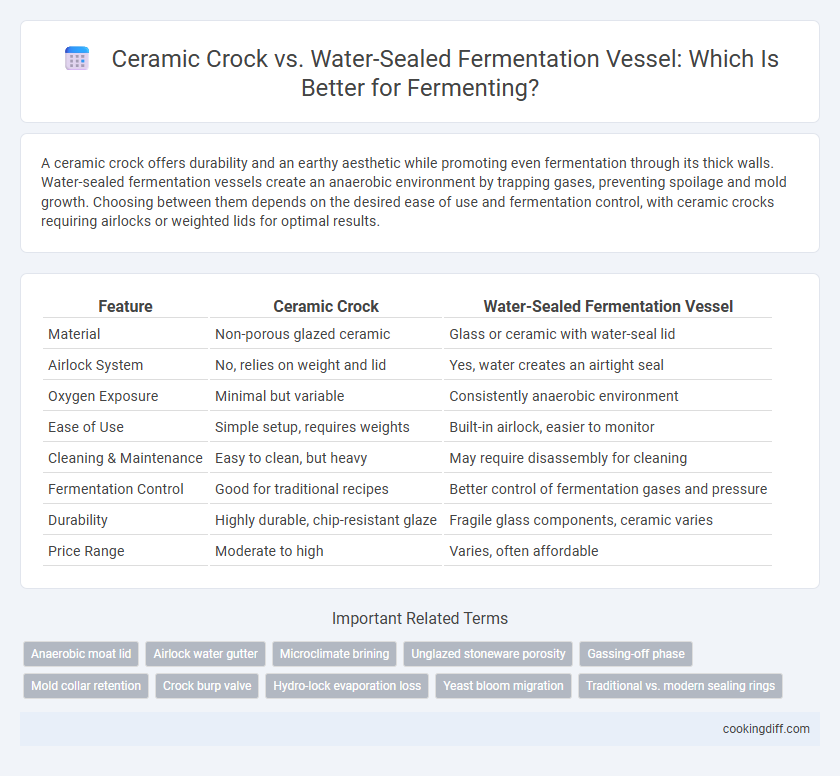
A ceramic crock offers durability and an earthy aesthetic while promoting even fermentation through its thick walls. Water-sealed fermentation vessels create an anaerobic environment by trapping gases, preventing spoilage and mold growth. Choosing between them depends on the desired ease of use and fermentation control, with ceramic crocks requiring airlocks or weighted lids for optimal results.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Crock | Water-Sealed Fermentation Vessel |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Non-porous glazed ceramic | Glass or ceramic with water-seal lid |
| Airlock System | No, relies on weight and lid | Yes, water creates an airtight seal |
| Oxygen Exposure | Minimal but variable | Consistently anaerobic environment |
| Ease of Use | Simple setup, requires weights | Built-in airlock, easier to monitor |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Easy to clean, but heavy | May require disassembly for cleaning |
| Fermentation Control | Good for traditional recipes | Better control of fermentation gases and pressure |
| Durability | Highly durable, chip-resistant glaze | Fragile glass components, ceramic varies |
| Price Range | Moderate to high | Varies, often affordable |
Introduction to Traditional Fermentation Vessels
| Ceramic crocks are traditional fermentation vessels known for their porous nature that allows air exchange, fostering natural fermentation environments for foods like sauerkraut and kimchi. |
| Water-sealed fermentation vessels use a water lock to create an anaerobic environment, preventing oxygen ingress and promoting lactic acid bacteria growth for consistent, controlled fermentation results. |
| Both vessel types prioritize maintaining optimal anaerobic conditions, but ceramic crocks rely on natural airlocks while water-sealed vessels employ a physical water barrier to minimize contamination risks during fermentation. |
Overview: Ceramic Crocks in Fermenting
Ceramic crocks are traditional fermentation vessels crafted from natural clay, offering a breathable environment that promotes slow, even fermentation. Their porous nature allows beneficial bacteria to thrive, enhancing the flavor and texture of fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi.
Unlike water-sealed fermentation vessels that rely on an airlock system to prevent oxygen exposure, ceramic crocks often use a weighted lid to keep vegetables submerged under brine. This method reduces risk of mold growth while preserving anaerobic conditions essential for lacto-fermentation.
What is a Water-Sealed Fermentation Vessel?
A water-sealed fermentation vessel utilizes a water-filled channel around the lid to create an airtight seal that allows gases to escape without letting oxygen in, preventing contamination during fermenting. This vessel is favored for its ability to maintain an anaerobic environment critical for fermenting foods like sauerkraut and kimchi. Compared to ceramic crocks, water-sealed fermentation vessels often provide more consistent airlock functionality, reducing the risk of mold or spoilage.
Airflow and Gas Release: How Each Vessel Works
Ceramic crocks allow for minimal airflow through tiny pores in the material, which helps maintain an anaerobic environment while slowly releasing gases produced during fermentation. This natural breathability prevents pressure buildup without exposing the contents to external contaminants.
Water-sealed fermentation vessels use an airlock filled with water to create a airtight seal, effectively trapping gases inside while allowing carbon dioxide to escape through the water barrier. This system prevents oxygen and airborne bacteria from entering, ensuring a controlled fermentation environment.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Ceramic crocks offer simplicity with fewer parts, making them easier to clean and maintain compared to water-sealed fermentation vessels that include additional components for water locks. Water-sealed vessels provide a more controlled fermentation environment but require more detailed cleaning and careful assembly to prevent mold and leakage.
- Ceramic Crock Ease of Use - Simple design involves just the crock and a weight, minimizing setup time.
- Water-Sealed Vessel Maintenance - The water seal needs frequent refilling and thorough cleaning to avoid contamination.
- Cleaning Convenience - Ceramic crocks can be scrubbed easily without disassembling multiple parts.
Ceramic crocks are generally favored for their straightforward maintenance and ease of use in home fermentation.
Flavor Profiles: Ceramic vs Water-Sealed Results
Ceramic crocks provide a stable environment that promotes the development of complex, earthy flavors due to their porous nature allowing subtle air exchange. Water-sealed fermentation vessels, by creating an airtight barrier, preserve bright, tangy, and consistent flavor profiles by preventing oxygen exposure.
The porous ceramic material absorbs and releases moisture, enhancing depth and richness in fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi. Water-sealed vessels maintain anaerobic conditions that inhibit spoilage organisms, resulting in crisp and clean flavors. Choosing between the two depends on desired taste nuances and fermentation control preferences.
Preventing Contamination and Mold Growth
Ceramic crocks provide a breathable environment that reduces the risk of mold by allowing gases to escape while maintaining an anaerobic atmosphere crucial for fermentation. Water-sealed fermentation vessels create an airtight seal that prevents airborne contaminants but require careful water management to avoid stagnant conditions promoting mold growth.
- Ceramic crock air exchange - Porous walls allow slight airflow, limiting pressure buildup and suppressing unwanted mold formation.
- Water-sealed airtight barrier - A water lock seals the fermenter, blocking oxygen and external spores that cause contamination.
- Maintenance necessity - Water levels in sealed vessels must be monitored to prevent mold growth from trapped moisture and residue.
Capacity and Batch Size Considerations
Ceramic crocks typically range from 1 to 5 gallons, making them suitable for small to medium batch fermenting. Water-sealed fermentation vessels often come in larger capacities, accommodating bigger batch sizes and extended fermentation processes.
- Ceramic Crock Capacity - Usually available in smaller sizes, ideal for home fermenters with limited space.
- Water-Sealed Vessel Size - Can accommodate larger volumes, perfect for commercial or large-scale fermentation.
- Batch Size Flexibility - Water-sealed vessels offer adjustable batch sizes due to their diverse capacity options.
Cost Comparison: Investment and Longevity
Which offers a better cost efficiency: ceramic crocks or water-sealed fermentation vessels? Ceramic crocks generally have a lower initial investment but may require more careful handling to avoid chipping or cracking. Water-sealed fermentation vessels tend to have a higher upfront cost but provide longer durability and a more consistent fermentation environment, reducing replacement frequency.
Related Important Terms
Anaerobic moat lid
Ceramic crocks with anaerobic moat lids create a gravity-sealed water barrier that effectively prevents oxygen and contaminants from entering the fermentation chamber, ensuring optimal anaerobic conditions for fermenting vegetables. This natural airlock system maintains consistent pressure release while preserving the integrity of beneficial microbes, unlike some water-sealed fermentation vessels that may allow slight air exchange or require external airlocks.
Airlock water gutter
Ceramic crocks with water-sealed fermentation vessels feature an airlock water gutter that creates an airtight environment, preventing oxygen and contaminants from entering while allowing gases to escape, essential for anaerobic fermentation. This water barrier maintains consistent fermentation conditions, reducing the risk of spoilage compared to traditional ceramic crocks without a sealed airlock system.
Microclimate brining
Ceramic crocks provide a stable microclimate for fermenting with natural air exchange and moisture retention, enhancing flavor development during brining. Water-sealed fermentation vessels create an anaerobic environment by trapping gases, which prevents oxygen exposure and ensures consistent fermentation results.
Unglazed stoneware porosity
Unglazed stoneware ceramic crocks offer natural porosity that allows for micro-oxygenation during fermentation, enhancing complex flavor development in fermented foods. In contrast, water-sealed fermentation vessels create an anaerobic environment that minimizes oxygen exposure, reducing oxidation but limiting microbial diversity.
Gassing-off phase
Ceramic crocks provide natural breathability that allows carbon dioxide to escape gradually during the gassing-off phase, minimizing pressure buildup and reducing the risk of fermentation spoilage. Water-sealed fermentation vessels create an airtight environment that captures CO2 bubbles in the water seal, offering a visual indicator of fermentation activity while preventing oxygen exposure and contamination.
Mold collar retention
Ceramic crocks provide a traditional mold collar that effectively seals out oxygen and contaminants, promoting anaerobic fermentation while allowing gas to escape. Water-sealed fermentation vessels create an airtight barrier that prevents mold growth by maintaining consistent moisture levels, reducing the risk of surface spoilage during the fermentation process.
Crock burp valve
Ceramic crocks with burp valves provide controlled gas release during fermentation, preventing pressure buildup while maintaining an anaerobic environment essential for lactic acid bacteria activity. Water-sealed fermentation vessels rely on submerged airlocks to block oxygen but require careful monitoring to avoid leaks and contamination risks, whereas burp valves offer easier manual pressure relief without compromising fermentation integrity.
Hydro-lock evaporation loss
Ceramic crocks offer porous walls that allow minimal moisture evaporation, while water-sealed fermentation vessels create a hydro-lock seal that significantly reduces evaporation loss by preventing air exchange. The hydro-lock system maintains consistent humidity and pressure, preserving ferment integrity and minimizing weight loss during prolonged fermentation periods.
Yeast bloom migration
Ceramic crocks provide a porous environment that can encourage natural yeast bloom migration, enhancing microbial diversity during fermentation. Water-sealed fermentation vessels create an anaerobic atmosphere that restricts yeast bloom movement, leading to more controlled fermentation and less oxygen exposure.
Ceramic crock vs Water-sealed fermentation vessel for fermenting. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com