comprehensive use of plant materials.
Full-Basket Stew
Full-Basket Stew exemplifies zero-waste root-to-stem cooking by utilizing the entire vegetable, peel to core, reducing food waste and maximizing nutritional value. This sustainable stew method contrasts traditional stewing by prioritizing eco-friendly practices and ingredient efficiency, aligning with environmental conservation goals.
Circular-Cuisine Stewing
Circular-Cuisine Stewing emphasizes maximizing ingredient use by integrating zero-waste root-to-stem techniques, reducing food waste and promoting sustainable cooking practices. This method transforms typically discarded parts into rich, flavorful stews, aligning with eco-friendly values and enhancing nutrient retention.
Reclaimed Veggie Bouillon
Stewing with reclaimed veggie bouillon maximizes sustainability by utilizing vegetable scraps like peels and cores, reducing food waste while intensifying flavor. Zero-waste root-to-stem stews transform often discarded parts into nutrient-rich broths, promoting eco-friendly cooking and resource efficiency.
Stewing vs Zero-waste root-to-stem stews for sustainability. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com