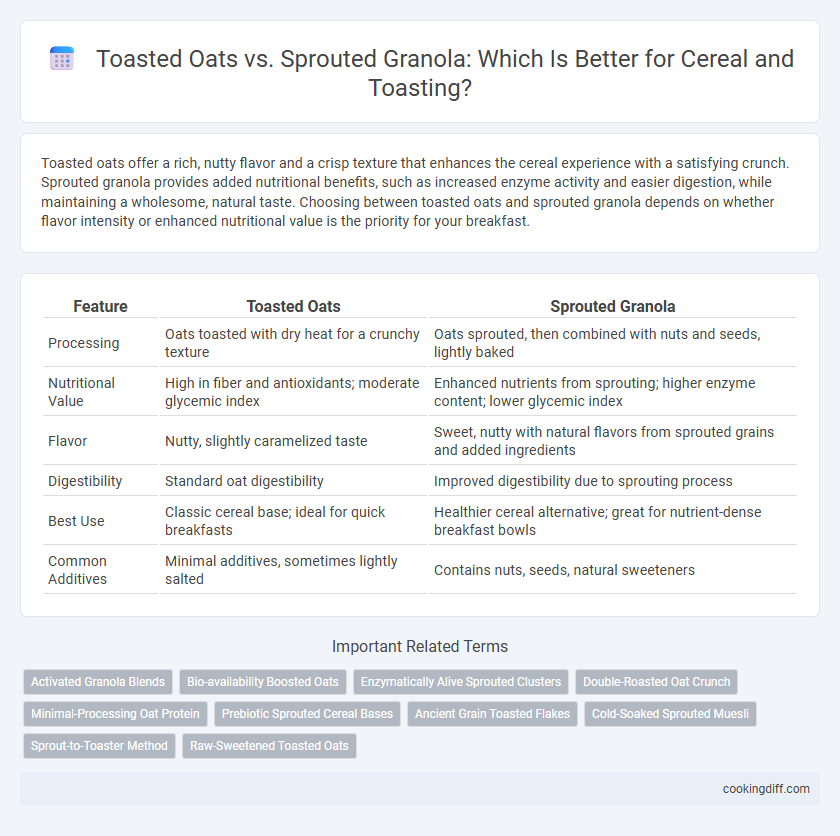
Toasted oats offer a rich, nutty flavor and a crisp texture that enhances the cereal experience with a satisfying crunch. Sprouted granola provides added nutritional benefits, such as increased enzyme activity and easier digestion, while maintaining a wholesome, natural taste. Choosing between toasted oats and sprouted granola depends on whether flavor intensity or enhanced nutritional value is the priority for your breakfast.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Toasted Oats | Sprouted Granola |
|---|---|---|
| Processing | Oats toasted with dry heat for a crunchy texture | Oats sprouted, then combined with nuts and seeds, lightly baked |
| Nutritional Value | High in fiber and antioxidants; moderate glycemic index | Enhanced nutrients from sprouting; higher enzyme content; lower glycemic index |
| Flavor | Nutty, slightly caramelized taste | Sweet, nutty with natural flavors from sprouted grains and added ingredients |
| Digestibility | Standard oat digestibility | Improved digestibility due to sprouting process |
| Best Use | Classic cereal base; ideal for quick breakfasts | Healthier cereal alternative; great for nutrient-dense breakfast bowls |
| Common Additives | Minimal additives, sometimes lightly salted | Contains nuts, seeds, natural sweeteners |
Nutritional Differences Between Toasted Oats and Sprouted Granola
Toasted oats and sprouted granola differ significantly in their nutritional profiles, impacting digestion and nutrient absorption. Sprouted granola contains higher levels of bioavailable vitamins and enzymes due to the sprouting process, while toasted oats offer a more traditional crunchy texture with moderate nutrient retention.
- Higher Enzyme Activity in Sprouted Granola - Sprouted granola contains increased natural enzymes that aid digestion and improve nutrient absorption compared to toasted oats.
- Vitamin Content Variation - Sprouted granola typically has elevated B vitamins and antioxidants due to the germination process, unlike toasted oats which lose some vitamins during heat processing.
- Caloric and Fiber Differences - Toasted oats generally contain fewer calories and less fiber per serving than sprouted granola, which is often mixed with additional seeds and nuts.
Choosing between toasted oats and sprouted granola depends on dietary preferences, digestive health, and nutrient needs.
Flavor and Texture: Toasted Oats vs Sprouted Granola
Toasted oats offer a rich, nutty flavor with a satisfying crunch that enhances the cereal experience. Sprouted granola delivers a slightly sweeter, earthier taste with a chewier, denser texture due to the sprouting process.
Toasted oats maintain a crisp texture throughout milk soaking, making them ideal for those who prefer a crunchy bite. Sprouted granola's moisture content and sprouting increase enzyme activity, resulting in a softer, more digestible texture. This contrast in flavor and texture helps consumers choose based on their preference for crunch versus chewiness in cereal.
Health Benefits of Sprouted Granola Compared to Toasted Oats
What makes sprouted granola healthier than toasted oats for cereal? Sprouted granola contains higher levels of bioavailable nutrients due to the germination process, which breaks down antinutrients and increases enzymatic activity. This results in improved digestion and better absorption of vitamins such as B-complex and minerals compared to traditional toasted oats.
Digestibility: Which Is Kinder to Your Stomach?
Toasted oats undergo a dry heating process that enhances flavor but may retain some anti-nutrients affecting digestibility, while sprouted granola benefits from enzyme activation that breaks down starches and proteins, making it easier on the stomach. Individuals with sensitive digestion often find sprouted granola gentler due to its reduced phytic acid and improved nutrient absorption.
- Reduced Anti-Nutrients in Sprouted Granola - Sprouting diminishes phytic acid content, which can inhibit mineral absorption and cause digestive discomfort.
- Enzyme Activation in Sprouted Grains - Sprouting activates enzymes that pre-digest complex carbohydrates, aiding smoother digestion.
- Heat Impact in Toasted Oats - Toasting intensifies flavor but may not sufficiently reduce compounds that challenge digestion for sensitive individuals.
Allergen Considerations for Toasted Oats and Sprouted Granola
Toasted oats are often processed in facilities that handle gluten-containing grains, posing a risk for cross-contamination in individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. Sprouted granola, typically made from sprouted whole grains, may contain nuts and seeds, which are common allergens requiring careful label scrutiny.
Both toasted oats and sprouted granola can contain trace amounts of dairy or soy depending on added ingredients, so those with allergies must verify product labels. Choosing certified gluten-free and allergen-free brands reduces the risk of exposure to unwanted allergens in breakfast cereals.
Preparation Methods: Toasted Oats vs Sprouted Granola
| Preparation Method | Toasted Oats | Sprouted Granola |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Oats are dry-roasted at moderate temperatures to enhance flavor and crunch without adding oils or sugars. | Grains are soaked and allowed to sprout, activating enzymes that increase nutrient availability before being baked with natural sweeteners and nuts. |
| Nutritional Impact | Toasting slightly reduces moisture and preserves the whole grain's fiber while intensifying taste. | Sprouting boosts vitamin content, particularly B vitamins and antioxidants, while improving digestibility. |
| Texture & Flavor | Produces a crisp, nutty flavor with a straightforward oat taste perfect for light cereals. | Yields a crunchy texture with complex flavors from nuts, seeds, and subtle natural sweetness. |
Sugar and Additive Content in Each Cereal Option
Toasted oats generally contain lower sugar levels and fewer additives compared to sprouted granola, making them a simpler cereal choice. Sprouted granola often includes added sugars and oils to enhance flavor and texture, increasing overall calorie content. Consumers seeking a low-sugar, minimally processed option may prefer toasted oats for breakfast cereal.
Suitability for Vegan and Gluten-Free Diets
Toasted oats are naturally gluten-free but must be processed in certified facilities to avoid cross-contamination, making them suitable for strict gluten-free diets. Sprouted granola often contains additional ingredients that may include gluten or animal products, so careful ingredient review is necessary for vegan and gluten-free suitability.
- Toasted oats' gluten-free status - Certified gluten-free toasted oats ensure safety for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
- Vegan compliance - Both toasted oats and sprouted granola can be vegan, depending on the absence of honey or dairy additives.
- Sprouted granola ingredient variability - Ingredients like nuts, seeds, and sweeteners in sprouted granola affect its alignment with vegan and gluten-free diets.
Best Uses in Breakfast Bowls and Recipes
Toasted oats provide a crunchy texture and nutty flavor, making them ideal for topping yogurt or smoothie bowls for added crunch and nutritional boost. Sprouted granola, rich in enzymes and easier to digest, works well in recipes requiring a softer texture, such as overnight oats or blended into pancake batter. Both options enhance breakfast bowls but the choice depends on desired texture and digestive benefits.
Related Important Terms
Activated Granola Blends
Activated granola blends featuring sprouted grains offer enhanced digestibility and nutrient absorption compared to traditional toasted oats, thanks to the enzymatic activity developed during the sprouting process. This biochemical transformation increases bioavailability of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making sprouted activated granola a superior choice for a nutrient-dense cereal option.
Bio-availability Boosted Oats
Toasted oats enhance nutrient bioavailability by breaking down antinutrients, increasing the absorption of vitamins and minerals compared to sprouted granola, which retains more raw enzymes but may offer lower immediate nutrient uptake. This improved digestion and nutrient release in toasted oats make them a superior choice for maximizing cereal-based energy and health benefits.
Enzymatically Alive Sprouted Clusters
Enzymatically alive sprouted clusters in sprouted granola offer enhanced nutrient absorption and digestive benefits compared to toasted oats, which undergo heat processing that can reduce enzyme activity. This preservation of natural enzymes supports better protein and carbohydrate breakdown, promoting improved gut health and sustained energy release in cereal consumption.
Double-Roasted Oat Crunch
Double-Roasted Oat Crunch offers a richer, more intense flavor compared to sprouted granola, achieved through a meticulous toasting process that enhances the natural nutty notes of oats while providing a satisfying crunch. Its twice-toasted oats retain a perfect balance of crispness and depth, making it a superior choice for cereal enthusiasts seeking both texture and robust taste.
Minimal-Processing Oat Protein
Toasted oats provide a rich, nutty flavor while preserving the natural integrity of oat protein through minimal processing, enhancing digestibility and nutrient retention. Sprouted granola, although offering sprouted grain benefits, often involves additional processing steps that can reduce the bioavailability of oat protein compared to toasted oats.
Prebiotic Sprouted Cereal Bases
Prebiotic sprouted cereal bases, such as sprouted granola, contain higher levels of dietary fiber and beneficial enzymes compared to toasted oats, promoting gut health and improved digestion. The sprouting process enhances nutrient bioavailability and prebiotic content, making sprouted granola a superior choice for a functional cereal base.
Ancient Grain Toasted Flakes
Ancient Grain Toasted Flakes offer a crunchy texture and rich nutty flavor, derived from carefully toasted oats that preserve essential nutrients and antioxidants. Compared to sprouted granola, these toasted flakes provide a lighter, less sweet option with higher fiber content, making them ideal for a heart-healthy, low-sugar cereal choice.
Cold-Soaked Sprouted Muesli
Cold-soaked sprouted muesli offers enhanced nutritional benefits compared to toasted oats, including higher enzyme activity, increased bioavailability of vitamins, and easier digestion due to the sprouting process. Unlike toasted oats or sprouted granola, cold-soaked sprouted muesli retains natural enzymes and moisture, providing a softer texture and more nutrient-dense breakfast option without the added sugars or oils typically found in granolas.
Sprout-to-Toaster Method
Sprouted granola using the Sprout-to-Toaster Method enhances nutrient absorption and reduces phytic acid by lightly toasting germinated oats, preserving their natural enzymes and fiber content. This technique offers a crisp texture and superior digestibility compared to traditional toasted oats, making it a functional choice for cereal enthusiasts.
Toasted oats vs sprouted granola for cereal. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com