Butter provides a rich, creamy flavor and adds moisture to baked goods, making it ideal for cakes and cookies. Ghee, with its higher smoke point and nutty taste, is perfect for recipes requiring higher heat and longer baking times. Choosing between butter and ghee depends on the desired texture, flavor, and baking temperature of your dish.
Table of Comparison
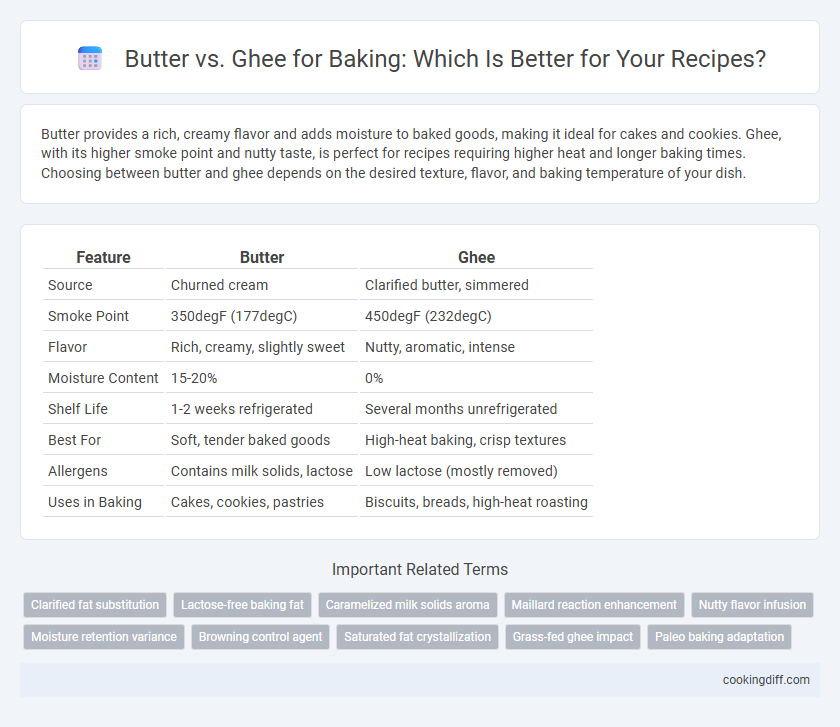
| Feature | Butter | Ghee |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Churned cream | Clarified butter, simmered |
| Smoke Point | 350degF (177degC) | 450degF (232degC) |
| Flavor | Rich, creamy, slightly sweet | Nutty, aromatic, intense |
| Moisture Content | 15-20% | 0% |
| Shelf Life | 1-2 weeks refrigerated | Several months unrefrigerated |
| Best For | Soft, tender baked goods | High-heat baking, crisp textures |
| Allergens | Contains milk solids, lactose | Low lactose (mostly removed) |
| Uses in Baking | Cakes, cookies, pastries | Biscuits, breads, high-heat roasting |
Introduction to Butter and Ghee in Baking
Butter is a dairy product made by churning cream, offering a rich flavor and creamy texture essential for many baked goods. Ghee, clarified butter originating from Indian cuisine, has a higher smoke point and a nuttier taste, making it suitable for high-temperature baking. Both ingredients provide moisture and fat but differ in water content and flavor profiles, influencing the texture and aroma of baked items.
Flavor Profiles: Butter vs Ghee
Butter imparts a rich, creamy flavor with subtle sweetness ideal for tender baked goods, while ghee offers a nutty, caramel-like taste due to its clarified nature. The absence of milk solids in ghee enhances its aromatic depth, making it suitable for recipes requiring intense flavor without moisture.
- Butter's creamy flavor - enhances moisture and tenderness in cakes and cookies.
- Ghee's nutty profile - intensifies aroma and adds complexity to breads and pastries.
- Milk solids in butter - contribute to browning and subtle sweetness during baking.
Choosing between butter and ghee depends on the desired flavor intensity and texture of the final baked product.
Nutritional Differences Between Butter and Ghee
Butter contains approximately 15% water and has a higher amount of lactose and milk solids compared to ghee, which is clarified butter with nearly zero lactose and casein. Ghee offers a higher concentration of fat, roughly 99%, making it a more calorie-dense option rich in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. Butter provides more protein due to milk solids, but ghee is favored for baking recipes requiring higher smoke points and less moisture for crisp textures.
Smoke Point Comparison: Which Is Safer for Baking?
Butter has a lower smoke point of approximately 350degF (175degC), making it prone to burning at high baking temperatures. Ghee, clarified butter with milk solids removed, boasts a higher smoke point around 485degF (252degC), offering greater heat stability.
Choosing ghee for baking minimizes the risk of smoke and burnt flavors, especially in recipes requiring high oven temperatures or prolonged baking times. Butter provides rich flavor but can break down and produce harmful compounds if exposed to excessive heat. Ghee's enhanced smoke point and longer shelf life make it a safer, more versatile option for various baked goods.
Texture and Moisture: Impact on Baked Goods
| Butter | Enhances moisture in baked goods due to its water content, resulting in a tender and soft texture. |
| Ghee | Contains negligible water, producing a denser texture with a crispier crust in cakes, cookies, and pastries. |
Substitution Ratios: Using Ghee Instead of Butter
Can ghee be used as a direct substitute for butter in baking recipes? Ghee can replace butter at a 1:1 ratio because it has a similar fat content but lacks water. The absence of milk solids in ghee provides a richer flavor and a slightly crispier texture in baked goods.
Best Uses: When to Choose Butter or Ghee
Butter is ideal for recipes requiring a rich, creamy texture and flavor, such as cakes and cookies, while ghee excels in high-heat baking due to its higher smoke point. Ghee provides a nutty taste and longer shelf life, making it perfect for breads and pastries that benefit from extended storage.
- Butter enhances moisture retention - Keeps baked goods soft and tender with its water content.
- Ghee withstands higher temperatures - Prevents burning and browning in intense baking methods.
- Butter contributes to flavor complexity - Adds creamy, dairy notes ideal for delicate desserts.
Dietary Considerations: Lactose-Free and Allergens
Ghee is lactose-free and contains minimal milk proteins, making it suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy sensitivities. Butter contains lactose and milk proteins, which can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
- Ghee is lactose-free - It is clarified butter with the milk solids removed, reducing lactose content significantly.
- Butter contains lactose - The presence of milk sugars and proteins can cause issues for those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies.
- Allergen considerations - Ghee is generally safer for people with dairy allergies, but severe allergies may still require caution.
Storage and Shelf Life in Baking Applications
Butter requires refrigeration and typically has a shelf life of about 1 to 3 months when stored properly. Ghee, with its clarified fat content, remains stable at room temperature for up to 6 months without refrigeration.
In baking applications, ghee's longer shelf life and resistance to spoilage make it ideal for extended storage. Butter's moisture content may lead to quicker degradation, affecting baked goods' quality over time.
Related Important Terms
Clarified fat substitution
Ghee, a form of clarified butter with a higher smoke point and zero milk solids, serves as an excellent substitute for butter in baking when a richer flavor and enhanced shelf life are desired. Substituting butter with ghee in recipes maintains moisture and texture while providing a nuttier taste and improved heat stability, especially in high-temperature baking.
Lactose-free baking fat
Ghee, clarified butter with milk solids removed, is an ideal lactose-free baking fat offering rich flavor and higher smoke point compared to regular butter. Its absence of lactose and casein makes ghee suitable for individuals with dairy sensitivities while maintaining moisture and tenderness in baked goods.
Caramelized milk solids aroma
Butter contains caramelized milk solids that provide a rich, nutty aroma essential for traditional baked goods, enhancing their flavor complexity and depth. Ghee, clarified by removing milk solids, lacks this caramelized aroma, resulting in a cleaner taste but less of the characteristic buttery aroma that develops during baking.
Maillard reaction enhancement
Butter and ghee both enhance the Maillard reaction in baking by providing fats that facilitate browning and flavor development, but ghee's higher smoke point and absence of milk solids allow for more intense caramelization without burning. The clarified nature of ghee promotes deeper, richer flavors and a crisper texture in baked goods compared to butter, which contains water and milk proteins that can inhibit optimal browning.
Nutty flavor infusion
Ghee offers a more intense nutty flavor infusion compared to butter due to its clarified, caramelized milk solids that enhance baked goods' richness and aroma. Butter provides a milder, creamier taste with less browning, making ghee the preferred choice for deeper, roasted nutty notes in baking.
Moisture retention variance
Butter contains approximately 15-20% water, which contributes to higher moisture retention in baked goods, resulting in a softer and more tender texture. Ghee, being clarified butter with almost no water content, produces crisper and flakier results but may lead to drier outcomes due to lower moisture retention.
Browning control agent
Butter contains milk solids that promote browning during baking, enhancing flavor and color but increasing the risk of burning at high temperatures. Ghee, clarified by removing milk solids, offers greater control over browning due to its higher smoke point, making it ideal for recipes requiring precise temperature management.
Saturated fat crystallization
Butter contains approximately 80% fat with a mix of saturated and unsaturated fats that crystallize at varying temperatures, promoting flakier textures in baked goods. Ghee, having a higher concentration of saturated fats and minimal water content, crystallizes more uniformly, resulting in a richer, denser crumb structure ideal for specific baking applications.
Grass-fed ghee impact
Grass-fed ghee offers a higher smoke point and rich nutty flavor compared to butter, enhancing baked goods' texture and taste while providing better stability under heat. Its concentrated fat content and absence of milk solids also make it ideal for achieving crispier crusts and moist interiors in pastries.
Butter vs Ghee for baking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com