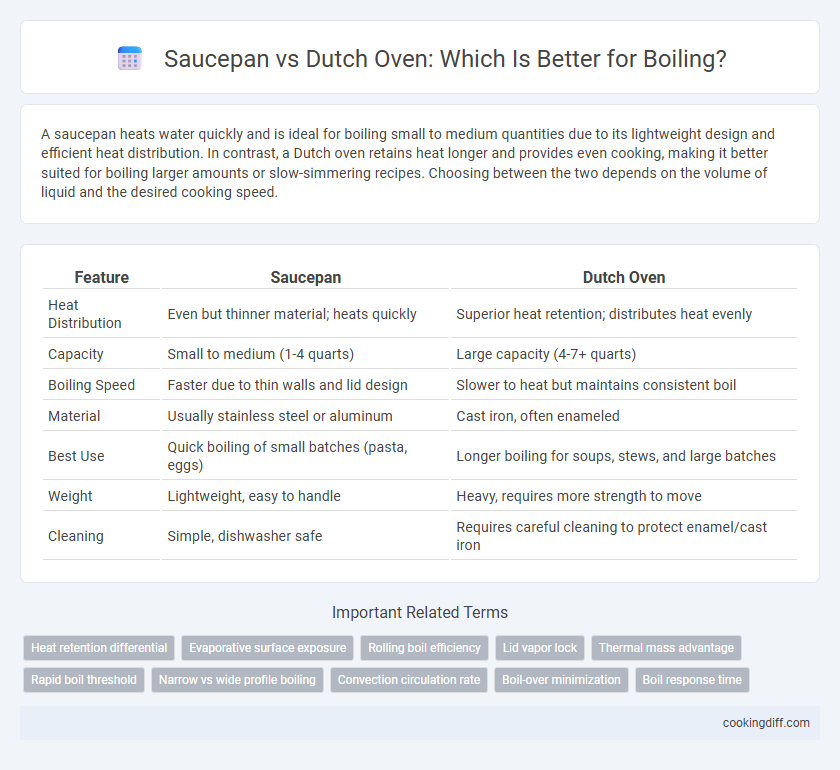
A saucepan heats water quickly and is ideal for boiling small to medium quantities due to its lightweight design and efficient heat distribution. In contrast, a Dutch oven retains heat longer and provides even cooking, making it better suited for boiling larger amounts or slow-simmering recipes. Choosing between the two depends on the volume of liquid and the desired cooking speed.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Saucepan | Dutch Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Distribution | Even but thinner material; heats quickly | Superior heat retention; distributes heat evenly |
| Capacity | Small to medium (1-4 quarts) | Large capacity (4-7+ quarts) |
| Boiling Speed | Faster due to thin walls and lid design | Slower to heat but maintains consistent boil |
| Material | Usually stainless steel or aluminum | Cast iron, often enameled |
| Best Use | Quick boiling of small batches (pasta, eggs) | Longer boiling for soups, stews, and large batches |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavy, requires more strength to move |
| Cleaning | Simple, dishwasher safe | Requires careful cleaning to protect enamel/cast iron |
Overview: Saucepan vs Dutch Oven for Boiling
Saucepans, typically made of stainless steel or aluminum, are ideal for boiling smaller quantities of water or liquids due to their rapid heat conduction and lightweight design. Dutch ovens, often crafted from cast iron with enamel coating, provide excellent heat retention and uniform distribution, making them suitable for boiling larger volumes efficiently.
Choosing between a saucepan and a Dutch oven depends on the boiling task size; saucepans heat up quickly but may lose heat faster, while Dutch ovens maintain consistent temperature longer. For recipes requiring prolonged boiling or simmering, the Dutch oven's heavy lid and thick walls prevent heat loss effectively, ensuring thorough cooking.
Design Features That Affect Boiling
Saucepans typically feature thinner walls and a flat, wide base that promotes quick and even boiling. Dutch ovens have thicker walls and a heavy lid, retaining heat longer which affects the boiling process by maintaining stable temperatures.
- Material thickness - Thicker walls of Dutch ovens conserve heat and provide even boiling but heat up slower compared to saucepans.
- Shape and depth - The tall, narrower design of saucepans accelerates boiling by concentrating heat at the base and reducing surface area.
- Lid design - Dutch ovens have tight-fitting lids that trap steam, preserving moisture and heat for consistent boiling.
Saucepans excel in rapid boiling, while Dutch ovens offer better heat retention for prolonged simmering and boiling stability.
Heat Distribution: Which Performs Better?
When boiling, a Dutch oven outperforms a saucepan in heat distribution due to its thicker base and heavy cast iron construction, which ensures even heat across the entire surface. This consistent heat prevents hotspots and maintains a steady boil, ideal for slow-cooked recipes requiring precise temperature control.
A saucepan heats up quickly but often has thinner walls, leading to uneven heat distribution and localized boiling. For rapid boiling and small quantities, saucepans are efficient, but for prolonged boiling with stable temperatures, Dutch ovens offer superior performance.
Capacity Differences: Boiling Large vs Small Quantities
A saucepan typically holds between 1 to 4 quarts, making it ideal for boiling small to medium quantities like sauces or pasta. Dutch ovens range from 5 to 8 quarts, providing ample capacity for boiling large batches such as soups or stews.
- Small Capacity Advantage - Saucepans heat up quickly, perfect for boiling small quantities efficiently.
- Large Capacity Versatility - Dutch ovens allow boiling large volumes, reducing the need for multiple batches.
- Heat Distribution - Dutch ovens offer even heat distribution, essential for consistent boiling of large quantities.
Material Considerations for Boiling
| Cookware Type | Material | Boiling Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Saucepan | Stainless steel or aluminum | Heats quickly, good for small to medium liquid volumes |
| Dutch Oven | Cast iron or enameled cast iron | Retains heat longer, ideal for slow boiling and large volumes |
Lid Fit and Moisture Retention
The lid fit on a Dutch oven is typically tighter than that of a saucepan, enhancing moisture retention during boiling. This tight seal helps trap steam, maintaining consistent temperature and preventing liquid evaporation. In contrast, saucepans often have looser-fitting lids, which can lead to faster moisture loss and reduced efficiency in boiling processes.
Energy Efficiency in Boiling
Saucepans typically heat up faster due to their thinner construction, making them more energy-efficient for boiling small quantities of water. Dutch ovens have thicker walls and retain heat longer, which conserves energy during longer cooking processes but may use more energy initially to reach boiling point. For quick boiling tasks, a saucepan reduces energy consumption by minimizing heat transfer time.
Versatility Beyond Boiling
While both saucepans and Dutch ovens excel at boiling, their versatility extends far beyond this function. Saucepan's lightweight design suits precise tasks, whereas Dutch oven's thick walls enable slow cooking and braising with rich flavor development.
- Saucepan offers quick heating - Ideal for boiling small quantities and delicate sauces with consistent control.
- Dutch oven facilitates even heat retention - Perfect for stews, roasting, and baking beyond simple boiling.
- Material composition varies - Steel or aluminum saucepans contrast with heavy cast iron Dutch ovens, influencing cooking methods.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Saucepans typically have smooth, non-porous surfaces that make cleaning straightforward, often requiring just warm soapy water and a soft sponge. Dutch ovens, especially those made from cast iron with enamel coating, need gentle cleaning to preserve their finish and prevent rust.
Using mild detergents and avoiding abrasive scrubbers helps maintain the Dutch oven's enamel integrity and extends its lifespan. Saucepans made of stainless steel are dishwasher-safe and more resistant to staining, simplifying maintenance. Regular seasoning of cast iron Dutch ovens is essential to enhance non-stick properties and prevent corrosion.
Related Important Terms
Heat retention differential
A Dutch oven provides superior heat retention compared to a saucepan due to its thicker walls and heavy lid, allowing for more consistent boiling temperatures. This enhanced heat retention makes Dutch ovens ideal for prolonged boiling tasks, conserving energy and ensuring even cooking.
Evaporative surface exposure
A saucepan offers a larger evaporative surface exposure compared to a Dutch oven, allowing faster water reduction and evaporation during boiling. In contrast, a Dutch oven's taller sides and narrower surface limit evaporation, making it ideal for retaining moisture in slow-cooked dishes.
Rolling boil efficiency
A Dutch oven's thick cast iron construction retains and distributes heat evenly, achieving a rolling boil more efficiently than a thin-walled saucepan, which often requires more time and energy due to variable heat retention. For prolonged boiling tasks, the Dutch oven maintains consistent high temperatures, reducing fuel consumption and improving cooking speed compared to typical saucepans.
Lid vapor lock
A Dutch oven's heavy lid creates a superior vapor lock by trapping steam more effectively than a typical saucepan lid, enhancing moisture retention and promoting faster, even boiling. This vapor seal reduces evaporation and concentrates heat within the pot, making Dutch ovens ideal for slow-cooking and recipes requiring prolonged boiling.
Thermal mass advantage
Dutch ovens offer superior thermal mass compared to saucepans, allowing them to retain and distribute heat more evenly during boiling processes. This thermal advantage ensures consistent temperature maintenance, reducing the risk of hot spots and improving cooking efficiency.
Rapid boil threshold
A saucepan typically reaches the rapid boil threshold faster than a Dutch oven due to its smaller volume and thinner material, allowing heat to transfer quickly to the liquid. Dutch ovens, with their thicker walls and larger capacity, maintain steady heat longer but require more time to achieve a rolling boil, making saucepans more efficient for quick boiling tasks.
Narrow vs wide profile boiling
A saucepan's narrow profile concentrates heat and steam, making it ideal for rapid boiling of small to medium liquid volumes, while a Dutch oven's wide, heavy base provides even heat distribution and retains temperature longer, suitable for large batches and prolonged boiling. Choosing between the two depends on the desired boiling speed and quantity, with saucepans excelling in quick, focused boiling and Dutch ovens offering stability and volume capacity.
Convection circulation rate
A Dutch oven's thicker walls and heavy lid promote slower convection circulation, maintaining even heat distribution and consistent boiling temperatures for stews and braises. In contrast, a saucepan's thinner material allows faster convection currents, enabling quicker boiling and more rapid temperature changes ideal for tasks requiring fast heat adjustments.
Boil-over minimization
A Dutch oven's heavy lid and thick walls provide superior heat retention and even distribution, effectively minimizing boil-over by maintaining a consistent simmer compared to a saucepan. Saucepans, with their lighter construction and higher sides, often require closer monitoring to prevent boil-over due to quicker temperature fluctuations.
Saucepan vs Dutch oven for boiling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com