Baking powder is a chemical leavening agent that releases carbon dioxide when mixed with moisture and heat, creating air bubbles that help baked goods rise and achieve a light, fluffy texture. Aquafaba, the viscous liquid from cooked chickpeas, acts as a natural leavening alternative by trapping air when whipped, providing lift and moisture to vegan or egg-free recipes. Both ingredients enhance the volume and texture of baked items, but baking powder offers consistent rising power while aquafaba adds moisture and a subtle flavor.
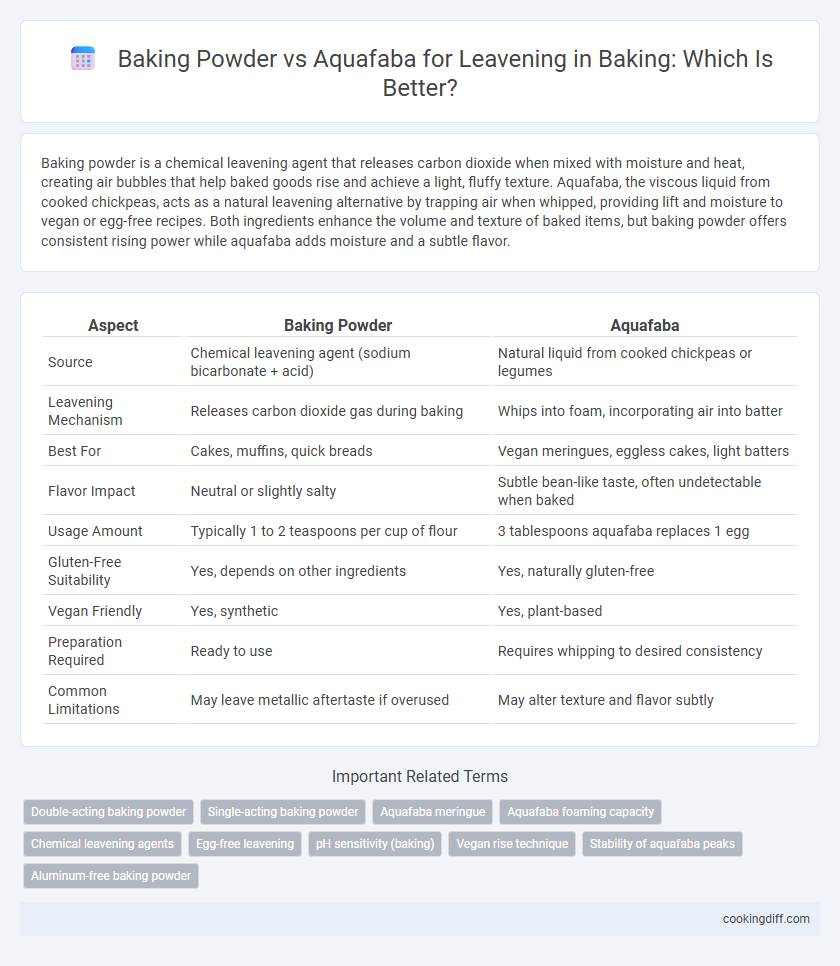
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Baking Powder | Aquafaba |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Chemical leavening agent (sodium bicarbonate + acid) | Natural liquid from cooked chickpeas or legumes |
| Leavening Mechanism | Releases carbon dioxide gas during baking | Whips into foam, incorporating air into batter |
| Best For | Cakes, muffins, quick breads | Vegan meringues, eggless cakes, light batters |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral or slightly salty | Subtle bean-like taste, often undetectable when baked |
| Usage Amount | Typically 1 to 2 teaspoons per cup of flour | 3 tablespoons aquafaba replaces 1 egg |
| Gluten-Free Suitability | Yes, depends on other ingredients | Yes, naturally gluten-free |
| Vegan Friendly | Yes, synthetic | Yes, plant-based |
| Preparation Required | Ready to use | Requires whipping to desired consistency |
| Common Limitations | May leave metallic aftertaste if overused | May alter texture and flavor subtly |
Baking Powder vs Aquafaba: An Introduction
Baking powder is a chemical leavening agent composed primarily of sodium bicarbonate and an acid that produces carbon dioxide gas to lighten and aerate baked goods. Aquafaba, the viscous water from cooked chickpeas, acts as a natural vegan egg substitute with foaming properties that can provide lift and moisture in eggless baking.
Baking powder offers reliable rise and crisp texture in cakes, muffins, and quick breads due to its precise chemical reaction. Aquafaba contributes structure and softness to vegan desserts, making it ideal for meringues, macarons, and some cakes where egg protein would traditionally be used.
Understanding Leavening Agents in Baking
Baking powder is a chemical leavening agent that produces carbon dioxide gas to create rise and fluffiness in baked goods. Aquafaba, the liquid from cooked chickpeas, acts as a natural leavening and binding agent, especially in vegan baking recipes.
- Baking powder - Contains acid and base compounds that react when wet to release CO2 bubbles, making dough or batter expand.
- Aquafaba - Mimics egg whites by trapping air and stabilizing foam, contributing to volume and texture in baked items.
- Usage difference - Baking powder offers consistent leavening power, whereas aquafaba provides moisture and structure with a subtle legume flavor.
What Is Baking Powder?
Baking powder is a chemical leavening agent composed of an acid, usually cream of tartar, and a base like sodium bicarbonate, which react to release carbon dioxide gas when moistened and heated. This gas creates bubbles in the dough or batter, causing it to rise and become light and fluffy. It is a reliable and widely used leavening option in baking, especially in recipes that do not contain natural acidic ingredients.
What Is Aquafaba?
Aquafaba is the viscous water in which legumes like chickpeas have been cooked, commonly used as a vegan egg substitute in baking. Its unique ability to trap air and mimic egg whites makes it an effective natural leavening agent, especially for meringues and cakes. Unlike baking powder, which relies on chemical reactions, aquafaba provides leavening through physical aeration and moisture retention.
How Each Ingredient Works as a Leavening Agent
Baking powder contains a combination of acid and alkaline components that react with moisture and heat to produce carbon dioxide gas, creating bubbles that cause dough or batter to rise. Aquafaba, the viscous water from cooked chickpeas, traps air when whipped, mimicking the structure of egg whites to provide lift and volume in baked goods.
Baking powder's chemical reaction is immediate upon hydration and intensifies with heat, making it ideal for quick breads and cakes requiring consistent rise. Aquafaba relies on physical aeration; its protein and carbohydrate content stabilizes air bubbles when whipped, allowing it to act as a vegan-friendly leavening substitute in recipes needing egg whites. Both agents impart rise, but baking powder provides predictable chemical leavening, while aquafaba depends on mechanical incorporation of air for volume.
Performance Comparison in Different Recipes
Baking powder consistently produces reliable rise and texture in a wide range of baked goods, including cakes, muffins, and quick breads, due to its chemical leavening agents that release carbon dioxide. Aquafaba, derived from chickpea water, offers a natural alternative that works well in vegan recipes, especially in light, airy desserts like meringues and mousses, but its leavening power can be less predictable in denser batters.
Recipes with high fat or sugar content often respond better to baking powder, ensuring uniform crumb structure and volume, while aquafaba's effectiveness varies depending on whipping technique and ingredient ratios. Aquafaba excels in providing moisture and subtle binding properties, yet for recipes requiring significant lift and firmness, baking powder remains the more consistent choice.
Health and Dietary Considerations
| Baking Powder | Contains sodium bicarbonate and acid salts, which may contribute to sodium intake concerns; not suitable for egg-allergic or vegan diets. |
| Aquafaba | Plant-based, low-calorie alternative derived from chickpea water, ideal for vegan and allergen-free baking; lacks added sodium and chemical leavening agents. |
Taste and Texture: What to Expect
How do baking powder and aquafaba compare in taste and texture when used for leavening? Baking powder provides a neutral taste with a light, airy crumb, ideal for classic baked goods. Aquafaba contributes a subtle legume flavor and creates a moister, denser texture with a slightly chewy bite.
Best Uses: When to Choose Baking Powder or Aquafaba
Baking powder is ideal for traditional baked goods requiring quick and reliable rise, such as cakes and muffins. Aquafaba works best as a vegan alternative in recipes like meringues and mousses where egg whites are typically used.
- Baking Powder for Consistency - Provides chemical leavening that ensures uniform texture and volume in quick breads and cakes.
- Aquafaba for Vegan Baking - Acts as an egg white substitute, creating airy, stable foams perfect for vegan meringues and macarons.
- Recipe Compatibility - Choose baking powder for dense, moist recipes and aquafaba for light, fluffy desserts requiring aeration.
Related Important Terms
Double-acting baking powder
Double-acting baking powder releases carbon dioxide twice during baking--once when mixed with wet ingredients and again when exposed to heat--providing consistent rise and structure in baked goods. Aquafaba, a natural foam derived from chickpea water, offers an egg-free leavening alternative by trapping air and creating volume but lacks the predictable chemical reaction of double-acting baking powder.
Single-acting baking powder
Single-acting baking powder releases carbon dioxide immediately upon moisture contact, providing quick leavening in baked goods, while aquafaba--a viscous liquid from cooked chickpeas--acts as a natural egg white substitute that traps air and adds moisture for rise. Unlike aquafaba's protein-based aeration, single-acting baking powder relies on chemical reactions, making it more predictable but less suitable for recipes requiring delayed or double-leavening effects.
Aquafaba meringue
Aquafaba meringue, derived from chickpea water, offers a vegan and allergen-friendly alternative to baking powder for leavening, providing a light, airy texture ideal for cakes and cookies. Unlike chemical leaveners, aquafaba also enhances moisture retention and contributes natural protein structure, resulting in stable, glossy peaks crucial for delicate baked goods.
Aquafaba foaming capacity
Aquafaba exhibits exceptional foaming capacity due to its high protein and carbohydrate content, enabling it to trap air effectively and provide consistent leavening in baked goods. Unlike baking powder, aquafaba acts as a natural emulsifier that enhances texture while offering a vegan-friendly alternative for creating stable, airy structures in cakes and meringues.
Chemical leavening agents
Baking powder, a chemical leavening agent composed of baking soda and an acid, produces carbon dioxide gas when moistened, creating aeration and volume in baked goods. Aquafaba, while effective as a vegan egg substitute due to its protein and carbohydrate content, lacks the chemical reaction necessary for leavening and primarily contributes to structure and moisture rather than rise.
Egg-free leavening
Baking powder produces carbon dioxide through acidic and alkaline reactions, creating consistent rise and light texture in egg-free baked goods. Aquafaba, the viscous water from cooked chickpeas, mimics egg whites by trapping air when whipped, offering a natural, vegan alternative for leavening and moisture retention.
pH sensitivity (baking)
Baking powder releases carbon dioxide through an acid-base reaction sensitive to pH levels, requiring precise pH balance to optimize leavening effectiveness. Aquafaba's leavening power depends less on pH and more on its protein and carbohydrate composition, providing stable foam formation even in varying pH environments.
Vegan rise technique
Baking powder uses chemical leavening agents like sodium bicarbonate and cream of tartar to produce carbon dioxide gas, creating a reliable rise in vegan baked goods. Aquafaba, the viscous water from cooked chickpeas, serves as a natural plant-based alternative by trapping air bubbles and providing moisture, making it ideal for light, fluffy textures in vegan cakes and meringues.
Stability of aquafaba peaks
Aquafaba forms stable peaks due to its unique protein and carbohydrate composition, providing a natural leavening alternative that maintains structure longer than traditional baking powder during mixing and baking. Its stability enhances the texture and rise in vegan and egg-free baked goods, making it an effective substitute in recipes requiring aeration.
Baking powder vs Aquafaba for leavening. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com