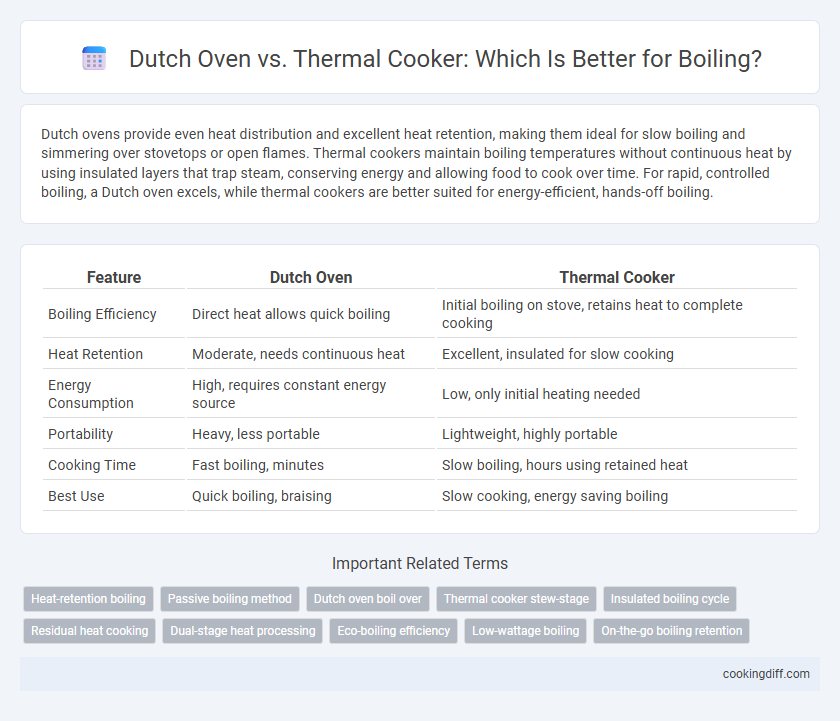
Dutch ovens provide even heat distribution and excellent heat retention, making them ideal for slow boiling and simmering over stovetops or open flames. Thermal cookers maintain boiling temperatures without continuous heat by using insulated layers that trap steam, conserving energy and allowing food to cook over time. For rapid, controlled boiling, a Dutch oven excels, while thermal cookers are better suited for energy-efficient, hands-off boiling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dutch Oven | Thermal Cooker |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling Efficiency | Direct heat allows quick boiling | Initial boiling on stove, retains heat to complete cooking |
| Heat Retention | Moderate, needs continuous heat | Excellent, insulated for slow cooking |
| Energy Consumption | High, requires constant energy source | Low, only initial heating needed |
| Portability | Heavy, less portable | Lightweight, highly portable |
| Cooking Time | Fast boiling, minutes | Slow boiling, hours using retained heat |
| Best Use | Quick boiling, braising | Slow cooking, energy saving boiling |
Introduction to Boiling: Dutch Oven vs Thermal Cooker
Boiling is a cooking method that involves heating water or other liquids to 100degC (212degF) to cook food thoroughly. A Dutch oven, made of cast iron, provides consistent heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for boiling soups, stews, and vegetables on a stovetop. In contrast, a thermal cooker uses insulation to retain heat for slow, energy-efficient boiling without continuous external heat, preserving nutrients and flavors effectively.
How Each Appliance Works for Boiling
A Dutch oven boils by direct heat transfer from the stovetop or oven, creating a consistent and even boiling environment ideal for soups and stews. Its thick cast iron construction retains and distributes heat efficiently, allowing liquids to reach a rolling boil quickly.
A thermal cooker uses residual heat to boil food, where ingredients are preheated to boiling temperature then sealed inside an insulated container, maintaining heat without continuous energy input. This method conserves energy and prevents overcooking by slowly completing the boiling process through retained heat. Thermal cookers are ideal for gentle boiling and simmering without constant supervision.
Heat Retention and Distribution Comparison
Dutch ovens excel in even heat distribution due to their heavy cast iron construction, ensuring consistent boiling without hot spots. Thermal cookers rely on advanced insulation to retain heat, allowing prolonged boiling without continuous energy use but may not distribute heat as evenly during initial cooking. Both appliances optimize heat retention, with Dutch ovens providing superior heat conduction and thermal cookers excelling in maintaining temperature after boiling.
Boiling Speed: Dutch Oven vs Thermal Cooker
The Dutch oven excels in boiling speed due to its heavy cast iron construction, which retains and evenly distributes high heat quickly. This allows water to reach boiling point faster compared to many other cooking vessels.
Thermal cookers rely on retained heat for slow, energy-efficient cooking and do not actively apply heat, resulting in a slower initial boiling process. While excellent for simmering and maintaining temperature, thermal cookers require pre-boiled water to achieve comparable boiling results.
Energy Efficiency in Boiling
Which is more energy-efficient for boiling, a Dutch oven or a thermal cooker? A thermal cooker uses retained heat to complete the boiling process without continuous energy input, significantly reducing fuel consumption. Dutch ovens require constant heat from an external source, making them less efficient for prolonged boiling tasks.
Flavor and Texture Outcomes
Boiling in a Dutch oven tends to enhance the flavor by allowing direct heat to caramelize and concentrate the ingredients, resulting in richer textures. Thermal cookers maintain a consistent low temperature that preserves delicate flavors and produces tender, evenly cooked textures without overcooking.
- Dutch oven caramelization - The thick cast iron promotes Maillard reactions, deepening flavor profiles during boiling.
- Thermal cooker heat retention - Slow heat retention prevents flavor loss and maintains moisture content for soft, succulent textures.
- Cooking time impact - Faster boiling in Dutch ovens intensifies textures, whereas thermal cookers yield more uniform tenderness over time.
Choosing between a Dutch oven and a thermal cooker significantly influences boiling outcomes related to flavor complexity and food texture.
Versatility Beyond Boiling
Dutch ovens offer exceptional versatility beyond boiling by enabling roasting, baking, and slow-cooking due to their heavy cast iron construction and ability to withstand high oven temperatures. Their heat retention and distribution make them ideal for developing rich flavors in stews, braises, and even artisan bread.
Thermal cookers excel in energy-efficient cooking by maintaining heat for hours, perfect for simmering or keeping food warm without continuous power. While less suited for baking or roasting, their insulated design allows for effortless preparation of soups, rice dishes, and delicate slow-cooked meals with minimal supervision.
Portability and Usability
The Dutch oven offers sturdy portability with its heavy cast iron construction, making it ideal for outdoor boiling but less convenient for frequent transport. The thermal cooker excels in usability by maintaining heat efficiently without continuous energy, perfect for on-the-go boiling and minimal supervision.
- Durability - Dutch ovens are highly durable with heat-retentive cast iron, suited for rugged outdoor use.
- Heat Retention - Thermal cookers trap and retain heat, allowing boiling to continue without external heat sources.
- Portability - Thermal cookers are lightweight and compact, offering superior portability compared to heavy Dutch ovens.
Cleaning and Maintenance Differences
| Dutch Oven | Typically made from cast iron or enameled cast iron, requiring thorough cleaning to prevent rust and maintain enamel integrity. Manual scrubbing is often necessary to remove burnt food residues, and seasoning is recommended for uncoated cast iron to preserve the non-stick surface. |
| Thermal Cooker | Features insulated layers with stainless steel or plastic components that are easy to clean using mild soap and water. Minimal maintenance is needed as the cooking pot is removable and dishwasher-safe, reducing the risk of rust and buildup. |
Related Important Terms
Heat-retention boiling
Dutch ovens excel in heat-retention boiling due to their heavy cast iron construction, which evenly distributes and retains heat for extended periods, allowing food to continue cooking off the heat. Thermal cookers maintain boiling temperatures by trapping steam and heat within insulated chambers, making them energy-efficient for slow, heat-retained cooking without needing continuous external heat sources.
Passive boiling method
A Dutch oven uses direct heat for boiling, allowing precise temperature control and efficient heat distribution, whereas a thermal cooker employs a passive boiling method by retaining heat within insulated walls to cook food slowly without continuous energy input. This passive boiling technique in thermal cookers conserves energy and maintains consistent temperatures over extended periods, ideal for slow-cooked dishes.
Dutch oven boil over
Dutch ovens excel at boiling due to their heavy cast iron construction, which provides even heat distribution and minimizes boil-over risks through precise temperature control. In contrast, thermal cookers retain heat without active boiling, reducing the chance of boil-over but requiring initial boiling in a separate pot.
Thermal cooker stew-stage
Thermal cookers excel at the stew-stage by maintaining consistent heat for prolonged boiling without additional energy, preserving flavors and nutrients more efficiently than Dutch ovens, which require constant heat supply. Their insulated design enables slow, gentle boiling perfect for tenderizing tougher cuts of meat and enhancing stew richness.
Insulated boiling cycle
A Dutch oven provides consistent high heat for boiling through direct stovetop or oven contact, ensuring rapid temperature rise but requiring active heat management. A thermal cooker uses insulated boiling cycles to trap heat inside, maintaining boiling temperatures without continuous external heat, offering energy efficiency and extended heat retention ideal for slow-cooked or simmered dishes.
Residual heat cooking
A Dutch oven retains heat in its thick cast iron walls, allowing extended residual heat cooking after boiling, which enhances flavor development and tenderness. Thermal cookers use insulated containers to trap steam and heat, maintaining boiling temperatures internally for hours without additional energy, ideal for slow boiling and simmering processes.
Dual-stage heat processing
A Dutch oven excels in dual-stage heat processing by allowing initial high-temperature searing followed by slow, even boiling, ensuring deep flavor extraction and tender textures. Thermal cookers utilize retained heat for gentle, sustained boiling without continuous energy input, ideal for energy-efficient dual-stage cooking with minimal supervision.
Eco-boiling efficiency
Dutch ovens excel in eco-boiling efficiency by retaining and evenly distributing heat over long periods, reducing fuel consumption during boiling. Thermal cookers maintain boiling temperatures through superior insulation, minimizing energy use by relying on stored heat rather than continuous heat sources.
Low-wattage boiling
A Dutch oven excels in low-wattage boiling due to its heavy cast iron construction, providing even heat distribution and excellent heat retention that minimizes energy use. Thermal cookers enhance low-wattage boiling by utilizing insulated chambers to maintain boiling temperatures without continuous power, making them highly efficient for simmering and slow cooking.
Dutch oven vs Thermal cooker for boiling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com