Broiling and plancha grilling both utilize high heat to quickly cook food, but broiling exposes food to direct radiant heat from above, creating a crisp exterior and tender interior. Plancha grilling uses a flat, heated metal surface, providing even heat distribution and the ability to cook delicate items without flare-ups. Choosing between the two depends on the desired texture and cooking control, with broiling ideal for intense searing and plancha perfect for consistent heat and versatility.
Table of Comparison
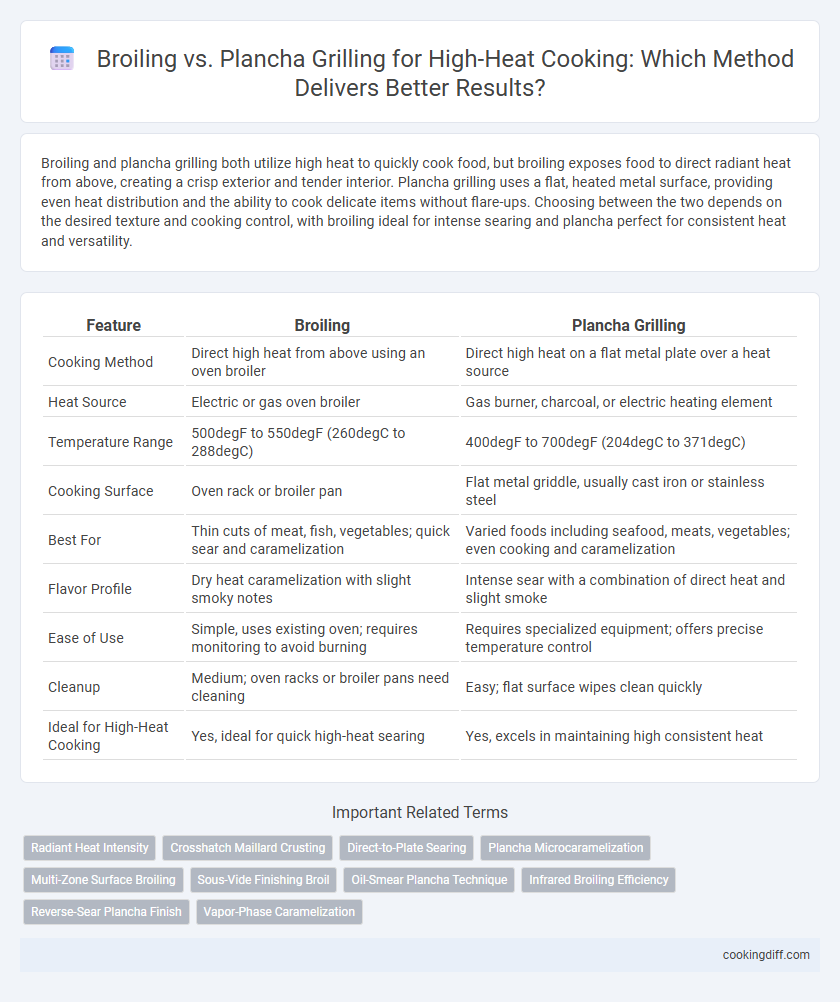
| Feature | Broiling | Plancha Grilling |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Direct high heat from above using an oven broiler | Direct high heat on a flat metal plate over a heat source |
| Heat Source | Electric or gas oven broiler | Gas burner, charcoal, or electric heating element |
| Temperature Range | 500degF to 550degF (260degC to 288degC) | 400degF to 700degF (204degC to 371degC) |
| Cooking Surface | Oven rack or broiler pan | Flat metal griddle, usually cast iron or stainless steel |
| Best For | Thin cuts of meat, fish, vegetables; quick sear and caramelization | Varied foods including seafood, meats, vegetables; even cooking and caramelization |
| Flavor Profile | Dry heat caramelization with slight smoky notes | Intense sear with a combination of direct heat and slight smoke |
| Ease of Use | Simple, uses existing oven; requires monitoring to avoid burning | Requires specialized equipment; offers precise temperature control |
| Cleanup | Medium; oven racks or broiler pans need cleaning | Easy; flat surface wipes clean quickly |
| Ideal for High-Heat Cooking | Yes, ideal for quick high-heat searing | Yes, excels in maintaining high consistent heat |
Introduction to High-Heat Cooking Methods
Broiling and plancha grilling are two popular high-heat cooking methods that use intense direct heat to cook food quickly, enhancing flavor and texture. Both techniques achieve caramelization and Maillard reactions but differ in heat source and cooking surface design.
- Broiling - Uses direct radiant heat from above, typically in an oven, allowing for quick searing of meats and vegetables.
- Plancha grilling - Utilizes a flat, very hot metal plate heated from below, providing even heat distribution and excellent searing capabilities.
- Heat intensity - Both methods operate at temperatures often exceeding 500degF (260degC), ideal for fast cooking and browning.
Choosing between broiling and plancha grilling depends on equipment availability and the desired texture and flavor profile.
What is Broiling?
| Broiling is a high-heat cooking method that uses direct radiant heat from an overhead source, typically an oven's broiler element. It cooks food quickly at temperatures ranging from 500degF to 550degF, ideal for tender cuts of meat, fish, and vegetables. Unlike plancha grilling, which uses a heated flat surface, broiling exposes food to intense heat from above, creating a distinct sear and caramelization. |
Understanding Plancha Grilling
Plancha grilling uses a flat, smooth metal surface heated to very high temperatures, allowing even heat distribution and quick searing of foods. Unlike broiling, which exposes food to direct radiant heat from above, plancha grilling cooks from beneath, preserving moisture and enhancing flavor through caramelization.
- Even Heat Distribution - The metal surface of a plancha ensures consistent temperature across the cooking area for uniform cooking results.
- Versatility with Ingredients - Plancha grilling can handle delicate items like seafood and vegetables without drying them out, unlike traditional broiling.
- Retained Moisture and Flavor - Contact with the hot surface sears food quickly, locking in juices and boosting taste through Maillard reactions.
Key Differences Between Broiling and Plancha Grilling
Broiling uses intense direct heat from above, typically in an oven, reaching temperatures around 500degF to 550degF, which quickly sears food. Plancha grilling involves cooking on a flat, metal griddle heated from below, providing consistent high heat usually between 400degF and 450degF for even cooking. Broiling is ideal for thin cuts and quick caramelization, while plancha grilling excels at delivering a uniform sear with greater surface contact and control.
Heat Distribution: Broiler vs Plancha
Broiling uses intense, direct radiant heat from an overhead source, creating rapid searing but often results in uneven heat distribution, especially with thicker cuts of meat. The concentrated heat can cause hotspots, requiring frequent rotation to cook food evenly.
Plancha grilling utilizes a solid, flat metal surface that provides consistent and uniform heat distribution across the cooking area. This even heat retention prevents flare-ups and allows for better control over cooking temperature, making it ideal for delicate proteins and vegetables.
Flavor Development and Maillard Reaction
Broiling and plancha grilling both utilize high-heat cooking methods that enhance flavor through the Maillard reaction, which occurs when proteins and sugars in food brown and develop complex flavors. Broiling applies intense direct heat from above, creating a crispy exterior quickly, while plancha grilling uses a heated flat surface that allows for even contact and caramelization. The choice between broiling and plancha grilling impacts the depth of flavor and texture, with broiling producing a distinct char and plancha delivering a more uniform sear and enhanced caramelized notes.
Versatility: Foods Best Suited for Each Method
Broiling is ideal for tender cuts of meat, fish, and vegetables that benefit from intense, direct heat to achieve a crispy exterior while remaining juicy inside. Plancha grilling excels with delicate foods like seafood and thinly sliced vegetables, allowing even cooking and minimal flare-ups due to its flat, heated surface.
Broiling provides high-heat intensity suitable for quickly searing steaks, chops, and thicker cuts, locking in moisture and flavor. Plancha grilling's versatility accommodates a broader range of foods, including eggs and small seafood, due to its stable cooking surface and controlled heat distribution. Each method enhances texture and taste by leveraging different heat applications tailored to specific food types.
Equipment and Setup Requirements
Broiling requires an oven equipped with a broiler element positioned close to the food, providing intense radiant heat from above. This setup is ideal for achieving a crisp exterior quickly without the need for additional equipment beyond a broiler pan or rack.
Plancha grilling demands a flat, highly conductive metal griddle typically heated by gas or charcoal, ensuring even heat distribution across the surface. The equipment setup is more versatile for outdoor cooking but requires a dedicated heat source and a sturdier setup compared to broiling.
Safety Tips for High-Heat Cooking
What safety precautions should be taken when broiling or plancha grilling at high heat? Use long-handled tools and keep a fire extinguisher nearby to prevent burns and flare-ups. Always monitor the cooking process closely to avoid overheating and potential kitchen fires.
Related Important Terms
Radiant Heat Intensity
Broiling generates intense radiant heat directly from above, reaching temperatures around 500-550degF, ideal for rapid searing and caramelization. Plancha grilling uses a flat metal plate heated from below, offering more even heat distribution but lower radiant heat intensity compared to broiling.
Crosshatch Maillard Crusting
Broiling achieves intense direct heat from above, promoting rapid Maillard reactions that create pronounced crosshatch crusting on meats, while plancha grilling provides even surface contact heat ideal for uniform browning but less distinct crosshatch marks. The vertical heat source in broiling enables higher temperatures reaching approximately 550degF (288degC), intensifying flavor development through caramelization compared to the flat, radiant heat of a plancha.
Direct-to-Plate Searing
Broiling delivers intense, direct heat from above, creating a caramelized crust ideal for direct-to-plate searing, whereas plancha grilling uses a flat, heated surface that sears evenly but with less intense radiant heat. This difference impacts the Maillard reaction speed and surface texture, making broiling superior for achieving a quick, high-heat sear with distinct charring on meats.
Plancha Microcaramelization
Plancha grilling achieves superior microcaramelization compared to broiling by maintaining consistent, direct contact with a heated metal surface, enhancing Maillard reactions and flavor complexity. This method optimizes high-heat cooking by evenly searing proteins and vegetables, resulting in a distinct texture and deeper caramelized notes than the radiant heat approach of broiling.
Multi-Zone Surface Broiling
Multi-zone surface broiling provides precise temperature control by dividing the cooking area into distinct heat zones, allowing simultaneous high-heat searing and gentle cooking, unlike plancha grilling which offers a uniformly hot surface. This method enhances flavor development and texture contrast by optimizing heat distribution, making it ideal for high-heat culinary applications.
Sous-Vide Finishing Broil
Sous-vide finishing with broiling provides precise temperature control before applying intense radiant heat, enhancing tenderness and caramelization without overcooking. Unlike plancha grilling, broiling delivers direct high-heat from above, achieving a crisp crust while maintaining juicy interior textures.
Oil-Smear Plancha Technique
Broiling uses intense direct heat from above to cook food quickly, while the oil-smear plancha technique applies a thin layer of oil on the flat metal surface, enabling even heat conduction and a flavorful crust. This method reduces flare-ups and enhances Maillard reactions, making plancha grilling ideal for delicate proteins compared to broiling's intense radiant heat.
Infrared Broiling Efficiency
Infrared broiling offers superior efficiency by delivering intense, concentrated heat directly to the food, ensuring rapid searing and enhanced caramelization compared to plancha grilling's broader, less focused heat distribution. This targeted infrared radiation reduces cooking time and energy consumption while achieving professional-quality results with precise temperature control.
Reverse-Sear Plancha Finish
Broiling uses intense direct heat from above, ideal for quick cooking and crisping, while Plancha grilling offers a flat, high-heat surface that evenly sears and locks in juices. A reverse-sear Plancha finish, starting with low and slow cooking followed by a high-heat sear on the Plancha, ensures tender, evenly cooked meat with a flavorful crust unmatched by broiling alone.
Broiling vs Plancha grilling for high-heat cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com