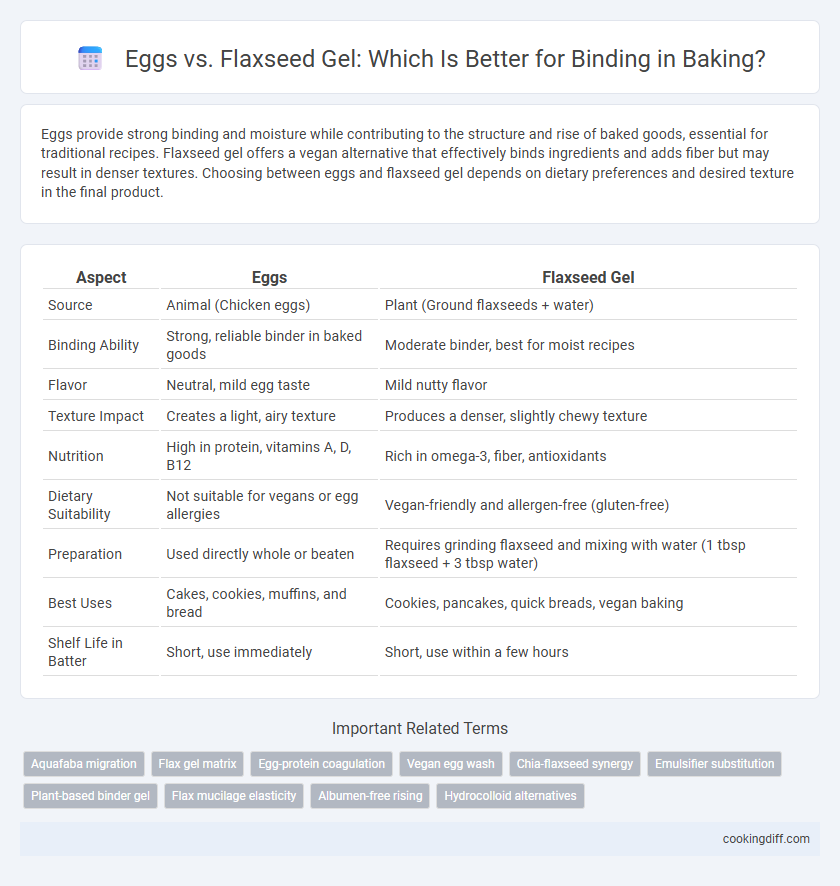
Eggs provide strong binding and moisture while contributing to the structure and rise of baked goods, essential for traditional recipes. Flaxseed gel offers a vegan alternative that effectively binds ingredients and adds fiber but may result in denser textures. Choosing between eggs and flaxseed gel depends on dietary preferences and desired texture in the final product.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Eggs | Flaxseed Gel |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Animal (Chicken eggs) | Plant (Ground flaxseeds + water) |
| Binding Ability | Strong, reliable binder in baked goods | Moderate binder, best for moist recipes |
| Flavor | Neutral, mild egg taste | Mild nutty flavor |
| Texture Impact | Creates a light, airy texture | Produces a denser, slightly chewy texture |
| Nutrition | High in protein, vitamins A, D, B12 | Rich in omega-3, fiber, antioxidants |
| Dietary Suitability | Not suitable for vegans or egg allergies | Vegan-friendly and allergen-free (gluten-free) |
| Preparation | Used directly whole or beaten | Requires grinding flaxseed and mixing with water (1 tbsp flaxseed + 3 tbsp water) |
| Best Uses | Cakes, cookies, muffins, and bread | Cookies, pancakes, quick breads, vegan baking |
| Shelf Life in Batter | Short, use immediately | Short, use within a few hours |
Introduction to Binders in Baking
Eggs serve as a traditional binder in baking, providing structure, moisture, and leavening through their protein content and emulsifying properties. Flaxseed gel, made by soaking ground flaxseeds in water, offers a popular vegan alternative, mimicking eggs' binding effects with high mucilage content that traps water and holds ingredients together. Understanding the different chemical interactions of these binders can optimize texture and consistency in various baked goods.
How Eggs Work as a Binding Agent
Eggs act as a powerful binding agent in baking by coagulating proteins when heated, which helps to hold ingredients together and provide structure. Their unique composition of proteins and lecithin contributes to moisture retention and improved texture.
When eggs are incorporated, the proteins unfold and form a network that traps air, enhancing the volume and stability of baked goods. This binding action also aids in emulsifying fats and liquids, ensuring an even distribution of ingredients throughout the batter or dough. As a result, eggs improve the overall integrity and mouthfeel of the final baked product.
The Science Behind Flaxseed Gel as a Binder
Flaxseed gel contains soluble fiber called mucilage, which forms a gel-like substance when mixed with water, mimicking the binding properties of eggs in baking. This gel traps moisture and creates a sticky texture that holds ingredients together, providing structural integrity in recipes. Rich in omega-3 fatty acids and lignans, flaxseed gel also enhances nutritional value while serving as an effective plant-based binder.
Nutritional Comparison: Eggs vs Flaxseed Gel
Eggs are a rich source of high-quality protein, essential amino acids, vitamins such as B12 and D, and minerals including iron and selenium, which contribute to improved nutrition in baked goods. Flaxseed gel provides dietary fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and lignans, offering heart-healthy benefits and antioxidants while being cholesterol-free and vegan.
While eggs enhance protein content and support muscle repair, flaxseed gel improves digestive health and reduces inflammation due to its high fiber and alpha-linolenic acid content. Choosing flaxseed gel as a binder can also lower cholesterol intake and introduce plant-based nutrients ideal for those with dietary restrictions or allergies.
Texture and Moisture: What Each Binder Offers
Eggs provide a rich, creamy texture and enhance moisture retention in baked goods, resulting in a tender crumb and cohesive structure. Their natural emulsifying properties contribute to a smooth, stable batter that traps air for better rise.
Flaxseed gel offers a slightly denser texture with increased moisture due to its high fiber content, creating a chewy, hearty crumb and a subtle nutty flavor. It works well as a plant-based binder, absorbing liquid and maintaining moisture while providing a gluten-free alternative to eggs.
Flavor Impact: Eggs vs Flaxseed Gel
| Binding Agent | Flavor Impact |
|---|---|
| Eggs | Eggs contribute a rich, creamy flavor that enhances the overall taste of baked goods without overpowering other ingredients. |
| Flaxseed Gel | Flaxseed gel imparts a mild, nutty flavor that can subtly influence the taste profile, often adding an earthy undertone to baked items. |
Allergy and Dietary Considerations
Eggs are a common binding agent in baking but pose allergy risks for individuals sensitive to poultry proteins. Flaxseed gel offers a plant-based, allergen-friendly alternative that accommodates vegan and gluten-free diets.
- Egg Allergy Risk - Eggs contain proteins that can trigger allergic reactions, making them unsuitable for those with egg allergies.
- Vegan-Friendly Binding - Flaxseed gel provides a plant-based binding option ideal for vegan and egg-free dietary needs.
- Gluten and Dairy-Free - Flaxseed gel is naturally gluten and dairy-free, supporting diverse dietary restrictions beyond egg allergies.
Best Recipes for Egg and Flaxseed Gel Substitutions
Eggs provide structure and moisture in baked goods, while flaxseed gel offers a vegan-friendly alternative with a slightly nutty flavor. Substituting eggs with flaxseed gel works best in recipes like muffins, pancakes, and quick breads where binding is essential but delicate texture is acceptable.
- Eggs in cakes - Eggs create lift and richness, ideal for fluffy and tender cakes.
- Flaxseed gel in cookies - Flaxseed gel binds ingredients well, giving a chewy texture in cookies.
- Egg replacement ratio - Use 1 tablespoon of flaxseed gel per egg for effective substitution in recipes.
Choosing between eggs and flaxseed gel depends on dietary preferences and desired texture outcomes in your baked goods.
Tips for Successfully Using Flaxseed Gel
How can you effectively use flaxseed gel as a binding agent in baking? Flaxseed gel requires precise measurement, typically one tablespoon of flaxseed meal mixed with three tablespoons of water per egg substitute, to achieve optimal texture. Stir the gel thoroughly and allow it to thicken before adding it to your batter for consistent binding results.
Related Important Terms
Aquafaba migration
Eggs provide superior binding and leavening properties in baking due to their protein structure and emulsifying agents, while flaxseed gel offers a plant-based alternative rich in mucilage for moisture retention and binding. The migration to aquafaba as an egg substitute is driven by its unique ability to mimic egg white foaming and binding properties, making it a preferred vegan option for improving texture and structure in baked goods.
Flax gel matrix
Flaxseed gel creates a strong, viscous matrix rich in soluble fibers and mucilage that effectively binds ingredients by mimicking the protein network of eggs. This plant-based gel offers superior moisture retention and a subtle nutty flavor, making it a popular vegan alternative for binding in baked goods.
Egg-protein coagulation
Eggs provide superior binding in baking due to the coagulation of egg proteins when heated, forming a stable network that traps moisture and holds ingredients together. Flaxseed gel, while a popular vegan alternative, lacks the same protein structure, resulting in less firm binding and a different texture in baked goods.
Vegan egg wash
Eggs provide natural binding and browning properties in baking, offering a rich texture and golden finish, while flaxseed gel serves as an effective vegan alternative by creating a sticky, moisture-retaining binder that enhances the structure and moisture of baked goods. Using flaxseed gel as a vegan egg wash can achieve a slightly matte surface with subtle browning, ideal for allergy-sensitive or plant-based recipes.
Chia-flaxseed synergy
Eggs provide strong binding and moisture retention in baking, enhancing texture through protein coagulation, while flaxseed gel offers a plant-based alternative rich in omega-3 fatty acids and fiber. The chia-flaxseed synergy combines mucilage content from chia seeds with flax's lignans, creating a superior vegan binder that improves elasticity and moisture, making it ideal for gluten-free and health-conscious recipes.
Emulsifier substitution
Eggs serve as a natural emulsifier in baking, providing structural stability and moisture retention, while flaxseed gel acts as a plant-based alternative by forming a sticky gel that binds ingredients and mimics egg's emulsifying properties. Flaxseed gel contains mucilage, which stabilizes oil-water mixtures and improves texture, making it an effective substitute for eggs in vegan and allergen-free recipes.
Plant-based binder gel
Flaxseed gel is a plant-based binder that mimics the binding properties of eggs in baking by forming a viscous, sticky consistency when ground flaxseeds are mixed with water. This egg substitute is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and antioxidants, making it a nutritious and vegan-friendly alternative that enhances moisture retention and structure in baked goods.
Flax mucilage elasticity
Flaxseed gel, rich in flax mucilage, provides superior elasticity and moisture retention compared to eggs, making it an effective vegan binding agent in baking. Its mucilaginous properties create a flexible gel that enhances dough structure and crumb softness while maintaining moisture for longer shelf life.
Albumen-free rising
Flaxseed gel serves as an effective egg substitute in baking by providing moisture and binding properties without albumen, which is essential for those seeking albumen-free rising agents. This plant-based alternative enhances texture and structure while maintaining a vegan-friendly profile and supporting allergen-free recipes.
Eggs vs Flaxseed gel for binding in baking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com