Boiling is a straightforward cooking method that uses direct heat to bring water to its boiling point, ideal for simple tasks like cooking pasta or blanching vegetables. The Anova technique, specifically sous vide cooking, offers precise temperature control by immersing food in a water bath, enhancing flavors and texture while preventing overcooking. Home kitchens benefit from sous vide's consistency and nutrient retention, whereas boiling suits quick, everyday meal preparation.
Table of Comparison
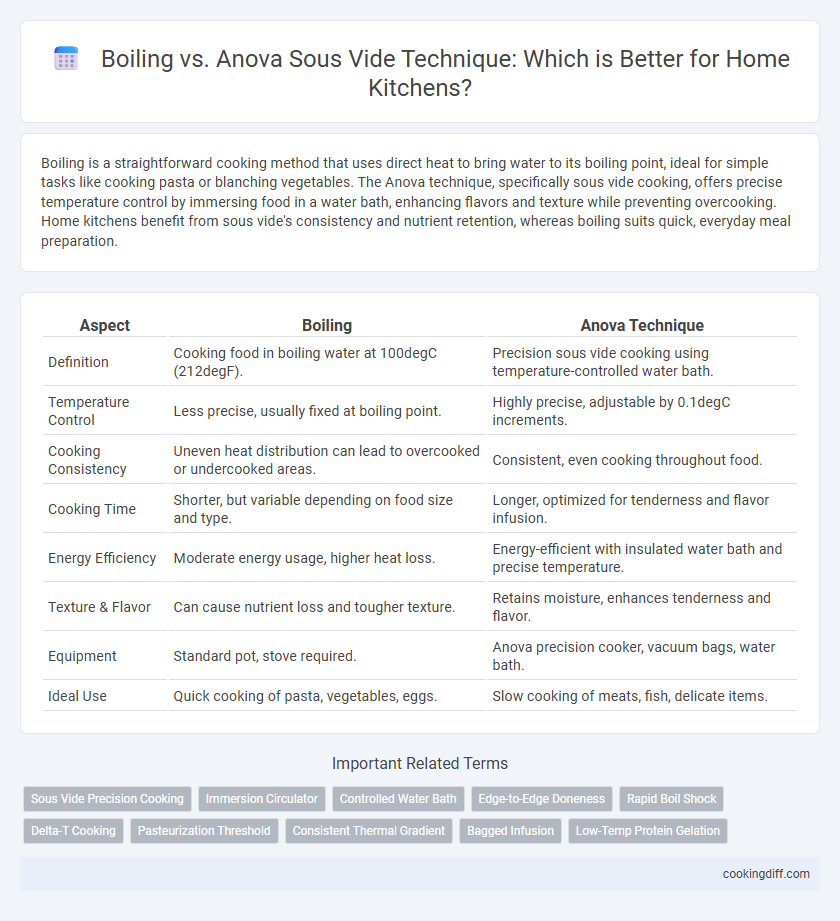
| Aspect | Boiling | Anova Technique |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking food in boiling water at 100degC (212degF). | Precision sous vide cooking using temperature-controlled water bath. |
| Temperature Control | Less precise, usually fixed at boiling point. | Highly precise, adjustable by 0.1degC increments. |
| Cooking Consistency | Uneven heat distribution can lead to overcooked or undercooked areas. | Consistent, even cooking throughout food. |
| Cooking Time | Shorter, but variable depending on food size and type. | Longer, optimized for tenderness and flavor infusion. |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate energy usage, higher heat loss. | Energy-efficient with insulated water bath and precise temperature. |
| Texture & Flavor | Can cause nutrient loss and tougher texture. | Retains moisture, enhances tenderness and flavor. |
| Equipment | Standard pot, stove required. | Anova precision cooker, vacuum bags, water bath. |
| Ideal Use | Quick cooking of pasta, vegetables, eggs. | Slow cooking of meats, fish, delicate items. |
Understanding Boiling and Anova Techniques
Boiling is a traditional cooking method involving heating water to 100degC to cook food evenly using direct heat. The Anova technique utilizes precision sous vide cooking, maintaining exact temperatures between 40degC and 90degC to achieve consistent and tender results.
Boiling offers faster cooking times but can lead to nutrient loss and uneven texture in home kitchens. Anova sous vide preserves vitamins and flavors by cooking food slowly in a water bath, providing greater control over doneness and texture.
Science Behind Boiling vs Anova Cooking
How does the science behind boiling compare to Anova cooking techniques in home kitchens? Boiling relies on convection to transfer heat through water at 100degC, rapidly cooking food but often causing nutrient loss. Anova's precision sous-vide method uses controlled low temperatures and vacuum-sealed bags to evenly cook food while preserving flavor and nutrients.
Equipment Needed: Traditional Pots vs Sous Vide Machines
Boiling requires traditional pots and stovetops, which are common in most home kitchens and involve straightforward equipment. Sous vide machines rely on precision immersion circulators and vacuum sealers to maintain consistent water temperature for even cooking. The initial investment in sous vide equipment is higher, but it offers greater control over cooking results compared to conventional boiling methods.
Temperature Control: Precision Showdown
Boiling offers a straightforward temperature control method by maintaining water at a consistent 100degC, ideal for simple cooking tasks. In contrast, the Anova technique utilizes precise sous-vide temperature regulation within 0.1degC, ensuring even heat distribution and optimal texture retention. This precision showdown reveals that while boiling is quick and effective, Anova excels in maintaining exact temperatures for delicate dishes.
Cooking Times: Boiling Vs Anova Efficiency
| Technique | Average Cooking Time | Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling | 10-15 minutes (vegetables) | Moderate energy use due to continuous high heat |
| Anova Precision Cooker (Sous Vide) | 30-60 minutes (vegetables), longer for meats | High energy efficiency with precise temperature control |
Food Texture and Flavor Differences
Boiling typically results in softer food textures and can cause flavor loss due to leaching into water, whereas the Anova technique, a precision sous-vide cooking method, preserves texture and enhances flavor concentration by cooking food in vacuum-sealed bags at controlled temperatures. Anova's low-temperature cooking prevents overcooking and maintains nutrient retention, impacting both taste and texture quality in home kitchens.
- Boiling softens food - Prolonged exposure to high temperatures breaks down fibers, resulting in mushier textures.
- Anova preserves texture - Controlled temperature cooking minimizes cellular damage, keeping food firmer and more appealing.
- Flavor retention difference - Boiling dilutes flavors into cooking water, while Anova locks flavors inside vacuum-sealed bags.
Choosing Anova sous-vide for home kitchens enhances food texture and intensifies natural flavors compared to traditional boiling methods.
Nutritional Retention: Which Technique Wins?
Boiling often causes significant nutrient loss due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures and water-soluble vitamin leaching. In contrast, the Anova technique, utilizing precise temperature control through sous-vide cooking, better preserves vitamins and minerals by cooking food gently and evenly.
- Boiling reduces water-soluble vitamins - Nutrients like vitamin C and B-complex degrade quickly in boiling water.
- Anova sous-vide maintains nutrient integrity - Controlled low temperatures minimize nutrient degradation.
- Retention of antioxidants - Anova cooking better preserves antioxidants compared to conventional boiling.
Safety Considerations in Home Kitchens
Boiling is a traditional cooking method that ensures food reaches safe temperatures, minimizing the risk of harmful bacteria. Anova technique, or sous vide, requires precise temperature control and vacuum sealing to maintain safety, but improper use can lead to foodborne illnesses.
- Boiling Safety - Boiling water reaches 100degC, effectively killing most pathogens and providing a reliable safety margin.
- Anova Temperature Control - Sous vide cooking maintains temperatures typically between 55degC and 60degC, requiring strict adherence to time and temperature guidelines to ensure food safety.
- Equipment Risks - Sous vide relies on vacuum-sealed bags and immersion circulators, which must be sanitized properly to prevent bacterial contamination.
Cost Analysis: Boiling vs Anova Investment
Boiling requires minimal upfront cost, limited to basic kitchen equipment like pots and stoves, making it highly accessible for most households. Conversely, the Anova precision cooker demands a significant initial investment, often priced between $100 and $300, reflecting its advanced temperature control technology.
Ongoing expenses for boiling mainly involve conventional energy use from gas or electricity, which can vary based on frequency and duration. The Anova device, while energy-efficient due to precise temperature settings, may incur additional costs from maintenance and potential software updates, influencing long-term affordability.
Related Important Terms
Sous Vide Precision Cooking
Sous Vide precision cooking offers precise temperature control between 120degF and 195degF, preserving moisture and enhancing flavors compared to traditional boiling methods that typically use temperatures above 212degF and can cause nutrient loss and texture degradation. Unlike boiling, Sous Vide combined with Anova immersion circulators ensures consistent heat distribution and even cooking, making it ideal for home kitchens seeking restaurant-quality results.
Immersion Circulator
Boiling is a traditional cooking method that rapidly heats water to 100degC, often resulting in uneven cooking and nutrient loss, while the Anova immersion circulator uses precise temperature control through sous vide technology to evenly cook food by maintaining water at a consistent temperature below boiling point. The immersion circulator enhances flavor retention, texture, and nutritional value compared to conventional boiling in home kitchens.
Controlled Water Bath
Controlled water baths in home kitchens provide precise temperature regulation essential for boiling techniques, ensuring consistent heat distribution and preventing overcooking. Unlike the ANOVA technique, which employs rapid pressure cooking, boiling with a controlled water bath maintains a stable environment ideal for delicate recipes and sous vide-style cooking.
Edge-to-Edge Doneness
Edge-to-Edge doneness is more consistently achieved with the Anova technique, which utilizes precise temperature control through sous vide cooking, compared to traditional boiling methods that often result in uneven heat distribution. Boiling can cause overcooking at the edges and undercooking in the center, while Anova's controlled water bath ensures uniform cooking from edge to edge.
Rapid Boil Shock
Rapid Boil Shock occurs during boiling when water reaches a sudden high temperature, causing uneven heating that can affect food texture and nutrient retention, unlike the controlled temperature variations in Anova sous vide cooking. Anova's precision temperature control minimizes Rapid Boil Shock, ensuring consistent results and preserving the quality of home-cooked meals.
Delta-T Cooking
Delta-T cooking leverages precise temperature differentials to gently and evenly cook food, preserving nutrients and texture, unlike boiling which relies on high temperatures that can cause nutrient loss and overcooking. While ANOVA (analysis of variance) is a statistical method not directly related to cooking, understanding temperature variations in Delta-T cooking optimizes heat transfer efficiency and enhances culinary outcomes in home kitchens compared to traditional boiling methods.
Pasteurization Threshold
Boiling reaches 100degC, sufficient to kill most pathogens but may not maintain Pasteurization Threshold for a consistent time to eliminate all harmful microorganisms. Anova precision cookers maintain exact temperatures between 55-72degC, ensuring consistent pasteurization by holding food at safe thresholds to reduce pathogens without overcooking.
Consistent Thermal Gradient
Boiling provides a consistent thermal gradient by maintaining water at a stable 100degC, ensuring even heat distribution for cooking, unlike the Anova technique which relies on precise temperature control through circulators but may introduce fluctuations due to device variability. The stable thermal environment during boiling prevents localized hotspots, optimizing food safety and texture in home kitchens.
Bagged Infusion
Boiling rapidly heats water to 100degC, ensuring efficient extraction of flavors during bagged infusion, whereas the Anova technique employs precise temperature control via sous-vide immersion, maintaining optimal infusion temperature without surpassing boiling point to preserve delicate aromas. For home kitchens, Anova sous-vide devices offer superior consistency and flavor retention in bagged infusions compared to conventional boiling methods.
Boiling vs Anova technique for home kitchens. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com