Convection bake uses a fan to circulate hot air, resulting in evenly browned, crisp crusts and faster cooking times, ideal for cakes needing a firm outer layer. Steam bake introduces moisture into the oven, which keeps cakes tender and moist, producing a softer crumb and preventing dryness. Choosing between convection and steam bake depends on the desired texture and moisture level of the cake.
Table of Comparison
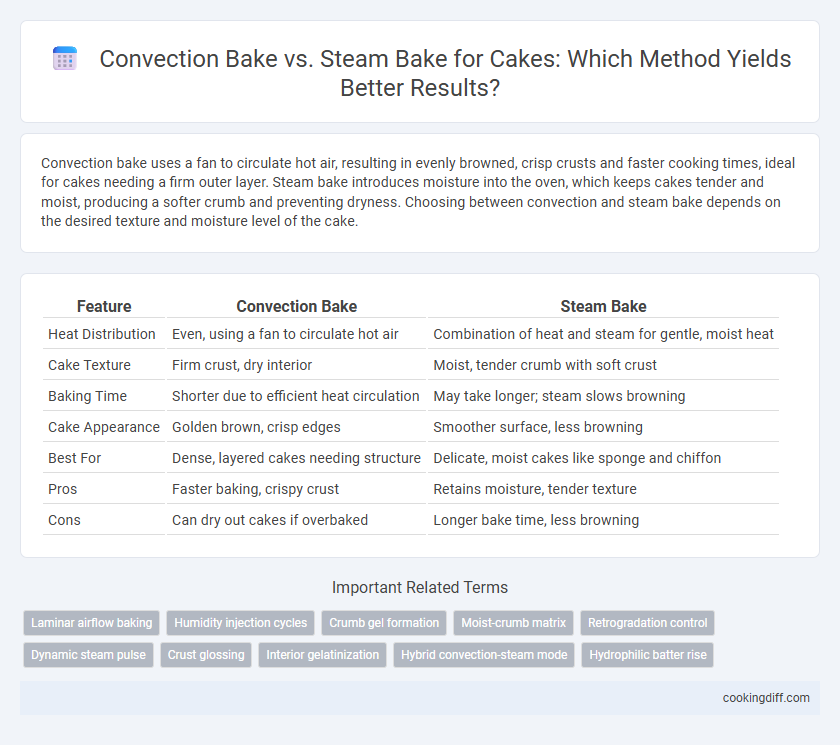
| Feature | Convection Bake | Steam Bake |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Distribution | Even, using a fan to circulate hot air | Combination of heat and steam for gentle, moist heat |
| Cake Texture | Firm crust, dry interior | Moist, tender crumb with soft crust |
| Baking Time | Shorter due to efficient heat circulation | May take longer; steam slows browning |
| Cake Appearance | Golden brown, crisp edges | Smoother surface, less browning |
| Best For | Dense, layered cakes needing structure | Delicate, moist cakes like sponge and chiffon |
| Pros | Faster baking, crispy crust | Retains moisture, tender texture |
| Cons | Can dry out cakes if overbaked | Longer bake time, less browning |
Introduction to Convection Bake vs Steam Bake
Convection bake utilizes a fan to circulate hot air evenly around cakes, promoting consistent browning and faster cooking times. This method is ideal for achieving a golden crust and a uniform texture in a variety of cake recipes.
Steam bake introduces moisture into the oven environment during baking, helping to keep cakes soft and moist. It is particularly effective for delicate cakes, as the steam prevents drying and enhances the cake's tenderness.
How Convection Baking Works for Cakes
Convection baking uses a fan to circulate hot air evenly around cakes, promoting uniform cooking and browning. This method reduces baking time and creates a crisp outer layer while maintaining moist interiors in cakes.
- Even heat distribution - The fan ensures hot air reaches all surfaces of the cake, preventing hot spots and uneven baking.
- Faster baking process - Circulated air speeds up heat transfer, resulting in quicker bake times for cakes.
- Crisp crust formation - Enhanced airflow helps develop a golden, firm crust, ideal for certain cake textures.
How Steam Baking Works for Cakes
Steam baking for cakes involves injecting moisture into the oven, creating a humid environment that helps maintain the cake's moisture and prevents drying. This method enhances the texture by producing a tender crumb and a glossy, evenly browned crust.
During steam baking, water vapor penetrates the batter more effectively than dry heat alone, promoting a soft and moist interior. The steam helps to evenly distribute heat, reducing the risk of cracks and ensuring the cake rises uniformly. Unlike convection bake, which relies on dry hot air circulated by a fan, steam baking preserves the delicate structure and flavor of cakes by maintaining optimal humidity levels.
Key Differences Between Convection and Steam Baking
Convection baking uses a fan to circulate hot air, creating even heat distribution that results in consistent browning and texture in cakes. Steam baking introduces moisture into the oven, helping to retain the cake's moisture and produce a tender crumb with a glossy crust.
- Heat Circulation - Convection baking relies on a fan to distribute dry heat evenly throughout the oven cavity.
- Moisture Retention - Steam baking adds controlled humidity, preventing cakes from drying out during the baking process.
- Crust Texture - Steam baking creates a slightly glossy and delicate crust compared to the drier and crispier crust typical of convection baking.
Choosing between convection and steam baking depends on the desired cake texture and crust finish for optimal results.
Cake Texture: Convection vs Steam Bake
Convection bake circulates hot air evenly around the cake, promoting a consistent rise and a slightly crisp crust. Steam bake introduces moisture during baking, resulting in a tender, moist crumb with enhanced softness. Choosing between convection and steam bake impacts cake texture by balancing crust crispness and interior moisture retention.
Moisture and Crumb: What Each Method Delivers
How do convection bake and steam bake differ in moisture retention and crumb texture for cakes? Convection bake circulates hot air, producing a drier, firmer crumb with a slightly crisp exterior. Steam bake injects moisture, resulting in a softer, moister crumb that enhances cake tenderness and prevents drying out during baking.
Best Cake Types for Convection Baking
Convection baking is ideal for cakes that require even heat distribution, such as pound cakes and sponge cakes, as the fan circulates hot air to ensure consistent browning. These cake types benefit from the dry heat which creates a firm crust while maintaining a moist interior. In contrast, steam baking is better suited for delicate desserts like chiffon cakes that need moisture to prevent drying out.
Ideal Cakes for Steam Baking
Steam baking is ideal for delicate cakes such as chiffon, sponge, and angel food cakes, where moisture retention is crucial for a tender crumb. The steam environment prevents drying out and promotes even rising, resulting in a soft, moist texture.
Convection baking, by circulating hot air, is better suited for denser cakes like pound or fruit cakes that benefit from a crisp crust. Steam baking enhances cakes requiring lightness and moisture, delivering superior texture and flavor compared to dry heat methods.
Equipment Needed for Each Baking Method
Convection baking requires an oven with a fan to circulate hot air evenly around the cake, promoting uniform browning and faster cooking times. Steam baking involves an oven capable of injecting steam to maintain moisture, resulting in a tender crumb and moist texture.
- Convection Oven - Equipped with a fan and exhaust system to circulate hot air for even baking.
- Steam Oven or Combination Oven - Features a steam injection system to add moisture during baking.
- Baking Trays and Racks - Standard equipment compatible with both convection and steam baking methods.
Related Important Terms
Laminar airflow baking
Convection bake utilizes laminar airflow to circulate hot air evenly around the cake, promoting uniform browning and consistent texture by minimizing temperature fluctuations. Steam bake introduces moisture into this laminar airflow environment, enhancing cake moisture retention and crumb softness while maintaining an even bake without surface dryness.
Humidity injection cycles
Convection bake uses a fan to circulate dry hot air, promoting even browning and crisp crusts, whereas steam bake injects humidity cycles to maintain moisture in cakes, resulting in softer textures and enhanced rise. The humidity injection cycles in steam baking reduce surface drying, prevent cracks, and improve crumb structure by regulating moisture levels throughout the baking process.
Crumb gel formation
Steam baking promotes superior crumb gel formation in cakes by maintaining high humidity that prevents crust hardening, resulting in a moist and tender interior. In contrast, convection baking circulates dry hot air, which enhances crust development but may lead to denser crumb texture due to rapid moisture loss.
Moist-crumb matrix
Convection bake uses circulating hot air to create even browning and a slightly drier crumb, while steam bake introduces moisture during baking, resulting in a tender, moist-crumb matrix ideal for cakes. Steam baking helps retain water content and enhances texture, producing soft, fluffy cakes with prolonged freshness.
Retrogradation control
Convection baking uses circulating hot air to create even heat distribution, which helps prevent excessive moisture loss and reduces starch retrogradation, preserving cake softness longer. Steam baking introduces moisture during baking, significantly slowing retrogradation by maintaining higher humidity and starch gelatinization, resulting in a moister, fresher crumb texture that delays staling.
Dynamic steam pulse
Convection bake utilizes hot air circulation to create even heat distribution, resulting in a consistent cake rise and golden crust, while steam bake with dynamic steam pulse introduces regulated bursts of steam that enhance moisture retention and improve cake texture by promoting delicate crumb structure and preventing dryness. Dynamic steam pulse technology injects timed steam during baking, which optimizes heat transfer and ensures cakes remain tender and evenly baked without sogginess.
Crust glossing
Convection bake circulates hot air evenly around cakes, producing a uniform golden crust with moderate gloss. Steam bake introduces moisture during baking, enhancing crust gloss and creating a shiny, tender exterior ideal for delicate cake finishes.
Interior gelatinization
Convection bake uses dry hot air circulation to promote even heat distribution, resulting in consistent interior gelatinization of starches essential for cake structure. Steam bake introduces moisture during baking, enhancing gelatinization by maintaining high humidity that prevents crust formation and ensures a tender, moist crumb.
Hybrid convection-steam mode
Hybrid convection-steam mode combines the rapid, even heat distribution of convection bake with the moisture retention of steam bake, resulting in cakes with tender crumb structure and enhanced volume. This method reduces baking time while preventing crust dryness, ensuring optimal texture and flavor in delicate baked goods.
Convection bake vs Steam bake for cakes Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com