Ceramic jars provide natural insulation and breathability, promoting beneficial microbial growth during pet fermenting, while vacuum fermentation containers create an anaerobic environment that accelerates fermentation and preserves flavor by eliminating oxygen exposure. Choosing between ceramic and vacuum containers depends on desired fermentation speed, flavor development, and ease of use. Ceramic jars offer traditional, slow fermentation ideal for complex flavors, whereas vacuum containers enhance fermentation efficiency and consistency.
Table of Comparison
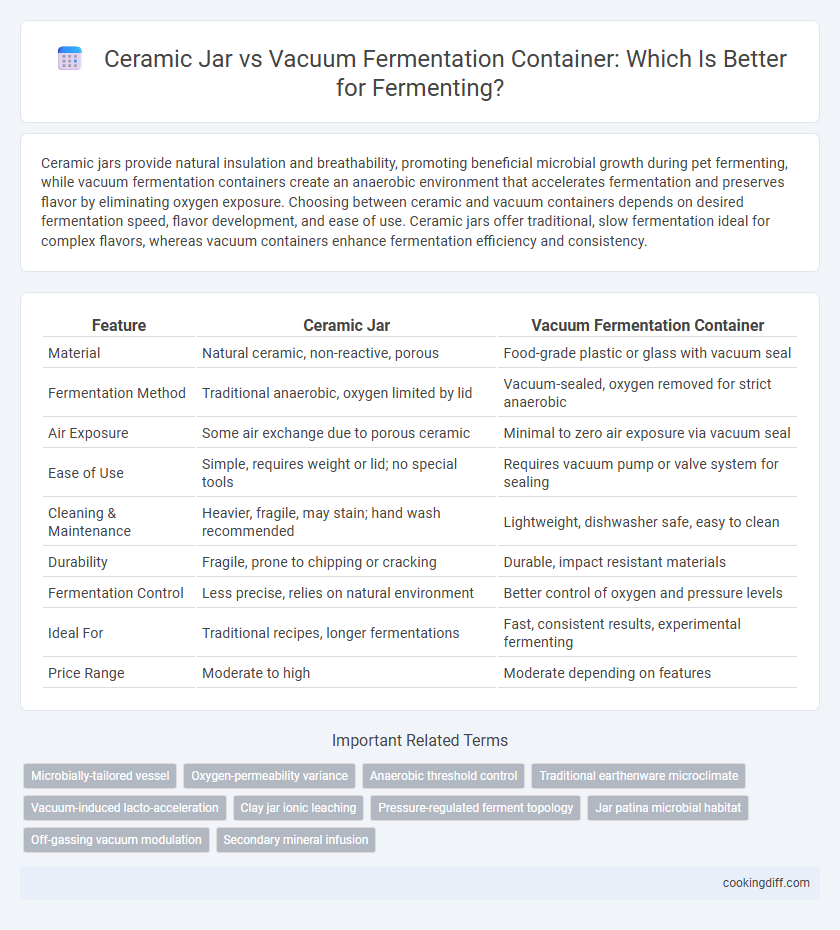
| Feature | Ceramic Jar | Vacuum Fermentation Container |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural ceramic, non-reactive, porous | Food-grade plastic or glass with vacuum seal |
| Fermentation Method | Traditional anaerobic, oxygen limited by lid | Vacuum-sealed, oxygen removed for strict anaerobic |
| Air Exposure | Some air exchange due to porous ceramic | Minimal to zero air exposure via vacuum seal |
| Ease of Use | Simple, requires weight or lid; no special tools | Requires vacuum pump or valve system for sealing |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Heavier, fragile, may stain; hand wash recommended | Lightweight, dishwasher safe, easy to clean |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to chipping or cracking | Durable, impact resistant materials |
| Fermentation Control | Less precise, relies on natural environment | Better control of oxygen and pressure levels |
| Ideal For | Traditional recipes, longer fermentations | Fast, consistent results, experimental fermenting |
| Price Range | Moderate to high | Moderate depending on features |
Introduction to Fermentation Containers
Fermentation containers create optimal environments for beneficial microbes to thrive, influencing flavor and texture. Ceramic jars and vacuum fermentation containers offer distinct advantages in maintaining anaerobic conditions and temperature stability.
- Ceramic jars - Provide natural breathability and resist odors, ideal for traditional fermentation like kimchi or sauerkraut.
- Vacuum fermentation containers - Remove air to minimize oxidation and increase shelf life while preserving vitamin content.
- Material impact - Non-reactive materials prevent contamination and ensure consistent microbial activity during fermentation.
Choosing the right fermentation vessel depends on the fermentation style and desired control over environmental factors.
Overview of Ceramic Jars for Fermentation
| Ceramic jars offer natural breathability and maintain consistent temperature, ideal for slow fermentation processes. Their non-reactive surface prevents contamination and preserves the flavor profile of fermented foods. These jars often feature traditional designs that enhance anaerobic conditions without the need for vacuum sealing mechanisms. |
Vacuum Fermentation Containers Explained
Vacuum fermentation containers create an anaerobic environment by removing oxygen, which accelerates fermentation and enhances flavor development in foods like kimchi and sauerkraut. Unlike ceramic jars that allow some air exchange, vacuum containers reduce oxidation and bacterial contamination, ensuring a more consistent and controlled ferment. This method results in faster fermentation times and improved preservation of nutrients and probiotics.
Material Composition and Safety
Ceramic jars are composed of natural clay fired at high temperatures, making them non-reactive and ideal for long-term fermentation without leaching chemicals into food. They provide a breathable environment that supports anaerobic fermentation while maintaining food safety.
Vacuum fermentation containers are typically made from BPA-free plastic or glass with airtight seals to prevent oxygen exposure, promoting controlled fermentation and reducing contamination risk. Their materials are engineered to withstand pressure changes, ensuring both durability and food-grade safety during the process.
Airflow Control and Oxygen Exposure
Ceramic jars provide moderate airflow control, allowing slight oxygen exposure which can enhance the growth of beneficial aerobic microbes during fermentation. Vacuum fermentation containers create a nearly oxygen-free environment by eliminating air, reducing the risk of spoilage and promoting anaerobic fermentation processes. Choosing between the two depends on the desired fermentation style and microbial activity control.
Flavor Development Differences
How does flavor development differ between ceramic jars and vacuum fermentation containers? Ceramic jars promote slow, consistent fermentation by allowing micro-oxygenation, enhancing complex, earthy flavors. Vacuum fermentation containers reduce oxidation and limit microbial diversity, resulting in cleaner, more controlled flavor profiles.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Ceramic jars offer a straightforward approach to fermenting, requiring minimal setup and easy cleaning due to their non-porous surfaces. Their heavy weight and fragile nature can pose challenges during handling and maintenance.
Vacuum fermentation containers enhance ease of use with airtight seals that prevent oxidation, reducing the need for frequent monitoring and adjustments. Their durable plastic construction is lightweight and dishwasher-safe, simplifying cleaning tasks. The built-in airlock mechanisms prevent contamination, minimizing maintenance efforts compared to traditional ceramic jars.
Durability and Longevity
Ceramic jars offer exceptional durability due to their thick walls and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for long-term fermenting projects. Vacuum fermentation containers, while innovative for maintaining anaerobic conditions, typically consist of plastic components that may degrade faster over time.
- Ceramic Jar Durability - Ceramic materials resist scratches and chemical damage, ensuring they last for many years without compromising the fermentation process.
- Vacuum Container Longevity - Plastic seals and parts in vacuum containers may wear out or crack, reducing their effective lifespan and requiring replacements.
- Maintenance Requirements - Ceramic jars require minimal upkeep, whereas vacuum fermentation containers need regular inspection to maintain airtight seals and prevent failures.
Cost Comparison and Accessibility
Ceramic jars are generally more affordable and widely available for home fermenters compared to vacuum fermentation containers, which tend to be higher priced due to specialized technology. Accessibility for ceramic jars is greater in many regions, making them a popular choice for beginners and casual fermenters.
- Ceramic Jar Cost-Effectiveness - Ceramic jars usually cost less, ranging from $20 to $50, making them budget-friendly for most users.
- Vacuum Container Price - Vacuum fermentation containers can exceed $100, reflecting their advanced air-sealing features and materials.
- Accessibility Differences - Ceramic jars are available in kitchen stores and online globally, whereas vacuum containers are less common and often require specialty retailers.
Related Important Terms
Microbially-tailored vessel
Ceramic jars provide a naturally porous environment that promotes beneficial microbial activity and enhances flavor complexity during fermentation, whereas vacuum fermentation containers create an anaerobic atmosphere that selectively encourages the growth of specific microorganisms, reducing spoilage and preserving desired microbial metabolites. Microbially-tailored vessels like ceramic jars support a diverse microbial ecosystem integral to traditional fermentation, while vacuum containers offer controlled conditions ideal for precision fermentation workflows.
Oxygen-permeability variance
Ceramic jars allow limited oxygen permeability, fostering the growth of beneficial aerobic bacteria and contributing to complex flavor profiles during fermentation. In contrast, vacuum fermentation containers create an anaerobic environment by minimizing oxygen exposure, promoting lactic acid bacteria dominance and resulting in faster, tangier fermentation outcomes.
Anaerobic threshold control
Ceramic jars provide natural breathability that aids in maintaining a balanced anaerobic threshold, while vacuum fermentation containers offer precise control over oxygen levels to prevent aerobic contamination during fermentation. Monitoring the anaerobic environment in vacuum containers enhances consistency in flavor development and reduces spoilage risks compared to ceramic jars.
Traditional earthenware microclimate
Ceramic jars create a unique earthenware microclimate that naturally regulates humidity and temperature, enhancing microbial activity crucial for traditional fermentation processes. In contrast, vacuum fermentation containers prioritize airtight conditions that limit oxygen exposure but may lack the dynamic environmental balance provided by porous ceramic materials.
Vacuum-induced lacto-acceleration
Vacuum fermentation containers enhance lacto-acceleration by reducing oxygen exposure, which promotes the growth of Lactobacillus species and accelerates the fermentation process compared to traditional ceramic jars. The controlled anaerobic environment in vacuum systems optimizes acid production and flavor development, resulting in faster and more consistent fermentation outcomes.
Clay jar ionic leaching
Clay jars used in fermentation can pose a risk of ionic leaching, where trace minerals and ions from the ceramic material may infuse into the ferment, potentially altering flavor and acidity. Vacuum fermentation containers, made from inert materials like stainless steel or food-grade plastic, prevent ionic leaching, ensuring a more controlled and neutral environment for consistent fermentation results.
Pressure-regulated ferment topology
Ceramic jars maintain a naturally stable, anaerobic environment ideal for traditional fermentation but lack precise pressure regulation, which can lead to inconsistent gas release and risk of spoilage. Vacuum fermentation containers utilize pressure-regulated ferment topology to control gas buildup meticulously, optimizing microbial activity and reducing oxidation, thereby enhancing fermentation consistency and flavor development.
Jar patina microbial habitat
Ceramic jars develop a unique patina rich in diverse microbial communities that enhance fermentation by creating a stable, oxygen-controlled environment conducive to robust microbial growth. In contrast, vacuum fermentation containers limit oxygen exposure but lack the porous surface and microbial habitat that ceramic jar patinas naturally cultivate, impacting flavor complexity and fermentation dynamics.
Off-gassing vacuum modulation
Ceramic jars provide natural porosity that allows gradual off-gassing during fermentation, promoting balanced pressure release and flavor development. Vacuum fermentation containers use adjustable vacuum modulation to tightly control off-gassing, preventing oxidation while maintaining an anaerobic environment for precise fermentation results.
Ceramic jar vs vacuum fermentation container for fermenting. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com