Stewing involves slow-cooking ingredients in liquid to develop deep flavors, often using fresh meats and vegetables. Zero-waste stewing optimizes this method by incorporating food scraps, such as vegetable peels and meat bones, reducing waste while enhancing nutrient and flavor extraction. This sustainable approach minimizes kitchen waste and maximizes resource efficiency without compromising the richness of the stew.
Table of Comparison
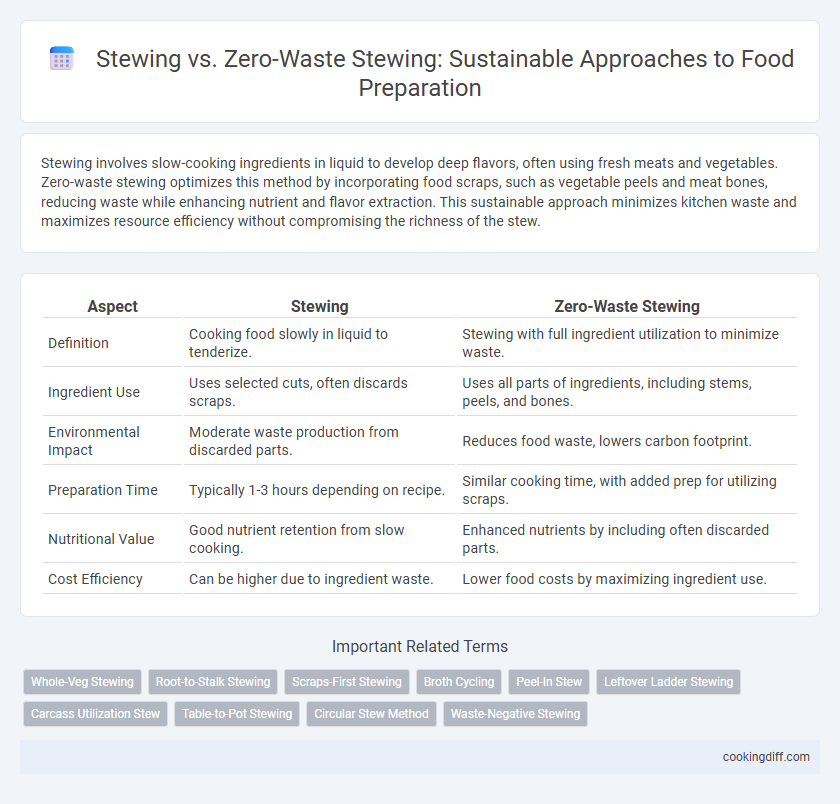
| Aspect | Stewing | Zero-Waste Stewing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking food slowly in liquid to tenderize. | Stewing with full ingredient utilization to minimize waste. |
| Ingredient Use | Uses selected cuts, often discards scraps. | Uses all parts of ingredients, including stems, peels, and bones. |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate waste production from discarded parts. | Reduces food waste, lowers carbon footprint. |
| Preparation Time | Typically 1-3 hours depending on recipe. | Similar cooking time, with added prep for utilizing scraps. |
| Nutritional Value | Good nutrient retention from slow cooking. | Enhanced nutrients by including often discarded parts. |
| Cost Efficiency | Can be higher due to ingredient waste. | Lower food costs by maximizing ingredient use. |
Understanding Traditional Stewing Methods
Traditional stewing involves slow cooking ingredients in liquid at low temperatures to tenderize tougher cuts of meat and develop rich flavors. This method often uses precise ingredient ratios and long cooking times to extract maximum taste and nutrition. Stewing preserves the integrity of whole ingredients but can produce food waste through trimming and discarding parts deemed unsuitable for consumption.
What Is Zero-Waste Stewing?
Zero-waste stewing is a sustainable cooking method that uses all parts of the ingredients, minimizing food waste by incorporating scraps and less popular cuts. This approach contrasts traditional stewing, which often discards peels, stems, and bones, leading to higher food waste.
- Maximizes Ingredient Use - Zero-waste stewing creatively uses vegetable peels, meat bones, and herb stems to enrich flavor and nutrition.
- Promotes Environmental Sustainability - Reducing food waste lowers landfill contributions and the carbon footprint associated with food production.
- Enhances Economic Efficiency - Utilizing all edible parts cuts grocery costs by making full use of purchased ingredients.
Zero-waste stewing transforms cooking into an eco-friendly practice without sacrificing taste or quality.
Key Differences: Stewing vs. Zero-Waste Stewing
Traditional stewing involves cooking meats and vegetables slowly in liquid, often discarding peels, trimmings, and bones, which contribute to food waste. This method prioritizes flavor extraction but typically overlooks the sustainability aspect of ingredient utilization.
Zero-waste stewing maximizes resource use by incorporating vegetable scraps, bones, and tougher cuts of meat to create rich broths and meals, significantly reducing food waste. It emphasizes sustainability, nutrient preservation, and creative reuse, aligning with eco-friendly cooking practices.
Ingredient Selection: Maximizing Use in Both Approaches
Stewing involves selecting fresh ingredients that complement each other to enhance the overall dish without excessive waste. Zero-waste stewing prioritizes using every part of the ingredient, from stems to skins, to minimize food waste and maximize flavor extraction.
- Ingredient Freshness - Choosing fresh, high-quality ingredients ensures optimal texture and taste in traditional stews.
- Whole-Ingredient Utilization - Zero-waste stewing incorporates peels, stems, and trimmings to create nutrient-rich stocks and bases.
- Waste Reduction - Zero-waste methods focus on repurposing scraps to reduce environmental impact and enhance sustainability.
Reducing Food Waste with Zero-Waste Stewing
How does zero-waste stewing contribute to reducing food waste in the kitchen? Zero-waste stewing involves using every edible part of ingredients, such as vegetable peels, stems, and meat trimmings, to create flavorful broths and dishes, minimizing discarded food. This method significantly lowers waste production by transforming leftovers into nutritious meals, promoting sustainability in food preparation.
Flavor Impact: Does Zero-Waste Affect Taste?
Zero-waste stewing utilizes all parts of ingredients, enhancing depth and complexity of flavors through natural nutrient retention and reduced waste. Stewing traditionally may discard often nutritious elements like stems and peels, potentially losing subtle flavor notes.
Incorporating zero-waste practices in stewing intensifies umami and richness by maximizing ingredient utilization. The taste impact of zero-waste stewing often results in more robust, layered flavors compared to standard stewing methods.
Nutritional Benefits Compared
Stewing retains essential nutrients by gently cooking food in liquid, preserving vitamins like B-complex and minerals such as potassium. Zero-waste stewing maximizes nutritional intake by utilizing all parts of ingredients, reducing food waste and enhancing fiber and micronutrient consumption.
- Enhanced Nutrient Retention - Slow simmering in stewing helps preserve heat-sensitive vitamins that are often lost in other cooking methods.
- Comprehensive Nutrient Usage - Zero-waste stewing incorporates vegetable peels, stems, and bones, increasing the diversity of nutrients consumed.
- Improved Dietary Fiber - Using entire produce parts in zero-waste stewing elevates fiber content, promoting better digestion and gut health.
Environmental Impact of Stewing Methods
Traditional stewing often generates significant food waste and increases energy consumption due to longer cooking times and discarded ingredients. Zero-waste stewing minimizes environmental impact by utilizing all edible parts of ingredients and optimizing cooking efficiency, reducing overall resource use.
Zero-waste stewing reduces methane emissions from decomposing food scraps by diverting them from landfills. This method also lowers water usage by repurposing cooking liquids and enhances energy conservation through shorter cooking periods or multi-purpose meal preparation. By embracing zero-waste techniques, households contribute to resource sustainability and decrease their carbon footprint associated with food preparation.
Step-by-Step Guide: Transitioning to Zero-Waste Stewing
| Step 1 | Use all edible parts of vegetables and meats to minimize scraps during preparation. |
| Step 2 | Collect vegetable peels and meat trimmings to create homemade stock, reducing food waste. |
| Step 3 | Store leftovers properly in reusable containers to extend shelf life and avoid disposables. |
| Step 4 | Plan meals in advance to utilize ingredients efficiently and prevent excess purchases. |
| Step 5 | Compost unavoidable scraps to ensure sustainable waste management and enrich soil health. |
Related Important Terms
Whole-Veg Stewing
Whole-veg stewing preserves the nutritional integrity and flavors of entire vegetables by cooking them with skins, stems, and leaves, reducing food waste significantly compared to traditional stewing methods that often discard these parts. Zero-waste stewing leverages the full vegetable, turning typically discarded components into a resource for richer broths and enhanced texture, promoting sustainable cooking practices.
Root-to-Stalk Stewing
Root-to-stalk stewing maximizes nutrient retention and reduces food waste by utilizing entire vegetables, including stems, leaves, and roots, in flavorful slow-cooked dishes. This zero-waste stewing approach enhances sustainability and culinary creativity by transforming typically discarded parts into rich, wholesome meals.
Scraps-First Stewing
Scraps-First Stewing maximizes ingredient use by incorporating vegetable peels, stems, and meat trimmings into dishes, significantly reducing food waste compared to traditional stewing methods. This zero-waste cooking approach enhances flavor complexity and nutritional value, promoting sustainable food preparation practices.
Broth Cycling
Broth cycling in zero-waste stewing maximizes nutrient extraction by reusing cooking liquids multiple times, reducing food waste and enhancing flavor complexity. Traditional stewing typically discards broth after one use, missing opportunities for sustainability and resource efficiency in food preparation.
Peel-In Stew
Peel-In Stew maximizes ingredient utilization by cooking vegetables with their peels intact, enhancing nutrient retention and flavor complexity compared to traditional stewing methods that often discard peels. This zero-waste stewing technique reduces kitchen waste and supports sustainable cooking practices without compromising taste or texture.
Leftover Ladder Stewing
Leftover Ladder Stewing innovatively repurposes food scraps and excess ingredients to minimize waste while maximizing flavor and nutritional value. This zero-waste stewing method reduces environmental impact by transforming leftovers into hearty, satisfying meals without compromising taste or quality.
Carcass Utilization Stew
Carcass utilization stew maximizes ingredient efficiency by transforming typically discarded bones and scraps into rich, flavorful broths, enhancing nutrient extraction and reducing food waste. Zero-waste stewing emphasizes complete use of all parts of the carcass, aligning with sustainable cooking practices that promote resource conservation and environmental responsibility.
Table-to-Pot Stewing
Table-to-Pot Stewing minimizes food waste by using vegetable scraps, meat bones, and peels directly in the pot, enhancing flavor while promoting sustainability. This zero-waste approach contrasts with traditional stewing methods that often discard nutritious offcuts, reducing both food waste and environmental impact.
Circular Stew Method
Stewing traditionally involves simmering ingredients in liquid to blend flavors and tenderize food, while Zero-Waste Stewing emphasizes repurposing all food parts to minimize waste, enhancing sustainability. The Circular Stew Method integrates vegetable scraps, bones, and herbs from previous meals to create rich, nutrient-dense broths, promoting an eco-friendly, resource-efficient cooking cycle.
Stewing vs Zero-Waste Stewing for food preparation. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com