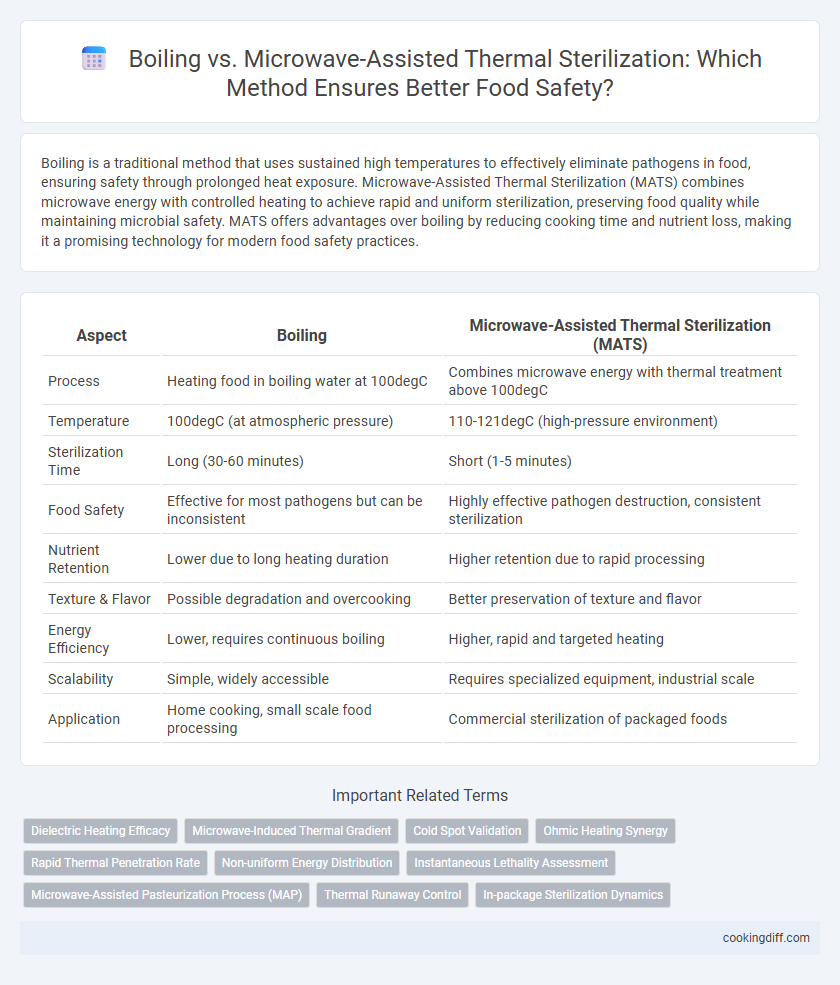
Boiling is a traditional method that uses sustained high temperatures to effectively eliminate pathogens in food, ensuring safety through prolonged heat exposure. Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MATS) combines microwave energy with controlled heating to achieve rapid and uniform sterilization, preserving food quality while maintaining microbial safety. MATS offers advantages over boiling by reducing cooking time and nutrient loss, making it a promising technology for modern food safety practices.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Boiling | Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MATS) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Heating food in boiling water at 100degC | Combines microwave energy with thermal treatment above 100degC |
| Temperature | 100degC (at atmospheric pressure) | 110-121degC (high-pressure environment) |
| Sterilization Time | Long (30-60 minutes) | Short (1-5 minutes) |
| Food Safety | Effective for most pathogens but can be inconsistent | Highly effective pathogen destruction, consistent sterilization |
| Nutrient Retention | Lower due to long heating duration | Higher retention due to rapid processing |
| Texture & Flavor | Possible degradation and overcooking | Better preservation of texture and flavor |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower, requires continuous boiling | Higher, rapid and targeted heating |
| Scalability | Simple, widely accessible | Requires specialized equipment, industrial scale |
| Application | Home cooking, small scale food processing | Commercial sterilization of packaged foods |
Introduction to Food Thermal Processing Methods
Boiling is a conventional food thermal processing method that uses water at 100degC to inactivate microorganisms, ensuring food safety. Microwave-assisted thermal sterilization (MATS) combines microwave energy with heat to achieve rapid and uniform heating, enhancing sterilization efficiency.
While boiling relies on conduction and convection to transfer heat, MATS benefits from volumetric heating, reducing processing time and preserving food quality. Both methods aim to eliminate pathogens, but MATS offers improved nutrient retention and texture compared to traditional boiling.
Understanding Traditional Boiling: Safety and Limitations
How does traditional boiling compare to microwave-assisted thermal sterilization in ensuring food safety? Traditional boiling effectively eliminates many pathogens by maintaining water at 100degC, but it often requires longer times and may unevenly heat food, risking incomplete sterilization. Microwave-assisted thermal sterilization offers faster, more uniform heating, enhancing microbial kill rates while preserving food quality.
What Is Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization?
Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MATS) is an advanced food safety technology that combines microwave energy with conventional thermal processes to sterilize food rapidly and effectively. This method reduces cooking time while preserving the nutritional quality and sensory attributes of the food better than traditional boiling.
- Rapid Heating - MATS uses microwave energy to heat food uniformly and quickly, minimizing nutrient loss.
- Improved Food Quality - The process retains taste, texture, and nutritional value compared to conventional boiling.
- Enhanced Safety - MATS effectively eliminates pathogens while reducing thermal exposure time, ensuring safe food products.
Comparative Mechanisms: Boiling vs MAT Sterilization
Boiling relies on consistent heat transfer through water at 100degC to inactivate microorganisms by denaturing proteins. Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MAT) combines microwave energy with pressurized steam, enabling more rapid and uniform heating throughout the food matrix.
- Heat Transfer - Boiling uses conduction and convection, resulting in slower, surface-to-center heat penetration.
- Heating Uniformity - MAT employs volumetric heating, reducing cold spots and accelerating microbial inactivation.
- Processing Time - MAT significantly shortens sterilization duration compared to traditional boiling methods.
MAT sterilization enhances food safety by ensuring efficient microbial inactivation while preserving sensory and nutritional qualities better than boiling.
Heat Penetration and Microbial Inactivation Efficiency
Boiling achieves microbial inactivation through sustained high temperatures, but its heat penetration is often slower and less uniform compared to microwave-assisted thermal sterilization (MATS). MATS uses microwave energy to generate rapid, volumetric heating, resulting in more efficient and consistent heat distribution within the food matrix.
Heat penetration during boiling relies on conduction and convection, which can create temperature gradients and prolong processing time, potentially affecting food quality. In contrast, MATS delivers targeted thermal energy that accelerates microbial inactivation while preserving nutritional and sensory properties. Studies indicate that MATS can reduce sterilization times significantly, enhancing both efficiency and food safety outcomes.
Nutrient Retention in Boiled vs MAT-Treated Foods
Boiling causes significant nutrient loss, particularly water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex, due to leaching into the cooking water. Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MAT) preserves nutrients better by reducing cooking time and minimizing exposure to high temperatures. Studies indicate MAT-treated foods retain higher antioxidant levels and essential minerals compared to traditionally boiled counterparts.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
Boiling requires significantly more energy due to prolonged heating times compared to Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MATS), which uses focused microwave energy to rapidly achieve sterilization temperatures. MATS reduces carbon emissions by shortening processing duration and enhancing energy efficiency, lowering the environmental footprint of food safety procedures. The advanced technology in MATS promotes sustainable food sterilization by minimizing energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas production.
Impact on Taste, Texture, and Quality
Boiling often leads to nutrient loss and texture softening due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures, impacting the overall quality of food. Microwave-assisted thermal sterilization preserves taste and texture better by using rapid, uniform heating that minimizes nutrient degradation.
- Boiling causes nutrient leaching - Water-soluble vitamins and minerals are frequently lost during the boiling process, reducing the nutritional value of the food.
- Microwave-assisted sterilization enhances texture retention - This method maintains firmer and more desirable food textures by minimizing heat exposure time.
- Microwave treatment improves flavor preservation - Rapid heating helps retain natural flavors and aromas that are often diminished in traditional boiling.
Practical Applications in Home and Industrial Settings
Boiling remains a widely accessible method for food safety in home kitchens, effectively eliminating pathogens through sustained high temperatures. It is simple and requires minimal equipment, making it practical for everyday use but often results in nutrient loss and extended cooking times.
Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MATS) offers a rapid alternative in industrial food processing, combining microwave heating with thermal treatment to preserve food quality while ensuring safety. This method reduces processing time and retains more nutrients, making it ideal for large-scale sterilization of ready-to-eat meals.
Related Important Terms
Dielectric Heating Efficacy
Dielectric heating in Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MATS) enables rapid and uniform temperature elevation, significantly enhancing microbial inactivation compared to conventional boiling. This efficient energy transfer improves food safety by minimizing thermal degradation while ensuring consistent sterilization throughout the food matrix.
Microwave-Induced Thermal Gradient
Microwave-assisted thermal sterilization creates a rapid and uniform microwave-induced thermal gradient that enhances microbial inactivation compared to conventional boiling, preserving food quality while ensuring safety. This method leverages volumetric heating, reducing processing time and minimizing nutrient loss, making it superior for food safety and quality retention.
Cold Spot Validation
Cold spot validation in boiling ensures consistent thermal penetration by maintaining food temperatures at or above 100degC for sufficient time to inactivate pathogens, whereas microwave-assisted thermal sterilization relies on advanced sensors and thermal mapping to identify and validate cold spots within packaged food, ensuring precise microbial lethality while preserving food quality. The effectiveness of cold spot validation directly impacts the safety and shelf-life of sterilized products, with microwave methods offering faster processing and enhanced uniformity compared to traditional boiling methods.
Ohmic Heating Synergy
Ohmic heating synergizes with boiling and microwave-assisted thermal sterilization by providing rapid, uniform heat distribution that enhances microbial inactivation while preserving food quality. This combined approach reduces processing time and energy consumption, improving overall food safety and efficiency in thermal sterilization methods.
Rapid Thermal Penetration Rate
Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MATS) achieves a significantly faster thermal penetration rate compared to traditional boiling, enabling more uniform and rapid heating of packaged foods. This rapid thermal penetration not only reduces overall processing time but also enhances food safety by minimizing microbial survival and preserving nutritional quality.
Non-uniform Energy Distribution
Boiling ensures uniform heat distribution by submerging food in water heated to 100degC, effectively reducing microbial contamination through consistent thermal exposure. Microwave-assisted thermal sterilization often faces challenges with non-uniform energy distribution, leading to cold spots that can compromise sterilization efficacy and food safety.
Instantaneous Lethality Assessment
Instantaneous lethality assessment in boiling involves measuring precise temperature and time parameters to ensure pathogen inactivation, while microwave-assisted thermal sterilization (MATS) achieves rapid, uniform heating that enhances microbial kill efficacy. MATS provides real-time monitoring of lethality values, enabling optimized sterilization cycles that preserve food quality and safety more effectively than traditional boiling methods.
Microwave-Assisted Pasteurization Process (MAP)
Microwave-Assisted Pasteurization Process (MAP) offers rapid and uniform heating that significantly reduces microbial load while preserving food quality compared to traditional boiling methods. This technology enhances food safety by minimizing nutrient loss and maintaining texture, making MAP a superior alternative for thermal sterilization in food processing.
Thermal Runaway Control
Boiling relies on consistent water temperature around 100degC to achieve microbial inactivation, but its thermal transfer is slower compared to Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MATS), which uses electromagnetic waves to rapidly elevate internal food temperatures minimizing thermal runaway risks. MATS systems integrate precise thermal runaway control algorithms and real-time temperature monitoring to ensure uniform heating, preventing overprocessing and preserving food safety while enhancing sterilization efficiency.
Boiling vs Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization for food safety. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com