Stir-frying uses high heat and constant movement to quickly cook ingredients, preserving texture and enhancing flavor with slight caramelization. Steam-fry combines steaming and frying, providing a moist cooking environment that retains nutrients while delivering a crispy exterior. Hybrid methods balance these techniques to achieve both tenderness and crunch, optimizing taste and health benefits in one dish.
Table of Comparison
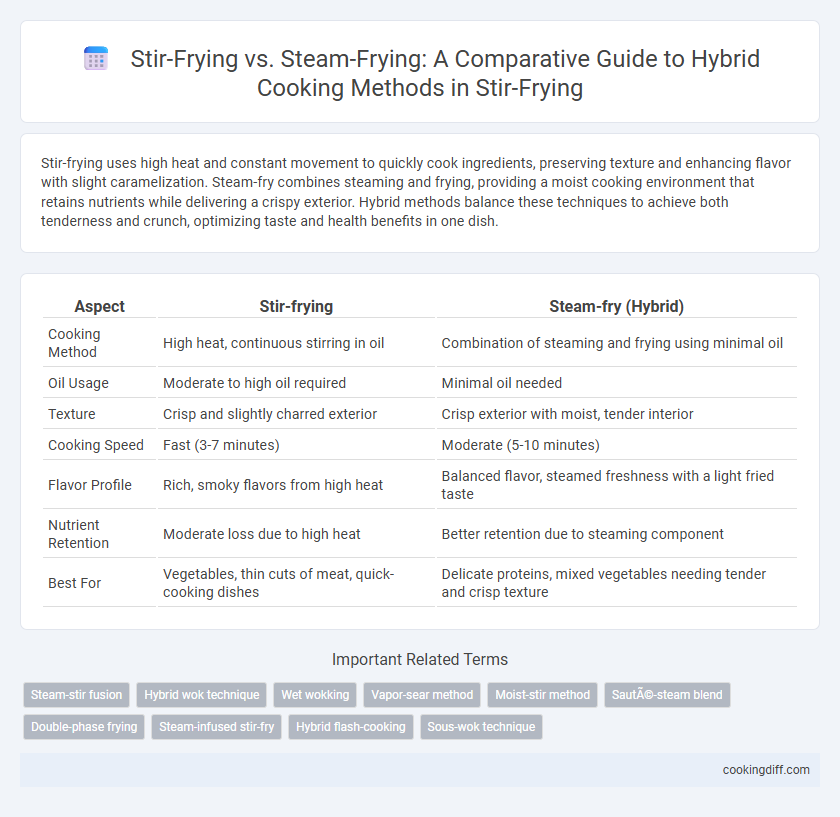
| Aspect | Stir-frying | Steam-fry (Hybrid) |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | High heat, continuous stirring in oil | Combination of steaming and frying using minimal oil |
| Oil Usage | Moderate to high oil required | Minimal oil needed |
| Texture | Crisp and slightly charred exterior | Crisp exterior with moist, tender interior |
| Cooking Speed | Fast (3-7 minutes) | Moderate (5-10 minutes) |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, smoky flavors from high heat | Balanced flavor, steamed freshness with a light fried taste |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate loss due to high heat | Better retention due to steaming component |
| Best For | Vegetables, thin cuts of meat, quick-cooking dishes | Delicate proteins, mixed vegetables needing tender and crisp texture |
Understanding Stir-Frying: Traditional Techniques Explained
Stir-frying is a traditional Chinese cooking technique that uses high heat and a small amount of oil to quickly cook ingredients while preserving their texture and flavor. Steam-frying combines the benefits of stir-frying with steaming, allowing foods to retain moisture while developing a tender, crispy exterior.
- Stir-frying utilizes intense heat - Rapid cooking in a wok maintains the color, nutrients, and crunch of vegetables and proteins.
- Steam-frying adds moisture retention - Steam helps prevent drying out while enhancing tenderness and juiciness.
- Hybrid methods optimize texture - Combining stir-frying and steaming achieves both crispness and softness in a single dish.
Traditional stir-frying relies on high heat and continuous agitation to deliver vibrant dishes with distinct flavors and textures.
What is Steam-Fry? Modern Hybrid Cooking Unveiled
What is steam-fry and how does it differ from traditional stir-frying? Steam-fry is a modern hybrid cooking method that combines the high heat and rapid cooking technique of stir-frying with the moisture-retaining benefits of steaming. This method enhances flavor retention and nutrient preservation while ensuring food remains tender and evenly cooked.
Key Differences Between Stir-Frying and Steam-Fry
| Aspect | Stir-Frying | Steam-Fry |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Technique | High-heat cooking with continuous stirring in a small amount of oil | Combination of steaming and frying, starting with steaming followed by a brief frying stage |
| Oil Usage | Uses moderate oil to coat ingredients quickly for caramelization | Uses less oil than traditional stir-frying as initial steaming reduces oil absorption |
| Texture Outcome | Produces crisp, slightly charred exterior with tender insides | Delivers moist, tender textures with lightly crisp finishes from frying phase |
| Cooking Time | Faster, typically a few minutes due to direct high heat | Longer than pure stir-frying owing to initial steaming step |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate retention; some nutrients lost to high heat and oil | Higher nutrient retention by steaming prior to frying |
Equipment Essentials: Woks vs Steam-Fry Pans
Woks provide high heat retention and a unique shape that facilitates rapid stir-frying with intense heat distribution. Steam-fry pans combine the benefits of steaming and frying by incorporating a perforated layer for steam circulation alongside a frying surface.
- Woks - Traditional carbon steel woks heat quickly and evenly, ideal for tossing ingredients at high temperatures.
- Steam-fry pans - Designed with a dual cooking surface that allows simultaneous steaming and frying for tender yet crispy dishes.
- Hybrid cooking - Using woks or steam-fry pans enhances versatility in the kitchen, accommodating a range of stir-fry and steam-fry recipes.
Heat Management: High Heat Impact on Ingredients
Stir-frying utilizes intense, direct high heat that rapidly sears ingredients, preserving texture and flavor by minimizing moisture loss. Steam-frying combines steaming and frying, applying moderate heat with steam to gently cook ingredients while retaining juiciness and nutrients. Effective heat management in hybrid cooking balances high temperature for crispness and steam for moisture, optimizing the overall quality of stir-fried dishes.
Flavor Development: Maillard Reaction vs Gentle Cooking
Stir-frying drives intense flavor development through the Maillard reaction, which occurs at high temperatures and creates rich, savory notes by caramelizing proteins and sugars. This technique delivers a crisp texture and deep roasted flavors that are key to many Asian dishes.
Steam-frying combines the Maillard reaction with gentle steam cooking to retain moisture and enhance tenderness without sacrificing browning. This hybrid method balances robust flavor creation with delicate, juicy textures, ideal for achieving complex taste profiles in a single cooking process.
Texture Contrast: Crispy vs Tender Outcomes
Stir-frying produces a crispy texture by quickly cooking ingredients in high heat with minimal oil, preserving a satisfying crunch in vegetables and proteins. The rapid sear seals in flavors while maintaining a slightly caramelized exterior, ideal for dishes requiring crispness.
Steam-frying incorporates steam during cooking, resulting in tender and moist textures by gently softening ingredients while retaining nutrients. This hybrid method balances crispness and tenderness, making it perfect for delicate vegetables and seafood that benefit from both heat and moisture.
Nutritional Comparison: Retaining Vitamins & Minerals
Stir-frying uses high heat and rapid cooking to preserve water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex, while steam-frying combines steaming and frying to further reduce nutrient loss by minimizing oil absorption. Research shows steam-frying retains higher levels of minerals such as potassium and magnesium compared to traditional stir-frying.
Steam-frying's gentle steaming component helps maintain heat-sensitive antioxidants, enhancing the overall nutrient profile of vegetables. Stir-frying offers a quick cooking method that limits vitamin degradation but may cause slight nutrient leaching due to oil exposure. Both methods promote nutrient retention better than deep-frying, making them healthy options for preserving vitamins and minerals in hybrid cooking.
Ideal Ingredients for Stir-Fry vs Steam-Fry
Stir-frying is ideal for ingredients that benefit from high heat and quick cooking, such as thinly sliced vegetables, tender meats, and firm proteins like tofu, which retain crispness and develop a caramelized flavor. Steam-frying combines steaming and frying, making it perfect for denser or thicker items like dumplings, chicken breasts, and root vegetables that require thorough cooking without drying out. Understanding the ideal ingredients ensures optimal texture and flavor in hybrid cooking methods, enhancing the overall dish quality.
Related Important Terms
Steam-stir fusion
Steam-stir fusion cooking combines the high heat and quick tossing of stir-frying with the moisture retention and gentle cooking of steaming, resulting in dishes that are both flavorful and tender. This hybrid method enhances nutrient preservation while creating a balanced texture, making it ideal for vibrant vegetables and delicate proteins.
Hybrid wok technique
The hybrid wok technique combines stir-frying's high-heat, quick-cooking benefits with steam-fry's moisture retention, enhancing flavor and texture by balancing intense searing with gentle steaming. This method optimizes nutrient preservation while delivering crisp vegetables and tender proteins, making it ideal for versatile, health-conscious cooking.
Wet wokking
Wet wokking combines stir-frying's high heat and quick cooking with steam-frying's moisture retention, enhancing texture and flavor while preserving nutritional value. This hybrid method leverages controlled water infusion to maintain juiciness and achieve a balanced, tender-crisp finish in ingredients.
Vapor-sear method
The vapor-sear method combines stir-frying's high-heat searing with steam-frying's moisture retention, enhancing texture and flavor by creating a crispy exterior while preserving juiciness inside. This hybrid technique optimizes cooking efficiency by using steam to gently cook foods before searing, resulting in evenly cooked dishes with intensified aromas and vibrant colors.
Moist-stir method
Moist-stir method combines stir-frying's high-heat, quick cooking with steam-frying's moisture retention to enhance flavor and texture while preserving nutrients. This hybrid technique uses minimal oil and a controlled amount of water or broth to create a tender yet crisp dish, optimizing taste and health benefits.
Sauté-steam blend
Saute-steam blend cooking combines intense stir-frying heat with gentle steaming, preserving nutrients while enhancing texture and flavor through quick searing followed by moisture retention. This hybrid method balances Maillard reactions with even, moist cooking, resulting in vibrant, tender, and well-cooked dishes ideal for vegetables and lean proteins.
Double-phase frying
Double-phase frying in hybrid cooking combines stir-frying's high-heat, quick-sear technique with steam-frying's moisture retention to enhance texture and flavor while preserving nutrients. This method utilizes an initial rapid stir-fry to develop caramelization and browning, followed by steam-frying to tenderize ingredients and optimize juiciness, resulting in balanced, healthier dishes.
Steam-infused stir-fry
Steam-infused stir-fry combines high-heat sauteing with gentle steam injection, preserving nutrient content and enhancing moisture retention compared to traditional stir-frying. This hybrid method accelerates cooking time while maintaining the crisp texture and vibrant color of vegetables, offering a balanced approach between stir-fry and steam-cooking techniques.
Hybrid flash-cooking
Hybrid flash-cooking combines stir-frying's intense, high-heat searing with steam-frying's moisture retention, optimizing flavor and texture by rapidly cooking ingredients while preserving tenderness. This method enhances nutritional value and reduces cooking time by balancing Maillard reaction benefits with gentle steam infusion.
Stir-frying vs Steam-fry for hybrid cooking methods Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com