Butter provides a rich, creamy flavor and contributes to a tender, flaky texture in pastries due to its water and milk solids content. Ghee, being clarified butter, has a higher smoke point and imparts a nuttier taste, making it ideal for pastries requiring higher heat or a distinct flavor profile. Choosing between butter and ghee depends on the desired texture, flavor intensity, and baking temperature for the pastry.
Table of Comparison
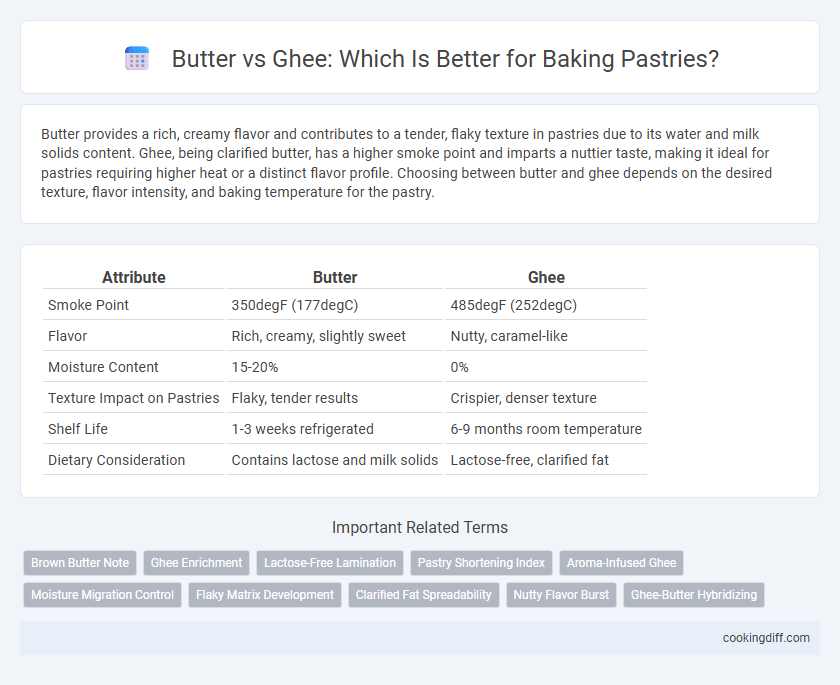
| Attribute | Butter | Ghee |
|---|---|---|
| Smoke Point | 350degF (177degC) | 485degF (252degC) |
| Flavor | Rich, creamy, slightly sweet | Nutty, caramel-like |
| Moisture Content | 15-20% | 0% |
| Texture Impact on Pastries | Flaky, tender results | Crispier, denser texture |
| Shelf Life | 1-3 weeks refrigerated | 6-9 months room temperature |
| Dietary Consideration | Contains lactose and milk solids | Lactose-free, clarified fat |
Introduction: Butter vs Ghee in Pastry Baking
Butter and ghee are both fat sources commonly used in pastry baking, each offering distinct characteristics that affect texture and flavor. Butter contains milk solids and water, while ghee is clarified butter with these components removed, resulting in different baking properties.
- Flavor Impact - Butter provides a rich, creamy taste with slight sweetness, enhancing pastry flavor complexity.
- Moisture Content - Ghee is free of water, producing flakier and crisper pastry crusts compared to butter's softer texture.
- Smoke Point - Ghee has a higher smoke point, allowing for better heat stability during baking at higher temperatures.
Choosing between butter and ghee depends on desired pastry texture, flavor depth, and baking temperature requirements.
Key Differences Between Butter and Ghee
Butter contains milk solids and water, which contribute to its rich flavor and moisture content in pastries, while ghee is clarified butter with the milk solids removed, resulting in a higher smoke point and longer shelf life. Ghee adds a nutty aroma and crisp texture to baked goods, whereas butter provides a creamier taste and softer crumb.
Due to its lower water content, ghee produces flakier pastries and resists burning at high baking temperatures, making it ideal for puff pastries and pie crusts. Butter's emulsifying properties enhance the tenderness and moisture of cakes and cookies but may require careful temperature control to avoid browning.
Flavor Impact: Butter or Ghee in Pastries
How does the flavor of butter compare to ghee in baking pastries? Butter imparts a rich, creamy taste with a slight sweetness that enhances the overall flavor profile of pastries. Ghee offers a nutty, caramelized aroma and deeper buttery notes, creating a unique complexity in baked goods.
Texture Effects of Using Butter vs Ghee
| Fat Type | Texture Effect in Pastries |
|---|---|
| Butter | Butter's water content creates steam during baking, resulting in a flaky and tender pastry texture with light layers and a slightly crisp exterior. |
| Ghee | Ghee, being clarified butter without water, produces pastries with a denser and crumbly texture while imparting a rich, nutty flavor and longer shelf life. |
Melting Points: How They Affect Baking Results
Butter melts at approximately 90-95degF (32-35degC), providing a rich, creamy texture that helps create tender and flaky pastries. Its water content evaporates during baking, contributing to a light crumb but can cause slight spreading in doughs.
Ghee, with a higher melting point around 98-102degF (37-39degC), remains solid longer, resulting in pastries with a crisper, more structured texture. The absence of milk solids in ghee also reduces moisture, enhancing browning and shelf life in baked goods.
Nutritional Comparison: Butter vs Ghee
Butter contains more water and milk solids, contributing to a creamier texture in pastries, while ghee is clarified butter with almost all water removed, providing a higher concentration of fat. Ghee has a higher smoke point than butter, making it better for high-temperature baking but with a slightly nuttier flavor profile.
- Fat Content - Ghee contains around 99% fat, whereas butter has approximately 80% fat, influencing the richness and flakiness of baked goods.
- Caloric Value - Ghee has a higher calorie density, offering about 112 calories per tablespoon compared to butter's 102 calories.
- Lactose and Casein - Ghee is virtually free of lactose and casein, making it a suitable alternative for those with dairy sensitivities when baking pastries.
Shelf Life and Storage Considerations
Ghee offers a significantly longer shelf life than butter due to its low moisture content and removal of milk solids, making it ideal for long-term storage without refrigeration. Butter requires refrigeration to prevent spoilage and typically lasts about one to two months, whereas ghee can remain stable at room temperature for up to a year.
- Butter shelf life - Typically lasts 1-2 months in the refrigerator but spoils quickly at room temperature due to high moisture.
- Ghee shelf life - Can be stored unopened at room temperature for up to 12 months because of its clarified nature and absence of milk solids.
- Storage conditions - Butter must be kept cold and sealed, while ghee remains shelf-stable in airtight containers away from light and heat.
Best Pastry Recipes for Butter and Ghee
Butter enhances the flakiness and rich flavor in pastries due to its water content, which creates steam during baking, essential for perfect layers. Ghee, with its higher smoke point and nutty taste, is ideal for recipes requiring longer baking times or higher temperatures, providing a crisp texture without burning. Best pastry recipes for butter include classic croissants and puff pastries, while ghee excels in spiced tarts and savory pies where robust flavors and crispness are desired.
Substitution Tips: Swapping Butter with Ghee
When substituting butter with ghee in baking pastries, use slightly less ghee since it is more concentrated and lacks the water content found in butter. Ghee enhances flavor with its nutty aroma and allows for flakier textures due to its pure fat composition. For best results, reduce other liquids in the recipe by about 15% to account for the moisture difference when swapping butter with ghee.
Related Important Terms
Brown Butter Note
Brown butter imparts a rich, nutty flavor to pastries that ghee cannot match due to its milk solids being caramelized during the browning process. Butter's water content creates steam for flaky layers, while ghee's pure fat consistency offers a denser texture without the distinctive brown butter aroma.
Ghee Enrichment
Ghee enriches baking pastries by providing a higher smoke point and a rich, nutty flavor that enhances texture and depth, unlike butter which contains milk solids that can burn easily. Its long shelf life and clarified nature contribute to a flakier, more tender pastry with consistent moisture retention during baking.
Lactose-Free Lamination
Ghee is ideal for lactose-free lamination in pastries due to its clarified nature, which removes milk solids and lactose while providing a rich, nutty flavor. Unlike butter, ghee offers higher smoke points and improved shelf stability, resulting in crisp, flaky layers without compromising texture or taste.
Pastry Shortening Index
Butter provides a higher Pastry Shortening Index due to its water content and milk solids, resulting in flakier and more tender pastries. Ghee, with a pure fat composition and higher smoke point, lacks water, making it less effective in creating the ideal pastry crumb structure compared to butter.
Aroma-Infused Ghee
Aroma-infused ghee enhances pastries with a rich, nutty flavor profile and a higher smoke point, allowing for crispier, more golden-brown crusts without burning. Unlike butter, ghee's clarified nature removes milk solids, resulting in a pure fat that delivers a unique aroma and longer shelf-life, making it ideal for delicate, aromatic baked goods.
Moisture Migration Control
Butter contains about 15-18% water, which can cause moisture migration affecting pastry texture and shelf life, while ghee is clarified butter with nearly zero water content, offering superior control over moisture migration and maintaining flakiness in baked goods. Using ghee in pastries reduces the risk of sogginess and helps achieve a crisp, tender crumb by preventing excess moisture from disrupting dough layers.
Flaky Matrix Development
Butter's higher water content promotes steam generation during baking, essential for creating a flaky matrix in pastries, while ghee's pure fat composition lacks this moisture, resulting in a denser texture. The water-to-fat ratio in butter contributes to laminated layers and crispiness, making it the preferred fat for flaky pastry development.
Clarified Fat Spreadability
Butter offers superior spreadability in baking pastries due to its higher moisture content and softer consistency at room temperature, enhancing dough pliability and even layering. Ghee, being clarified butter with removed milk solids and water, has a higher melting point and firmer texture, making it less ideal for applications requiring delicate spreading or folding in pastry preparation.
Nutty Flavor Burst
Butter provides a creamy, rich base with a subtle sweetness, while ghee delivers a deeper, more intense nutty flavor burst that enhances the complexity of pastries. The caramelization of milk solids in ghee imparts a toasted aroma and robust taste, making it ideal for recipes seeking a pronounced, buttery-nutty essence.
Butter vs Ghee for baking pastries. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com