Stir-frying noodles involves high heat and constant tossing to quickly cook and evenly coat them with sauce, resulting in a crispy texture and balanced flavors. Reverse-stirring, a technique where noodles are gently folded rather than tossed, helps maintain their softness and prevents breakage, ideal for delicate or thinner noodles. Choosing between these methods depends on the desired noodle texture and dish style, with stir-frying enhancing crispness and reverse-stirring preserving tenderness.
Table of Comparison
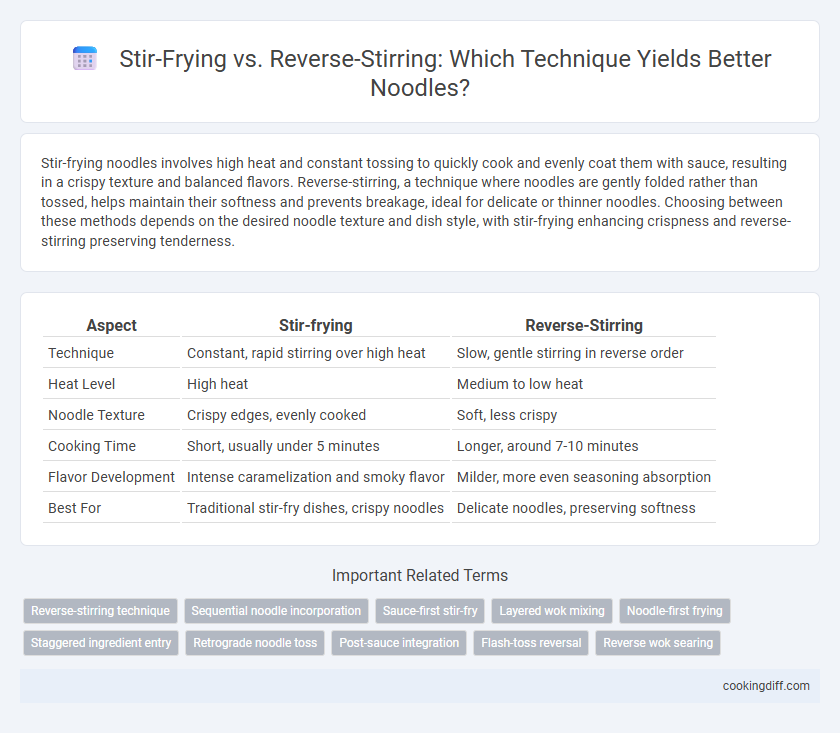
| Aspect | Stir-frying | Reverse-Stirring |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Constant, rapid stirring over high heat | Slow, gentle stirring in reverse order |
| Heat Level | High heat | Medium to low heat |
| Noodle Texture | Crispy edges, evenly cooked | Soft, less crispy |
| Cooking Time | Short, usually under 5 minutes | Longer, around 7-10 minutes |
| Flavor Development | Intense caramelization and smoky flavor | Milder, more even seasoning absorption |
| Best For | Traditional stir-fry dishes, crispy noodles | Delicate noodles, preserving softness |
Introduction to Stir-Frying and Reverse-Stirring
Stir-frying is a high-heat cooking technique that uses constant tossing to cook noodles quickly, ensuring even heat distribution and preventing sticking. Reverse-stirring, a variation, involves stirring in the opposite direction to create unique textures and enhance ingredient integration. Both methods optimize flavor development and preserve the noodles' ideal bite by controlling heat exposure and movement.
Key Differences: Stir-Frying vs Reverse-Stirring
Stir-frying involves continuously stirring noodles in a hot pan to ensure even cooking and a slightly crispy texture, while reverse-stirring moves noodles gently to prevent breakage and maintain softness. Stir-frying typically uses higher heat for faster caramelization, whereas reverse-stirring employs moderate heat to enhance flavor absorption. The choice depends on desired noodle texture and dish characteristics, with stir-frying favored for crispiness and reverse-stirring for tenderness.
Techniques Explained: Stir-Frying Noodles
Stir-frying noodles involves tossing them in high heat with constant motion to ensure even cooking and prevent sticking, while reverse-stirring focuses on pushing noodles to the center and cooking them in a static pool of sauce. Both techniques influence texture and flavor absorption significantly, with stir-frying producing a lighter, crispier finish and reverse-stirring yielding a saucier, more tender noodle dish.
- Stir-frying technique - Uses rapid, continuous tossing in a wok over high heat to evenly cook noodles and enhance their chewiness.
- Reverse-stirring technique - Involves gathering noodles in the wok center and simmering them in sauce to maximize flavor absorption.
- Texture impact - Stir-frying creates a drier, slightly crisp exterior while reverse-stirring results in a moist, soft noodle texture.
Understanding the Reverse-Stirring Method
| Stir-frying | Traditionally involves continuous, high-heat tossing of noodles to ensure even cooking and texture. |
| Reverse-Stirring Method | This technique reverses the typical motion by pushing noodles gently to the pan's edges, allowing gradual heat distribution and preventing clumping. |
| Advantages | Enhances noodle integrity, preserves moisture, and achieves a more uniform flavor absorption compared to conventional stir-frying. |
Flavor Development: Stir-Frying vs Reverse-Stirring
Stir-frying noodles rapidly over high heat caramelizes the ingredients, producing a rich, smoky flavor known as wok hei. This technique enhances the noodles' texture by creating a slight crispness while sealing in the savory taste of added sauces and aromatics.
Reverse-stirring, which involves gently folding the noodles over lower heat, allows for more even seasoning absorption without intense caramelization. This method preserves the noodles' softness and prevents burning, making it ideal for delicate flavors. However, it may lack the deep umami and smoky notes characteristic of traditional stir-frying.
Texture and Appearance: Which Method Wins?
Stir-frying noodles results in a consistently crisp texture with slight charring that enhances flavor, while reverse-stirring preserves a softer, chewier bite by gently tossing noodles to avoid breaking. The traditional stir-frying method promotes even browning and a glossy, appetizing appearance favored in many Asian dishes.
Reverse-stirring maintains noodle integrity and reduces clumping, creating a visually appealing layered effect, but may lack the signature caramelized texture of stir-frying. Chefs seeking a balance between texture and presentation often combine both techniques to achieve tender yet slightly crisp noodles with an attractive finish.
Nutritional Impact: Stir-Frying vs Reverse-Stirring
How does the nutritional impact of stir-frying compare to reverse-stirring for noodles? Stir-frying typically preserves nutrient content through rapid cooking at high heat, maintaining vitamins like B-complex and reducing oil absorption. Reverse-stirring, by intermittently mixing noodles at lower temperatures, may retain more antioxidants and prevent nutrient degradation caused by prolonged heat exposure.
Best Noodle Types for Each Technique
Traditional stir-frying works best with thin, firm noodles like rice vermicelli, which hold up well under high heat and quick tossing. Reverse-stirring suits thicker, more delicate noodles such as udon, allowing gentle heat distribution without breaking the strands.
- Rice vermicelli - Thin noodles that crisp slightly and retain texture when stir-fried quickly over high heat.
- Udon noodles - Thick, chewy noodles that benefit from the gentle stirring and slower cooking in reverse-stirring.
- Lo mein noodles - Medium thickness noodles versatile enough for either technique depending on the desired texture.
Step-by-Step Guide: Stir-Frying and Reverse-Stirring Noodles
Stir-frying noodles involves high heat and continuous tossing to evenly cook and coat the noodles with sauce and ingredients, preserving their texture and flavor. The process requires preheating the wok, adding oil, quickly cooking protein and vegetables, and then tossing in noodles with sauce to blend all elements.
Reverse-stirring starts by cooking the noodles separately before mixing them gently with the sauces and ingredients at the end, maintaining a firmer noodle texture and enhancing sauce absorption. This method uses controlled stirring to minimize breakage, resulting in a distinct layered flavor compared to traditional stir-frying.
Related Important Terms
Reverse-stirring technique
Reverse-stirring in noodle preparation enhances texture by gently separating strands, preventing clumping while preserving the noodles' integrity and releasing more aromatic flavors through controlled heat exposure. This method improves even cooking and absorbs sauces better compared to traditional stir-frying, making it ideal for achieving a delicate balance of taste and mouthfeel.
Sequential noodle incorporation
Stir-frying noodles involves continuously tossing them in a hot wok for even cooking and preventing clumping, while reverse-stirring sequentially incorporates noodles in stages to enhance texture and flavor absorption. Sequential noodle incorporation in reverse-stirring allows each batch to sear properly before combining, yielding a more distinct and layered taste profile.
Sauce-first stir-fry
Sauce-first stir-fry in noodles enhances flavor infusion by evenly coating each strand from the start, promoting a richer, more cohesive taste compared to reverse-stirring. This method prevents clumping and ensures the sauce's depth penetrates the noodles, resulting in a consistently savory dish.
Layered wok mixing
Layered wok mixing in stir-frying creates a consistent texture by continuously tossing noodles over high heat, ensuring even caramelization and flavor absorption. Reverse-stirring enhances this process by lifting and folding the noodles from the bottom, preventing clumping and promoting uniform heat distribution for perfectly cooked strands.
Noodle-first frying
Noodle-first frying in stir-frying techniques ensures even heat distribution and prevents clumping by cooking the noodles before adding other ingredients, enhancing texture and flavor absorption. Reverse-stirring, which involves stirring ingredients before the noodles, often results in uneven noodle cooking and a less cohesive dish.
Staggered ingredient entry
Staggered ingredient entry in stir-frying noodles ensures even cooking by adding components based on their required cooking times, preserving texture and flavor. Reverse-stirring, which involves stirring against the typical direction, can enhance heat distribution but may disrupt delicate ingredients if not timed correctly.
Retrograde noodle toss
Retrograde noodle toss, a key technique in reverse-stirring, ensures even heat distribution and prevents clumping by lifting and flipping noodles backward against the wok's curvature. This method enhances texture retention and flavor absorption compared to conventional stir-frying, which primarily pushes noodles forward with direct heat contact.
Post-sauce integration
Post-sauce integration in stir-frying evenly coats noodles with sauce through high heat and constant tossing, enhancing flavor absorption and texture. Reverse-stirring, involving gentle folding after sauce addition, preserves noodle integrity and prevents clumping, yielding a balanced sauce distribution without overcooking.
Flash-toss reversal
Flash-toss reversal in stir-frying noodles enhances even heat distribution and prevents overcooking by rapidly flipping the noodles in the wok, preserving texture and flavor. Compared to reverse-stirring, this technique accelerates cooking while maintaining the ideal chewiness and caramelization essential for authentic stir-fry dishes.
Stir-frying vs Reverse-stirring for noodles. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com