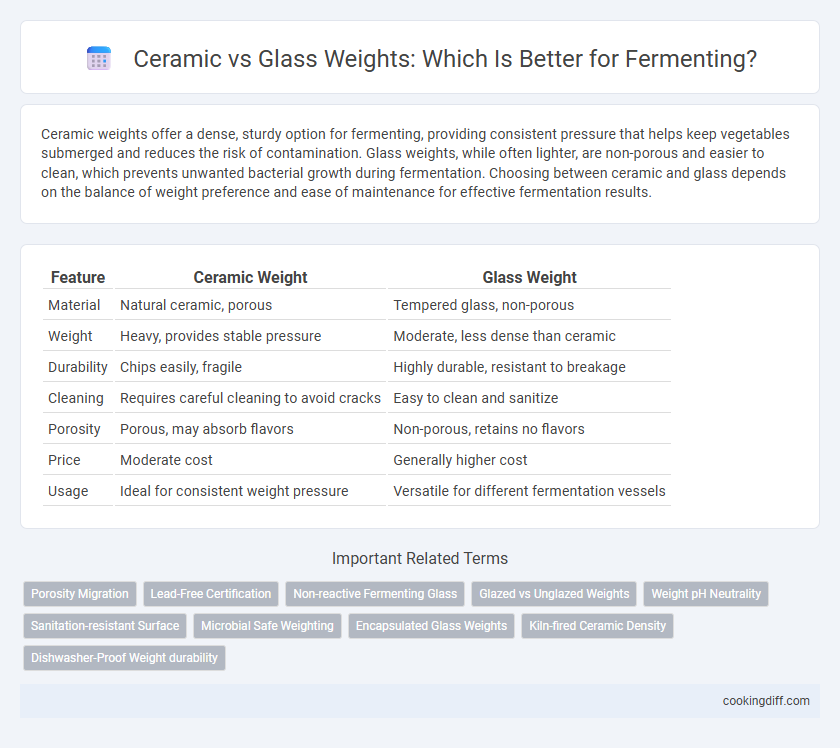
Ceramic weights offer a dense, sturdy option for fermenting, providing consistent pressure that helps keep vegetables submerged and reduces the risk of contamination. Glass weights, while often lighter, are non-porous and easier to clean, which prevents unwanted bacterial growth during fermentation. Choosing between ceramic and glass depends on the balance of weight preference and ease of maintenance for effective fermentation results.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Weight | Glass Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural ceramic, porous | Tempered glass, non-porous |
| Weight | Heavy, provides stable pressure | Moderate, less dense than ceramic |
| Durability | Chips easily, fragile | Highly durable, resistant to breakage |
| Cleaning | Requires careful cleaning to avoid cracks | Easy to clean and sanitize |
| Porosity | Porous, may absorb flavors | Non-porous, retains no flavors |
| Price | Moderate cost | Generally higher cost |
| Usage | Ideal for consistent weight pressure | Versatile for different fermentation vessels |
Introduction to Fermentation Weights
Fermentation weights are essential tools used to keep vegetables submerged in brine, preventing exposure to air and promoting an anaerobic environment. Both ceramic and glass weights serve this purpose effectively but differ in weight, durability, and ease of cleaning.
- Ceramic Weights - Ceramic weights are dense and heavy, providing firm pressure to keep ingredients submerged throughout the fermentation process.
- Glass Weights - Glass weights tend to be lighter but non-porous, making them easy to clean and resistant to absorbing odors or stains.
- Choosing Between Ceramic and Glass - Selecting the right material depends on the type of ferment, vessel size, and preference for weight versus ease of maintenance.
Understanding Ceramic Fermentation Weights
Ceramic fermentation weights provide consistent pressure and are less prone to breakage compared to glass weights, making them ideal for long-term fermenting projects. Their porous nature allows slight air exchange, which can benefit the fermentation process by preventing excess buildup of gases.
- Durability - Ceramic weights are more resistant to chipping and cracking compared to glass.
- Porosity - Ceramic materials allow minimal air permeability, enhancing natural fermentation.
- Weight stability - Ceramic weights maintain consistent pressure due to their dense yet slightly porous structure.
Choosing ceramic fermentation weights can improve fermentation quality and reduce contamination risks over time.
Overview of Glass Fermentation Weights
Glass fermentation weights provide a non-reactive, durable option for pressing down fermenting vegetables, ensuring even submersion and reducing contamination risks. These weights maintain stable acidity and are easy to sanitize compared to ceramic alternatives.
Glass weights are typically heavier than ceramic weights, offering consistent pressure that prevents air exposure during fermentation. Their smooth surface resists staining and odors, enhancing long-term usability and hygiene. Many home fermenters prefer glass for its transparency, allowing visual monitoring of the fermenting process without disturbance.
Material Composition: Ceramic vs Glass
How does the material composition of ceramic compare to glass in terms of weight for fermenting vessels? Ceramic fermenting containers are generally heavier than glass due to their dense clay composition and added mineral content. Glass, made from silica and soda ash, offers a lighter yet durable alternative that resists staining and odor absorption during fermentation.
Weight and Effectiveness in Brine Submersion
Ceramic weights generally offer a heavier, more stable option for fermenting, ensuring consistent brine submersion. Glass weights tend to be lighter but provide ease of handling and effective sealing within fermentation vessels.
- Ceramic weights provide superior mass - Their density helps maintain vegetables submerged under brine, reducing oxidation risks during fermentation.
- Glass weights offer lightweight convenience - Easier to maneuver and clean, making them ideal for small-batch fermenting projects.
- Weight affects fermentation quality - Proper submersion with heavier ceramic weights can lead to more consistent fermentation outcomes by preventing air exposure.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Ceramic fermenting vessels tend to be heavier, which can make handling and cleaning more cumbersome compared to glass containers. However, ceramic's non-porous glazed surface resists staining and odors, simplifying maintenance over time.
Glass fermenting jars are lighter and often have smoother surfaces that facilitate easier rinsing and scrubbing. Their transparent nature allows for quick visual inspection, reducing the need for frequent deep cleaning.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Ceramic fermenting vessels typically offer greater durability due to their thick walls and resistance to chipping compared to glass, which can be more fragile despite being heavier. Glass weights are often lighter inside the fermentation jar, making them easier to handle but potentially less resilient to accidental drops. The longevity of ceramic weights tends to surpass glass since ceramics withstand repeated use and cleaning without scratching or clouding.
Safety and Food-Grade Considerations
Ceramic fermenting weights are food-grade and non-reactive, ensuring safe contact with fermenting foods without leaching harmful substances. Glass weights also provide a non-toxic, inert surface ideal for fermentation, resisting stains and odors while maintaining food safety. Both materials offer durable, safe options, but ceramic weights may chip, affecting cleanliness, whereas glass weights tend to be heavier and more stable for consistent pressure.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Ceramic weights for fermenting tend to be more expensive due to the handcrafted nature and durable materials used, often costing 20-30% more than glass weights. Availability is typically limited to specialty kitchen stores or online retailers, which may affect accessibility for casual fermenters.
Glass weights are generally more affordable and widely available, with prices often under $15, making them a budget-friendly option for home fermentation. Their mass production enables easy sourcing from general kitchen supply stores, enhancing convenience for most consumers.
Related Important Terms
Porosity Migration
Ceramic weights used in fermenting have higher porosity compared to glass weights, which can lead to liquid migration and potential absorption of unwanted flavors or bacteria. Glass weights, being non-porous, prevent porosity migration, ensuring a more stable fermentation environment and reducing contamination risks.
Lead-Free Certification
Ceramic fermenting weights often feature lead-free certification, ensuring safe fermentation without harmful chemical leaching, whereas glass weights are naturally non-toxic but may lack specific certification assurances. Choosing lead-free certified ceramic weights provides reliable food safety compliance crucial for maintaining healthy fermentation environments.
Non-reactive Fermenting Glass
Non-reactive fermenting glass typically weighs less than ceramic fermenting vessels, providing a lighter and more manageable option for home fermenters. Glass's inert properties prevent flavor alteration or chemical reactions during fermentation, making it a preferred choice over heavier ceramic materials that may absorb odors or leach minerals.
Glazed vs Unglazed Weights
Unglazed ceramic fermenting weights tend to be denser and heavier than glazed ones due to their porous structure, which can absorb moisture and add weight over time; glass weights maintain a consistent weight since they are non-porous and inert. Choosing between glazed and unglazed ceramic weights impacts fermentation control, as glazed surfaces are easier to clean and resist bacteria, while unglazed options offer slight moisture absorption that can influence weight and fermentation environment stability.
Weight pH Neutrality
Ceramic fermenting vessels typically weigh more than glass jars, providing added stability during the fermentation process while maintaining pH neutrality to prevent unwanted chemical reactions. Glass containers are lighter and also pH neutral, ensuring no interference with the natural microbial activity essential for optimal fermentation.
Sanitation-resistant Surface
Ceramic weights for fermenting offer a non-porous, sanitation-resistant surface that prevents bacterial buildup and is easy to clean, making them ideal for maintaining a sterile environment. Glass weights are also non-reactive and sanitary but tend to be heavier and more prone to chipping, which can harbor contaminants over time.
Microbial Safe Weighting
Ceramic weights offer a non-reactive, microbial-safe solution for fermenting due to their dense, impermeable surfaces that prevent bacterial contamination and ensure consistent pressure on fermenting substrates. In contrast, glass weights, while also inert and easy to sanitize, are less dense and may require larger sizes to achieve the same pressure, potentially increasing the risk of microbial exposure through more frequent handling.
Encapsulated Glass Weights
Encapsulated glass weights provide a hygienic, non-porous surface ideal for fermenting, preventing contamination and maintaining even pressure on fermenting vegetables or fruits. Ceramic weights, while durable, can be more prone to chipping and porous surfaces that may harbor bacteria, making encapsulated glass weights a superior choice for consistent, safe fermentation results.
Kiln-fired Ceramic Density
Kiln-fired ceramic weights typically exhibit higher density compared to glass weights, providing superior stability during fermenting by resisting shifts and maintaining consistent pressure on fermenting substrates. This increased density enhances temperature retention and minimizes contamination risks, making ceramic weights more effective for precise fermentation control.
Ceramic Weight vs Glass Weight for fermenting. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com