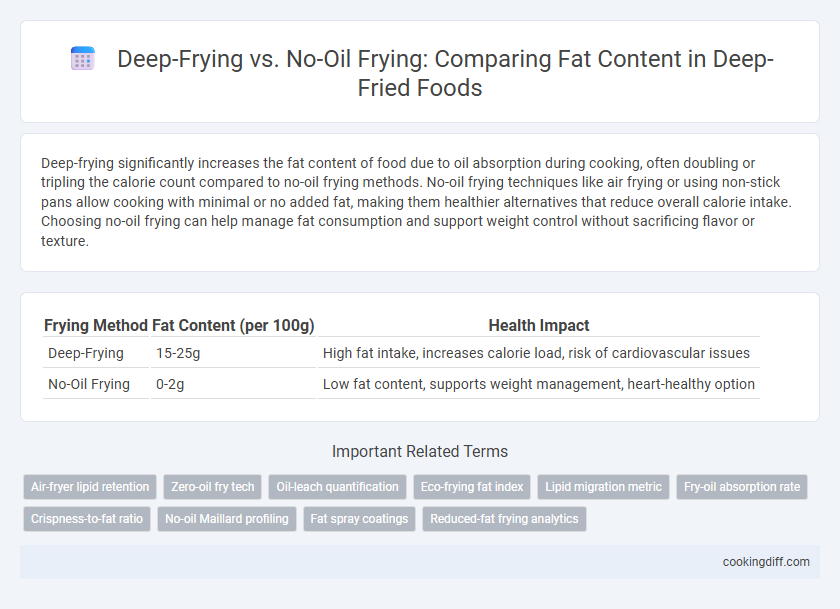
Deep-frying significantly increases the fat content of food due to oil absorption during cooking, often doubling or tripling the calorie count compared to no-oil frying methods. No-oil frying techniques like air frying or using non-stick pans allow cooking with minimal or no added fat, making them healthier alternatives that reduce overall calorie intake. Choosing no-oil frying can help manage fat consumption and support weight control without sacrificing flavor or texture.
Table of Comparison
| Frying Method | Fat Content (per 100g) | Health Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Deep-Frying | 15-25g | High fat intake, increases calorie load, risk of cardiovascular issues |
| No-Oil Frying | 0-2g | Low fat content, supports weight management, heart-healthy option |
Introduction to Deep-Frying and No-Oil Frying
How does the fat content in deep-frying compare to no-oil frying methods? Deep-frying involves submerging food in hot oil, resulting in higher fat absorption and calorie content. No-oil frying, such as air frying or dry sauteing, uses minimal to no added fats, significantly reducing overall fat intake while maintaining crispiness.
What is Deep-Frying?
Deep-frying involves cooking food by immersing it in hot oil, resulting in a crispy texture and rich flavor. This method significantly increases the fat content of food compared to no-oil frying, which cooks food without added fats.
- Oil Absorption - Foods deep-fried absorb a substantial amount of oil, increasing their overall fat and calorie content.
- No-Oil Frying - Techniques like air frying or grilling cook food with little to no added fat, preserving lower fat levels.
- Health Impact - Higher fat intake from deep-fried foods can contribute to health risks such as heart disease and obesity.
Choosing no-oil frying methods reduces fat consumption while still allowing for flavorful, crispy dishes.
What is No-Oil Frying?
No-oil frying is a cooking method that uses hot air circulation to cook food, eliminating the need for added fats or oils. This technique significantly reduces the fat content compared to traditional deep-frying methods.
Deep-frying immerses food in hot oil, leading to higher fat absorption and increased calorie content. In contrast, no-oil frying, often achieved with air fryers, produces crispy textures by circulating hot air around the food. This method appeals to health-conscious individuals aiming to reduce fat intake while maintaining flavor and texture.
Fat Content in Deep-Fried Foods
Deep-frying significantly increases the fat content of foods due to oil absorption during cooking, often doubling the fat compared to no-oil frying methods. No-oil frying techniques, such as air frying or baking, maintain lower fat levels by limiting or eliminating added fats.
- Oil absorption in deep-frying - Foods can absorb 10-30% of the frying oil, substantially raising their fat and calorie content.
- Fat reduction in no-oil frying - Methods like air frying reduce fat content by up to 80% compared to traditional deep-frying.
- Health implications - Lower fat content in no-oil fried foods supports healthier lipid profiles and calorie control.
Fat Content in No-Oil Fried Foods
No-oil frying methods significantly reduce the fat content in foods compared to traditional deep-frying, which immerses food in hot oil. This reduction leads to lower calorie intake and can contribute to healthier dietary choices.
Foods cooked without oil retain their natural fats without the additional fat absorption typical of deep-frying. As a result, no-oil frying supports weight management and minimizes the risk of heart disease linked to high fat consumption.
Nutritional Differences: Deep-Frying vs No-Oil Frying
Deep-frying significantly increases the fat content of foods due to oil absorption during cooking, often doubling or tripling the calorie count compared to no-oil frying methods. No-oil frying techniques, such as air frying or grilling, maintain lower fat levels while preserving essential nutrients and flavor. Choosing no-oil frying reduces unhealthy fat intake, supporting better heart health and weight management.
Texture and Flavor Impacts of Fat Content
Deep-frying significantly increases fat content, resulting in a crispy texture and rich flavor due to oil absorption. No-oil frying methods, such as air frying or grilling, produce a less greasy texture with a lighter flavor profile while maintaining lower fat levels. The presence of fat in deep-frying enhances mouthfeel and caramelization, offering a distinct sensory experience compared to no-oil frying alternatives.
Health Risks of High Fat Intake from Fried Foods
| Deep-frying introduces significantly higher fat content in foods compared to no-oil frying methods, leading to increased intake of unhealthy trans fats and saturated fats. Excessive consumption of deep-fried foods is linked to elevated risks of cardiovascular diseases, obesity, and type 2 diabetes due to these unhealthy fat profiles. Choosing no-oil frying methods reduces fat intake and associated health risks by preserving nutrients without adding unhealthy fats. |
Reducing Fat Content: Tips and Techniques
Deep-frying significantly increases fat content due to oil absorption, often doubling the calorie count compared to no-oil frying methods. Using air fryers or non-stick pans can reduce fat by minimizing or eliminating added oils during cooking.
Techniques like preheating oil to the correct temperature and draining food on paper towels help reduce excess fat in deep-fried dishes. No-oil frying methods such as steaming, baking, or grilling maintain lower fat levels, making them healthier alternatives.
Related Important Terms
Air-fryer lipid retention
Deep-frying significantly increases fat content in foods due to oil absorption, whereas no-oil frying methods like air-frying retain substantially lower lipid levels by circulating hot air to cook without added fat. Air-fryers reduce total fat by up to 80% compared to traditional deep-frying, making them a healthier alternative for lipid-sensitive diets.
Zero-oil fry tech
Zero-oil frying technology significantly reduces fat content by using rapid hot air circulation to crisp foods without submerging them in oil, achieving health benefits similar to traditional deep-frying but with up to 80-90% less fat. This method preserves texture and flavor while minimizing calorie intake, making it a preferred choice for health-conscious consumers seeking lower-fat alternatives to deep-fried foods.
Oil-leach quantification
Deep-frying significantly increases the fat content of foods due to oil absorption quantified by oil-leach rates between 15-35%, whereas no-oil frying methods maintain minimal fat levels by eliminating direct oil contact. Quantitative analysis using gravimetric or spectroscopic techniques reveals a marked oil-leach reduction, directly correlating with lower caloric density in no-oil fried products.
Eco-frying fat index
Deep-frying significantly increases fat content due to oil absorption, whereas no-oil frying methods, such as air frying or baking, maintain a substantially lower fat index in the Eco-frying metric. The Eco-frying fat index quantifies the environmental impact and nutritional influence of fat content, revealing that no-oil frying methods reduce both calorie density and ecological footprint compared to traditional deep-frying.
Lipid migration metric
Deep-frying significantly increases lipid migration into food, resulting in higher fat content compared to no-oil frying methods that minimize oil absorption. Lipid migration, defined as the transfer of fats from cooking oil into food, is a critical metric indicating elevated caloric and fat levels in deep-fried products versus the minimal lipid transfer observed in no-oil frying techniques.
Fry-oil absorption rate
Deep-frying typically results in a higher fat content due to the fry-oil absorption rate, which can vary between 8% to 25% depending on the food's moisture and coating. In contrast, no-oil frying methods like air frying significantly reduce fat absorption, often limiting it to less than 5%, making them a healthier alternative for controlling dietary fat intake.
Crispness-to-fat ratio
Deep-frying typically results in a higher fat content due to oil absorption but delivers a superior crispness-to-fat ratio compared to no-oil frying methods; air frying or baking reduces fat content but often compromises on the crisp texture. Optimizing cooking time and temperature in deep-frying can enhance crispness while controlling excessive fat uptake.
No-oil Maillard profiling
No-oil frying methods significantly reduce fat content compared to traditional deep-frying by eliminating oil absorption, making them healthier options for cooking. The Maillard reaction in no-oil frying is carefully controlled through precise temperature and time adjustments, enhancing flavor and browning without added fats.
Fat spray coatings
Fat spray coatings in deep-frying significantly increase the fat content of foods compared to no-oil frying methods, which typically eliminate added fats and reduce overall caloric intake. Studies show that foods prepared with fat spray coatings during deep-frying absorb more oil, leading to higher saturated fat levels and greater energy density than air-fried or no-oil alternatives.
Deep-frying vs No-oil frying for fat content. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com