Boiling water on a traditional stove often consumes more energy and takes longer compared to a hybrid stove, which combines multiple energy sources for optimized heat control. Hybrid stoves improve cooking efficiency by maintaining consistent temperatures and reducing fuel wastage during the boiling process. These advantages make hybrid stoves a more sustainable and cost-effective choice for boiling and other cooking tasks.
Table of Comparison
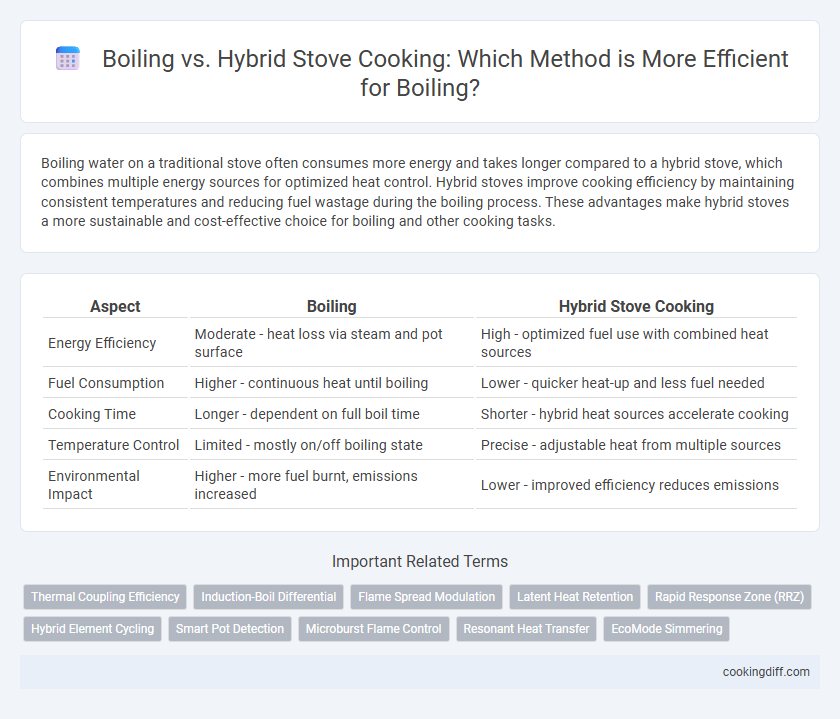
| Aspect | Boiling | Hybrid Stove Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate - heat loss via steam and pot surface | High - optimized fuel use with combined heat sources |
| Fuel Consumption | Higher - continuous heat until boiling | Lower - quicker heat-up and less fuel needed |
| Cooking Time | Longer - dependent on full boil time | Shorter - hybrid heat sources accelerate cooking |
| Temperature Control | Limited - mostly on/off boiling state | Precise - adjustable heat from multiple sources |
| Environmental Impact | Higher - more fuel burnt, emissions increased | Lower - improved efficiency reduces emissions |
Introduction to Boiling and Hybrid Stove Cooking
Boiling is a cooking method where water or liquid is heated to its boiling point, typically 100degC (212degF), causing rapid vaporization and efficient heat transfer to food. This technique ensures thorough cooking and is commonly used for pasta, vegetables, and eggs due to its simplicity and reliability.
Hybrid stove cooking combines traditional gas or electric heat with induction technology to optimize energy efficiency and reduce cooking times. This method leverages precise temperature control and rapid heat-up capabilities, enhancing overall kitchen performance while conserving fuel and electricity.
Understanding Boiling: Traditional Stove Methods
| Traditional stove boiling relies on direct flame heat transfer, typically using gas or electric elements that heat pots from the bottom. |
| This method achieves water boiling at 100degC under standard atmospheric pressure but often results in heat loss around the pot's sides and surface. |
| Efficiency ranges between 40-55%, as thermal energy dissipates without fully maximizing fuel consumption, impacting cooking times and energy use. |
What is Hybrid Stove Cooking?
Hybrid stove cooking combines traditional gas or electric stove heating with induction or infrared technology, enhancing energy efficiency by targeting heat more precisely. This method reduces overall cooking time and minimizes heat loss compared to conventional boiling techniques, leading to lower fuel consumption. Hybrid stoves often feature smart temperature controls, which optimize energy use while maintaining consistent cooking performance.
Energy Consumption: Boiling vs Hybrid Stove
Boiling on a traditional stove typically consumes more energy due to prolonged heating times and greater heat loss. Hybrid stoves, which combine electric and gas elements, optimize energy consumption by delivering heat more efficiently and maintaining consistent temperatures. Studies show hybrid stoves can reduce energy usage by up to 30% compared to conventional boiling methods.
Cooking Speed Comparison: Traditional vs Hybrid Techniques
How does boiling speed compare between traditional and hybrid stove cooking techniques? Hybrid stove cooking often reduces boiling time by optimizing heat distribution and combining fuel sources, resulting in faster water temperature rise. Traditional stoves may lag in efficiency due to uneven heat application and slower energy transfer, impacting overall cooking speed.
Heat Distribution and Its Impact on Efficiency
Boiling on a traditional stove often results in uneven heat distribution, causing energy loss and longer cooking times. Hybrid stove cooking utilizes advanced heat transfer technologies to provide consistent and efficient heat distribution, optimizing energy use.
- Uneven Heat Distribution in Traditional Stoves - Traditional burners create hot spots, leading to inefficient energy use and slower boiling.
- Consistent Heat Flow in Hybrid Stoves - Hybrid designs enhance surface contact and heat conduction, reducing energy waste and heating time.
- Impact on Cooking Efficiency - Improved heat distribution in hybrid stoves significantly lowers fuel consumption and accelerates boiling performance.
Fuel Types and Cost Analysis
Boiling water on a hybrid stove utilizes both electric and gas fuel types, offering a balance between energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional gas-only boiling methods. Electric elements heat water steadily while gas burners provide quick temperature control, reducing overall fuel consumption.
Fuel costs vary significantly, with electric energy generally cheaper per kilowatt-hour than propane or natural gas, making hybrid stoves more economical over time for frequent boiling tasks. Hybrid stoves also reduce gas usage, cutting down on carbon emissions and fuel expenses, especially in regions with high gas prices. The initial investment in a hybrid stove may be higher, but long-term savings from optimized fuel use and efficiency often offset the upfront cost.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Sustainability
Boiling water on a traditional stove emits higher levels of carbon dioxide and other pollutants due to inefficient fuel combustion. Hybrid stoves, combining electric and gas elements, reduce emissions by optimizing fuel use and lowering overall energy consumption.
Hybrid stove cooking enhances sustainability by decreasing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting cleaner energy sources. This reduction in environmental pollutants contributes to better air quality and lowers the carbon footprint associated with everyday cooking tasks.
Practical Tips for Maximizing Cooking Efficiency
Boiling water on a traditional stove consumes more energy compared to hybrid stove cooking, which combines electric and gas elements for faster heat distribution. Hybrid stoves optimize energy use by reducing heat loss and shortening cooking times.
- Use lids - Cover pots to trap heat and increase boiling speed, reducing cooking time and fuel consumption.
- Pre-boil water - Heat water partially with an electric element before finishing with gas to save energy.
- Maintain burner efficiency - Regularly clean stove burners to ensure consistent flame and optimal heat transfer.
Implementing these practical tips enhances cooking efficiency and lowers overall energy expenditure.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Coupling Efficiency
Boiling on a traditional stove typically achieves lower thermal coupling efficiency, wasting significant energy through heat loss to the surrounding environment. Hybrid stoves enhance thermal coupling efficiency by directly transferring heat to cookware using integrated conduction and convection mechanisms, resulting in faster boiling times and reduced fuel consumption.
Induction-Boil Differential
Induction stoves achieve up to 90% energy efficiency during boiling by directly heating the cookware through electromagnetic fields, significantly reducing heat loss compared to hybrid stoves that rely on indirect heat transfer combining electric and gas elements. The induction-boil differential highlights this efficiency gap, as hybrid stoves typically convert only 50-60% of energy into usable heat for boiling, leading to longer cook times and higher energy consumption.
Flame Spread Modulation
Boiling efficiency on hybrid stoves benefits significantly from flame spread modulation, which precisely adjusts heat distribution to maintain consistent temperatures and reduce fuel consumption. Unlike traditional boiling methods on single-flame stoves, this technology enhances thermal transfer and minimizes energy waste, resulting in faster boil times and improved fuel efficiency.
Latent Heat Retention
Boiling on a traditional stove requires significant energy to maintain water at its boiling point due to constant heat loss, whereas hybrid stove cooking leverages latent heat retention to reduce continuous fuel consumption by preserving residual heat within insulated components. This efficient management of latent heat results in lower overall energy usage and faster cooking times, enhancing both fuel savings and thermal efficiency.
Rapid Response Zone (RRZ)
The Rapid Response Zone (RRZ) in boiling significantly enhances heat transfer efficiency by quickly bringing water to a rolling boil, outperforming hybrid stove cooking methods that often exhibit slower and less consistent temperature control. Utilizing RRZ technology reduces energy consumption and cooking time, optimizing fuel use compared to the variable heat distribution typical of hybrid stoves.
Hybrid Element Cycling
Hybrid stove cooking with element cycling enhances boiling efficiency by alternating power between heating elements to maintain optimal temperature while reducing energy waste. This method outperforms traditional boiling by minimizing heat loss and providing precise temperature control, resulting in faster boiling times and lower energy consumption.
Smart Pot Detection
Smart pot detection technology in hybrid stoves optimizes boiling efficiency by automatically adjusting heat based on the pot's size and material, reducing energy waste compared to traditional boiling methods. This leads to faster boiling times and enhanced safety while conserving energy.
Microburst Flame Control
Microburst flame control in hybrid stoves optimizes energy use by delivering precise, high-intensity heat bursts directly to the pot, reducing heat loss compared to traditional boiling methods. This targeted combustion technology enhances cooking speed and fuel efficiency, making hybrid stoves significantly more effective for boiling tasks.
Resonant Heat Transfer
Resonant heat transfer in hybrid stove cooking significantly enhances boiling efficiency by minimizing energy loss through direct and controlled heat application, which contrasts with traditional boiling methods that often rely on less focused conduction and convection. This targeted energy delivery reduces fuel consumption and shortens boiling times, making hybrid stoves superior for rapid and efficient heat transfer in cooking processes.
Boiling vs Hybrid Stove Cooking for efficiency. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com