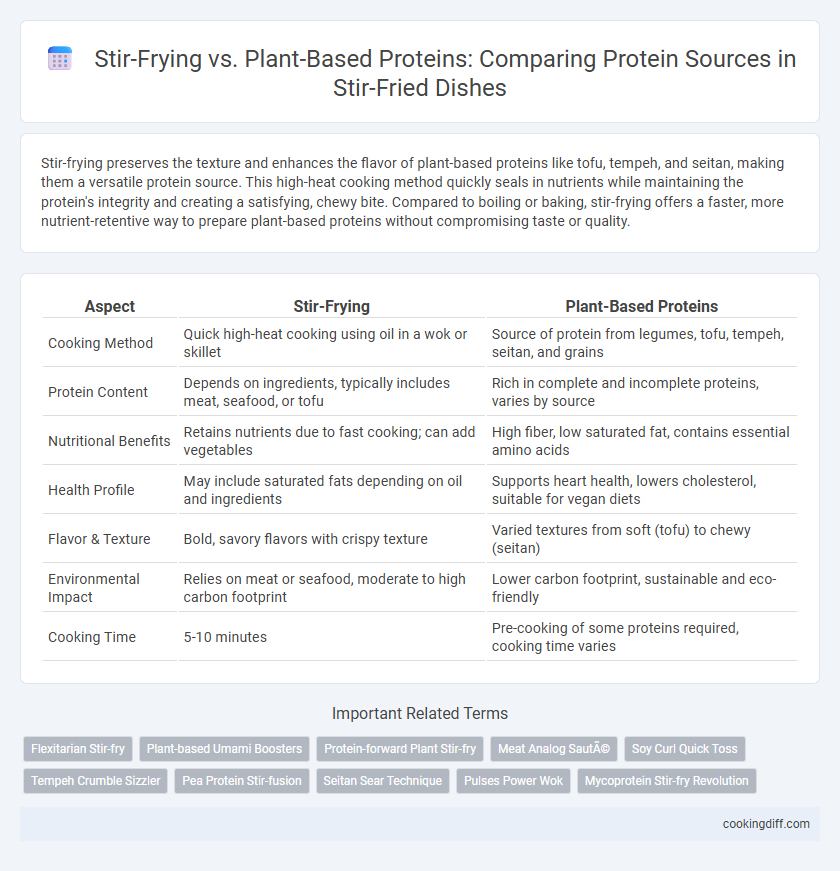
Stir-frying preserves the texture and enhances the flavor of plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, and seitan, making them a versatile protein source. This high-heat cooking method quickly seals in nutrients while maintaining the protein's integrity and creating a satisfying, chewy bite. Compared to boiling or baking, stir-frying offers a faster, more nutrient-retentive way to prepare plant-based proteins without compromising taste or quality.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stir-Frying | Plant-Based Proteins |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Quick high-heat cooking using oil in a wok or skillet | Source of protein from legumes, tofu, tempeh, seitan, and grains |
| Protein Content | Depends on ingredients, typically includes meat, seafood, or tofu | Rich in complete and incomplete proteins, varies by source |
| Nutritional Benefits | Retains nutrients due to fast cooking; can add vegetables | High fiber, low saturated fat, contains essential amino acids |
| Health Profile | May include saturated fats depending on oil and ingredients | Supports heart health, lowers cholesterol, suitable for vegan diets |
| Flavor & Texture | Bold, savory flavors with crispy texture | Varied textures from soft (tofu) to chewy (seitan) |
| Environmental Impact | Relies on meat or seafood, moderate to high carbon footprint | Lower carbon footprint, sustainable and eco-friendly |
| Cooking Time | 5-10 minutes | Pre-cooking of some proteins required, cooking time varies |
Introduction: Stir-Frying and Plant-Based Proteins in Modern Cooking
Stir-frying is a quick, high-heat cooking technique essential in modern culinary practices, especially for preserving the texture and flavor of plant-based proteins. Plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, and seitan are increasingly popular in stir-fry dishes due to their nutritional benefits and versatility in absorbing flavors.
- Efficient Cooking Method - Stir-frying uses intense heat and rapid cooking to retain nutrients and enhance the taste of plant-based proteins.
- Versatility of Plant-Based Proteins - Tofu and tempeh adapt well to stir-frying, offering diverse textures and flavors suitable for various diets.
- Health and Sustainability - Plant-based proteins provide essential amino acids while supporting sustainable food choices aligned with modern nutrition trends.
Combining stir-frying with plant-based proteins creates flavorful, nutrient-dense meals optimal for health-conscious consumers.
Nutritional Comparison: Stir-Fried Meats vs Plant-Based Protein Sources
Stir-fried meats typically provide higher amounts of complete proteins with all essential amino acids, along with vital nutrients like iron and vitamin B12. These animal-based proteins have greater bioavailability compared to many plant-based sources.
Plant-based proteins such as tofu, tempeh, and seitan offer lower saturated fat content and are rich in fiber and antioxidants, promoting heart health. While some plant proteins lack certain amino acids, combining different sources can create a complete protein profile suitable for a balanced diet.
Stir-Frying Techniques for Plant-Based Proteins
Stir-frying is an efficient cooking method that preserves the texture and flavor of plant-based proteins such as tofu, tempeh, and seitan. Mastering heat control and ingredient preparation enhances the nutrient retention and taste of these protein sources.
- High Heat Cooking - Using high heat quickly sears plant-based proteins, creating a crispy exterior while maintaining a tender interior.
- Proper Marination - Marinating proteins before stir-frying infuses them with flavor and improves moisture retention during cooking.
- Even Stirring - Consistent, rapid stirring ensures uniform cooking and prevents sticking or burning of delicate plant-based proteins.
Protein Quality: Animal vs Plant-Based Sources in Stir-Fry Dishes
Stir-frying animal proteins such as chicken or beef typically offers complete amino acid profiles, enhancing protein quality in dishes. Plant-based proteins like tofu or tempeh provide valuable nutrients but often require combination with other ingredients to achieve a balanced amino acid profile.
- Complete Amino Acids in Animal Proteins - Animal sources used in stir-fries deliver all essential amino acids necessary for muscle repair and growth.
- Complementary Plant Proteins - Combining plant-based proteins with legumes, grains, or vegetables during stir-frying increases the overall protein quality.
- Protein Digestibility - Animal proteins generally have higher digestibility scores compared to most plant proteins, influencing nutrient absorption.
Flavor Profiles: Enhancing Plant-Based Proteins in Stir-Fry Cooking
How can stir-frying enhance the flavor profiles of plant-based proteins compared to traditional methods? Stir-frying uses high heat and quick cooking times to create a caramelized, savory crust on plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, and seitan, intensifying their natural flavors. The combination of sesame oil, garlic, ginger, and soy sauce in stir-fry sauces further elevates the umami and depth, making plant-based proteins more appealing and satisfying in any dish.
Texture and Mouthfeel: Stir-Fried Meat vs Plant-Based Alternatives
Stir-frying enhances the texture of meat by creating a crisp, caramelized exterior while maintaining a tender interior, delivering a satisfying mouthfeel. The Maillard reaction during high-heat cooking intensifies flavor and adds a distinctive chewiness unique to animal proteins.
Plant-based proteins in stir-frying offer a diverse range of textures, from firm tofu to spongy seitan, mimicking meat's bite but often lacking the same juiciness. Textural variation depends on the protein source and preparation, with some alternatives requiring marination or added fats to improve mouthfeel.
Cooking Time and Efficiency: Stir-Frying with Different Protein Sources
Stir-frying significantly reduces cooking time compared to other methods, especially when using plant-based proteins like tofu or tempeh, which cook faster than traditional meats. The high heat and constant motion ensure even cooking and retention of texture, making stir-frying an efficient technique for plant-based protein dishes.
Plant-based proteins often require less preparation time due to their uniform texture and quicker heat absorption, enhancing overall cooking efficiency in stir-frying. Unlike dense meats, tofu and seitan crisp up rapidly without drying out, preserving nutritional value. This efficiency makes stir-frying ideal for quick, protein-rich meals using diverse protein sources.
Health Impacts: Benefits of Stir-Frying with Plant-Based Proteins
| Stir-frying preserves the nutrient density of plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, and seitan by using high heat for a short time, minimizing nutrient loss. The quick cooking method retains antioxidants and essential amino acids, enhancing the bioavailability of nutrients vital for muscle repair and metabolic health. Combining stir-frying with vegetables enriches the meal with fiber, vitamins, and phytochemicals, supporting cardiovascular health and reducing inflammation risk. |
Recipe Ideas: Creative Stir-Fry Dishes Using Plant-Based Proteins
Stir-frying offers a quick and flavorful method to cook plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, and seitan, retaining their texture and absorbing bold sauces. Creative stir-fry recipes often combine colorful vegetables with marinated plant-based proteins, enhancing both nutrition and taste. Incorporating ingredients such as edamame, mushrooms, and bell peppers boosts protein content while delivering vibrant, satisfying meals.
Related Important Terms
Flexitarian Stir-fry
Stir-frying enhances the texture and flavor of plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, and seitan, making them ideal for flexitarian diets seeking diverse protein sources. Quick high-heat cooking preserves nutrients while allowing crisp vegetables and proteins to blend, supporting balanced, nutrient-rich flexitarian meals.
Plant-based Umami Boosters
Stir-frying enhances the flavor profile of plant-based umami boosters such as shiitake mushrooms, miso, and soy sauce, intensifying their rich, savory taste while preserving their nutritional value. These ingredients serve as excellent protein sources in plant-based diets, providing essential amino acids alongside a depth of flavor that mimics traditional meat-based stir-fries.
Protein-forward Plant Stir-fry
Protein-forward plant stir-fries maximize nutrient retention by quickly cooking high-protein ingredients like tofu, tempeh, and edamame at high heat, preserving amino acid profiles. Stir-frying enhances the texture and flavor of plant-based proteins while maintaining their protein content, making it a superior method to extract maximum protein benefit compared to boiled or steamed alternatives.
Meat Analog Sauté
Stir-frying meat analog saute enhances the texture and flavor of plant-based proteins, making them more appealing and nutritionally valuable as a protein source. This cooking method preserves the proteins' integrity while infusing vegetables and sauces, creating a balanced and palatable dish suitable for plant-based dietary preferences.
Soy Curl Quick Toss
Stir-frying Soy Curl Quick Toss preserves its high protein content, making it an efficient method to prepare plant-based proteins with a crispy texture and rich flavor. This technique retains essential amino acids and enhances nutrient absorption compared to boiling or steaming plant-based protein sources.
Tempeh Crumble Sizzler
Tempeh crumble sizzler offers a nutrient-dense, plant-based protein option ideal for stir-frying due to its firm texture that absorbs flavors while retaining crunch. Stir-frying enhances the tempeh's natural umami with quick, high-heat cooking, preserving protein content and creating a savory, protein-rich meal alternative to animal sources.
Pea Protein Stir-fusion
Pea Protein Stir-fusion enhances stir-frying by delivering a high-quality, plant-based protein source that retains texture and nutrient density under high heat. This method optimizes amino acid availability and balances flavor while supporting sustainable, protein-rich meals.
Seitan Sear Technique
Seitan sear technique in stir-frying enhances the texture and flavor of plant-based proteins by creating a crispy, caramelized crust that locks in moisture and umami-rich taste. This method outperforms typical stir-fry approaches by maximizing protein retention and delivering a satisfying bite, making seitan a superior choice for plant-based dishes.
Pulses Power Wok
Pulses Power Wok maximizes the nutritional benefits of plant-based proteins by stir-frying pulses such as lentils, chickpeas, and beans, preserving their rich amino acid profiles and enhancing texture and flavor. This method promotes efficient nutrient retention and quick cooking, making it a superior choice for incorporating high-quality, plant-based protein sources into balanced meals.
Stir-frying vs Plant-based proteins for protein sources. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com