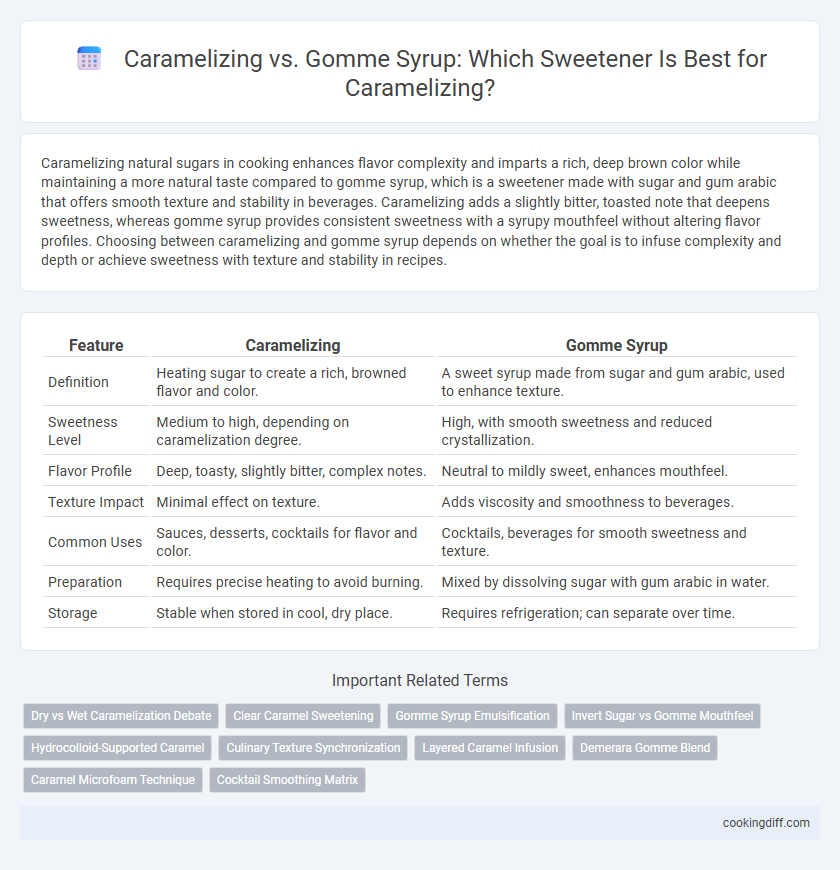
Caramelizing natural sugars in cooking enhances flavor complexity and imparts a rich, deep brown color while maintaining a more natural taste compared to gomme syrup, which is a sweetener made with sugar and gum arabic that offers smooth texture and stability in beverages. Caramelizing adds a slightly bitter, toasted note that deepens sweetness, whereas gomme syrup provides consistent sweetness with a syrupy mouthfeel without altering flavor profiles. Choosing between caramelizing and gomme syrup depends on whether the goal is to infuse complexity and depth or achieve sweetness with texture and stability in recipes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Caramelizing | Gomme Syrup |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heating sugar to create a rich, browned flavor and color. | A sweet syrup made from sugar and gum arabic, used to enhance texture. |
| Sweetness Level | Medium to high, depending on caramelization degree. | High, with smooth sweetness and reduced crystallization. |
| Flavor Profile | Deep, toasty, slightly bitter, complex notes. | Neutral to mildly sweet, enhances mouthfeel. |
| Texture Impact | Minimal effect on texture. | Adds viscosity and smoothness to beverages. |
| Common Uses | Sauces, desserts, cocktails for flavor and color. | Cocktails, beverages for smooth sweetness and texture. |
| Preparation | Requires precise heating to avoid burning. | Mixed by dissolving sugar with gum arabic in water. |
| Storage | Stable when stored in cool, dry place. | Requires refrigeration; can separate over time. |
Introduction to Caramelizing and Gomme Syrup
Caramelizing involves heating sugar to create rich, complex flavors and a deep amber color, making it a popular technique in cooking and baking. This process transforms sucrose into caramel through thermal decomposition, enhancing sweetness and adding a slightly bitter undertone.
Gomme syrup, a sweetener made from sugar and gum arabic, offers a smooth texture and enhanced mouthfeel without the characteristic bitterness of caramel. It is commonly used in beverages and desserts to provide consistent sweetness and improve viscosity.
Understanding the Science Behind Caramelization
Caramelizing involves heating sugar to create complex flavors and a rich amber color through the Maillard reaction and thermal decomposition, while gomme syrup is a pre-made sweetener that blends sugar with gum arabic to improve texture and sweetness. The science behind caramelization focuses on chemical changes that develop flavor compounds, which differ fundamentally from the stabilizing effects of gomme syrup.
- Caramelization - The process breaks down sugar molecules to form flavorful caramel compounds and dark pigments.
- Gomme Syrup - Contains gum arabic that enhances sweetness and gives drinks a smooth mouthfeel.
- Chemical Reactions - Caramelization occurs at high temperatures causing sugar to oxidize and polymerize, unlike the simple dissolution in gomme syrup.
Understanding these distinctions helps optimize sweetener choice for flavor development and texture in culinary applications.
What is Gomme Syrup?
Gomme syrup is a sweetener made from sugar and gum arabic, which gives it a smooth, viscous texture. It is commonly used in cocktails and beverages to provide sweetness and a silky mouthfeel without the crystallization issues of regular syrups. Unlike caramelizing sugar, gomme syrup does not develop a rich, burnt flavor but instead enhances sweetness while maintaining clarity and consistency.
Flavor Profiles: Caramelizing vs Gomme Syrup
How do the flavor profiles differ between caramelizing and gomme syrup as sweeteners? Caramelizing sugar develops rich, complex notes of toffee and burnt sugar, adding depth and a slightly bitter edge to recipes. Gomme syrup, on the other hand, imparts a smooth, sweet flavor with a silky texture but lacks the intense caramelized nuances.
Texture and Consistency Differences
Caramelizing sugar transforms it into a rich, amber syrup with a thicker, more viscous texture that adds depth and complexity to recipes. This process produces a slightly grainy consistency that can crystallize if not carefully managed.
Gomme syrup, containing gum arabic, offers a smooth, velvety texture that prevents crystallization and enhances liquidity in beverages and desserts. Its consistent viscosity provides a silky mouthfeel, distinguishing it from the denser texture of caramelized sugar.
Sweetening Power and Mixing Capabilities
Caramelizing enhances sweetness through the Maillard reaction, producing complex flavors and a deeper sweetness profile compared to gomme syrup. Gomme syrup offers a more consistent sweetening power with smoother texture and better solubility in cold and hot mixtures. While caramelized sugar adds rich, layered notes, gomme syrup excels in mixing capabilities, preventing crystallization and providing a stable, uniform sweetness in beverages and desserts.
Best Uses in Cooking and Cocktails
| Sweetener | Best Uses in Cooking | Best Uses in Cocktails |
|---|---|---|
| Caramelizing | Ideal for creating rich, complex flavors in desserts like caramel sauces, flans, and baked goods by transforming sugar through heat-induced browning. | Enhances depth and color in cocktails such as Old Fashioned and whiskey sours, providing a toasted sweetness and subtle bitterness. |
| Gomme Syrup | Preferred for adding smooth, consistent sweetness and texture in cocktails and certain desserts without altering flavor profiles significantly. | Commonly used in mixed drinks like Daiquiris and Sours to improve mouthfeel and balance acidity without introducing caramelized notes. |
Pros and Cons of Caramelizing as a Sweetener
Caramelizing sugar enhances flavor by creating complex, rich notes and a deep amber color, making it ideal for desserts and beverages. However, caramelizing requires careful temperature control to avoid burning, which can result in a bitter taste.
Caramelizing produces natural sweetness and a unique texture without added preservatives or chemicals. It allows for customization of sweetness intensity and flavor depth, but the process can be time-consuming and less consistent compared to gomme syrup. Unlike gomme syrup, caramelized sugar lacks the smooth, viscous texture that can improve mouthfeel in cocktails and culinary applications.
Pros and Cons of Gomme Syrup as a Sweetener
Gomme syrup is a sweetener favored for its smooth texture and ability to enhance mouthfeel without overpowering flavors. It offers a different profile compared to caramelizing sugar, providing sweetness with added viscosity.
- Enhanced Texture - Gomme syrup adds a rich, silky consistency to beverages and desserts, improving overall sensory experience.
- Neutral Sweetness - It delivers sweetness without the burnt or complex flavors that caramelized sugar introduces.
- Ingredient Sensitivity - The presence of gum arabic can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals, limiting its use in some recipes.
Related Important Terms
Dry vs Wet Caramelization Debate
Dry caramelization involves heating sugar directly until it melts and turns golden brown, creating a more complex, slightly bitter flavor ideal for savory dishes. Wet caramelization, or the use of gomme syrup, combines sugar with water, resulting in a smoother, sweeter profile and greater control over the caramelization process, making it preferable for delicate desserts.
Clear Caramel Sweetening
Clear caramel sweetening offers a natural, richly flavored alternative to gomme syrup, which relies on gum arabic for smooth texture and sweetness enhancement. Unlike gomme syrup's opaque consistency, clear caramel provides a transparent, deep amber hue that enhances sweetness without clouding beverages or desserts.
Gomme Syrup Emulsification
Gomme syrup enhances cocktail texture and mouthfeel through superior emulsification, creating a smoother and more stable mixture compared to caramelized sugar, which primarily adds color and flavor but lacks emulsifying properties. This emulsification capability makes gomme syrup a preferred sweetener for achieving consistent blending in complex drinks.
Invert Sugar vs Gomme Mouthfeel
Caramelizing transforms sucrose into rich, flavorful compounds enhancing complexity and color, while gomme syrup, rich in gum arabic, provides a smooth, silky mouthfeel without intense flavor changes. Invert sugar, a key component formed during caramelization, adds sweetness and moisture retention, contrasting with gomme syrup's primary role of improving texture rather than sweetness intensity.
Hydrocolloid-Supported Caramel
Hydrocolloid-supported caramel enhances sweetness by stabilizing caramelized sugars, providing a richer flavor profile and improved texture compared to gomme syrup, which primarily acts as a thickening agent without deep caramel notes. This method delivers superior thermal stability and reduced crystallization, making it ideal for complex confectionery applications requiring consistent sweetness and mouthfeel.
Culinary Texture Synchronization
Caramelizing sugar enhances complex flavor depth and creates a rich, thick texture that integrates seamlessly with baked goods and sauces, offering natural viscosity and a golden hue. Gomme syrup, enriched with gum arabic, provides a smoother, more uniform sweetness and superior moisture retention, optimizing texture synchronization in beverages and confections by preventing crystallization and improving mouthfeel.
Layered Caramel Infusion
Caramelizing sugar creates a rich, complex flavor profile with deep notes that enhance layered caramel infusion, providing a natural sweetness and bitterness that gomme syrup lacks. Gomme syrup, primarily a sugar and gum arabic blend, delivers smooth texture and sweetness but lacks the intricate flavor depth essential for authentic caramel complexity.
Demerara Gomme Blend
Demerara Gomme Blend offers a unique sweetening experience by combining the rich, molasses-like flavors of caramelized Demerara sugar with the smooth texture of gomme syrup, enhancing beverages with both depth and viscosity. Unlike traditional gomme syrup, this blend provides a complex caramelized sweetness that balances boldness and sweetness while maintaining the syrup's signature velvety mouthfeel.
Caramel Microfoam Technique
The Caramel Microfoam Technique enhances caramelizing by incorporating finely textured, steamed milk foam that balances the rich, complex flavors of caramelized sugar with a creamy consistency, unlike gomme syrup which primarily adds sweetness without depth. This method intensifies the caramel aroma and creates a smooth, velvety mouthfeel, making it a superior choice for sophisticated caramel-based beverages and desserts.
Caramelizing vs Gomme Syrup for sweeteners. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com