Fermentation crocks provide a traditional, water-sealed environment that naturally maintains anaerobic conditions ideal for fermenting vegetables, ensuring even weight distribution and easy access for monitoring. Anaerobic jars use airtight lids with airlocks to create a controlled, oxygen-free environment, minimizing spoilage risks and allowing convenient, space-saving fermentation. Choosing between a fermentation crock and an anaerobic jar depends on batch size, ease of use, and the specific fermentation style preferred.
Table of Comparison
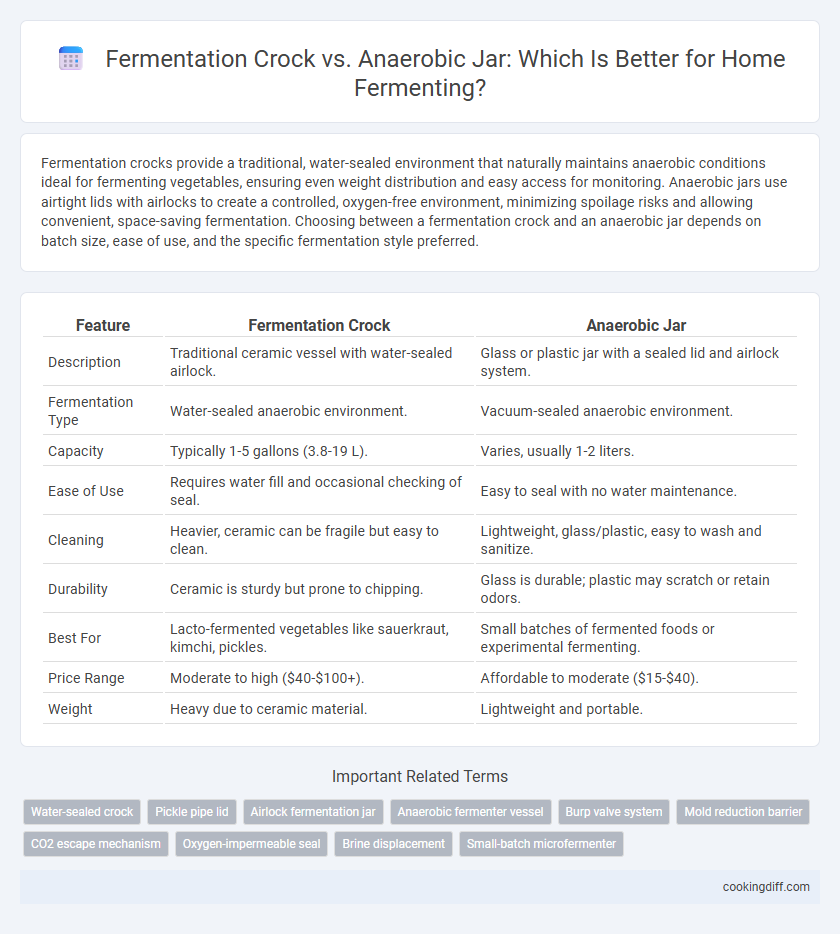
| Feature | Fermentation Crock | Anaerobic Jar |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Traditional ceramic vessel with water-sealed airlock. | Glass or plastic jar with a sealed lid and airlock system. |
| Fermentation Type | Water-sealed anaerobic environment. | Vacuum-sealed anaerobic environment. |
| Capacity | Typically 1-5 gallons (3.8-19 L). | Varies, usually 1-2 liters. |
| Ease of Use | Requires water fill and occasional checking of seal. | Easy to seal with no water maintenance. |
| Cleaning | Heavier, ceramic can be fragile but easy to clean. | Lightweight, glass/plastic, easy to wash and sanitize. |
| Durability | Ceramic is sturdy but prone to chipping. | Glass is durable; plastic may scratch or retain odors. |
| Best For | Lacto-fermented vegetables like sauerkraut, kimchi, pickles. | Small batches of fermented foods or experimental fermenting. |
| Price Range | Moderate to high ($40-$100+). | Affordable to moderate ($15-$40). |
| Weight | Heavy due to ceramic material. | Lightweight and portable. |
Overview: Fermentation Crocks vs Anaerobic Jars
Fermentation crocks provide a traditional, water-sealed environment that allows gases to escape while preventing oxygen from entering, ideal for preserving the natural flavors of fermented vegetables. Anaerobic jars create a completely oxygen-free atmosphere using airtight seals and gas traps, which can speed up the fermentation process and reduce spoilage risks.
Fermentation crocks are typically made of ceramic or stoneware, featuring a water-lock system that maintains an anaerobic environment through gravity and water barriers. Anaerobic jars often include silicone gaskets and airlocks that release carbon dioxide without allowing oxygen back inside, enhancing control over fermentation conditions. Both tools support lactic acid fermentation but differ in ease of cleaning, portability, and fermentation speed, with crocks favored for traditional fermentation and jars preferred for more controlled, faster results.
How Each Vessel Supports Anaerobic Fermentation
| Fermentation Crock | Uses water-sealed airlock system to create an oxygen-free environment, allowing gases to escape while preventing air entry, which is essential for successful anaerobic fermentation of vegetables and sauerkraut. |
| Anaerobic Jar | Features a fully sealed lid with an airlock or vacuum mechanism, maintaining strict oxygen exclusion that supports consistent lactic acid bacteria growth for controlled anaerobic fermentation of kimchi and pickles. |
Pros and Cons: Fermentation Crocks
What are the pros and cons of using a fermentation crock for fermenting? Fermentation crocks provide a traditional, oxygen-limiting environment with water-sealed airlocks that prevent mold growth and encourage beneficial bacteria, making them ideal for long-term fermentation. However, their large size can be bulky for small kitchens, and cleaning the heavy ceramic material can be more labor-intensive compared to anaerobic jars.
Pros and Cons: Anaerobic Jars
Anaerobic jars create a sealed environment ideal for preventing mold growth during fermentation but can be more expensive and less spacious compared to fermentation crocks. They offer precise oxygen control, which is beneficial for consistent fermentation results.
- Effective Oxygen Exclusion - Anaerobic jars maintain an oxygen-free environment that reduces spoilage and promotes lactic acid bacteria activity.
- Limited Capacity - These jars typically hold smaller batches, making them less suitable for large volume fermenting.
- Higher Cost - Anaerobic jars are generally more expensive than traditional fermentation crocks, impacting budget-conscious fermenters.
Comparing Oxygen Control in Both Vessels
Fermentation crocks utilize water-sealed airlocks that create an anaerobic environment by preventing oxygen from entering while allowing gases to escape. Anaerobic jars employ airtight lids with one-way valves to strictly control oxygen exposure, ensuring minimal air contact during fermentation.
- Fermentation crock - Maintains oxygen control through a water seal, creating a barrier that blocks air but allows carbon dioxide to escape.
- Anaerobic jar - Provides precise oxygen control with airtight seals and one-way valves that prevent ambient air from entering the vessel.
- Oxygen exposure impact - Both vessels reduce oxygen exposure, but anaerobic jars typically offer more consistent and measurable oxygen control for sensitive fermentations.
Choosing between a fermentation crock and an anaerobic jar depends on the desired level of oxygen control and the type of fermentation process.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Fermentation crocks offer straightforward setup and require minimal daily maintenance due to their built-in water seal that prevents oxygen entry while allowing gases to escape, making them ideal for beginners. Anaerobic jars provide a controlled oxygen-free environment using airtight lids and sometimes oxygen absorbers, but they often demand more careful monitoring and cleaning to avoid mold growth. Both options support successful fermentation, but crocks are generally favored for their ease of use and low upkeep.
Batch Size and Fermentation Volume Considerations
Fermentation crocks typically offer larger batch sizes, accommodating up to several liters, making them ideal for bulk fermenting vegetables. Anaerobic jars are designed for smaller fermentation volumes, usually between 1 to 2 liters, suitable for experimental or small-scale batches. Choosing between the two depends on the desired quantity, with crocks favoring volume and jars providing compact, controlled environments.
Flavor and Texture Differences
Fermentation crocks promote natural airflow while minimizing oxygen exposure, resulting in complex, tangy flavors and a crisp texture due to controlled aerobic conditions. Anaerobic jars create a fully oxygen-free environment, often producing milder flavors and softer textures because of strict anaerobic fermentation.
Using a crock typically enhances the development of beneficial wild yeasts and bacteria, intensifying depth in flavor and maintaining crunchiness in pickled vegetables. Anaerobic jars favor lactic acid bacteria dominance, leading to smoother, more uniform fermentation with less textural variation.
Cost and Availability
Fermentation crocks generally come with a higher upfront cost but offer long-term durability for consistent fermenting projects. Anaerobic jars are typically more affordable and widely available, making them accessible for beginners and casual fermenters.
- Fermentation Crock Cost - Usually priced between $50 to $150, depending on size and material quality.
- Anaerobic Jar Cost - Often available for under $40, making them budget-friendly options.
- Availability - Anaerobic jars are commonly found in online stores and local kitchenware shops, while fermentation crocks may require specialty retailers or online purchase.
Related Important Terms
Water-sealed crock
Water-sealed fermentation crocks provide an airtight barrier by using a water moat that traps gases while preventing oxygen and contaminants from entering, creating an ideal anaerobic environment for fermenting vegetables. Unlike anaerobic jars with rubber gaskets, water-sealed crocks offer more consistent pressure regulation and traditional craftsmanship favored by fermenting enthusiasts for natural lacto-fermentation processes.
Pickle pipe lid
Fermentation crocks with Pickle Pipe lids provide an anaerobic environment by allowing gas to escape while preventing air from entering, crucial for consistent lactic acid fermentation in vegetables. Compared to traditional anaerobic jars, crocks with Pickle Pipes reduce mold risk and maintain optimal pressure, enhancing the safety and flavor profile of fermented pickles.
Airlock fermentation jar
Airlock fermentation jars provide a controlled anaerobic environment that minimizes oxygen exposure, reducing the risk of mold and spoilage during fermentation. Compared to fermentation crocks, airlock jars offer a precise seal with a water or silicone barrier that allows gas release while maintaining an airtight environment, enhancing the consistency and safety of fermenting vegetables and beverages.
Anaerobic fermenter vessel
Anaerobic fermenter vessels create an oxygen-free environment essential for precision-controlled fermentation, preventing mold growth and ensuring consistent lactic acid bacteria proliferation. These jars typically feature airtight seals and one-way airlocks that release carbon dioxide while blocking oxygen, optimizing conditions for fermenting vegetables and kimchi.
Burp valve system
Fermentation crocks with built-in burp valve systems offer optimal anaerobic conditions by allowing carbon dioxide to escape while preventing oxygen ingress, ensuring consistent fermentation quality. Anaerobic jars may require manual burping or additional equipment to achieve similar gas exchange control, making crocks with integrated valves more user-friendly and reliable for maintaining ideal fermenting environments.
Mold reduction barrier
Fermentation crocks offer a physical water-seal barrier that effectively reduces mold growth by preventing air from entering the fermenting environment, creating an anaerobic condition ideal for preserving lactic acid bacteria. Anaerobic jars utilize airtight lids with rubber gaskets and airlocks to minimize oxygen exposure, but fermentation crocks provide a more consistent mold reduction barrier through their traditional water-seal design.
CO2 escape mechanism
Fermentation crocks utilize an open water-seal system that allows CO2 to escape through a moat-like barrier, preventing oxygen exposure while maintaining an anaerobic environment. Anaerobic jars rely on airtight lids with one-way valves or gas release plugs to expel CO2 and prevent oxygen from entering, ensuring precise control over fermentation gas exchange.
Oxygen-impermeable seal
Fermentation crocks provide a traditional water-seal lid that creates an anaerobic environment by allowing gases to escape without letting oxygen in, preserving the oxygen-impermeable seal crucial for lactic acid fermentation. Anaerobic jars use rubber gaskets and clamps to achieve a tighter oxygen-impermeable seal, offering more reliable control over oxygen exposure and preventing contamination during fermentation.
Brine displacement
Fermentation crocks utilize a water-sealed moat to create an anaerobic environment through brine displacement, effectively preventing oxygen exposure and promoting lactic acid bacteria growth. Anaerobic jars rely on airtight seals and sometimes chemical oxygen absorbers but may not provide the same natural brine displacement system critical for traditional vegetable fermentation.
Fermentation crock vs anaerobic jar for fermenting Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com