Plastic containers offer a lightweight and affordable option for fermenting pet food, but they may absorb odors and are prone to scratching, which can harbor bacteria over time. Fermentation chambers provide a controlled environment with consistent temperature and humidity, enhancing the safety and quality of the fermentation process. Choosing the right vessel impacts the flavor development and microbiological stability of fermented pet products.
Table of Comparison
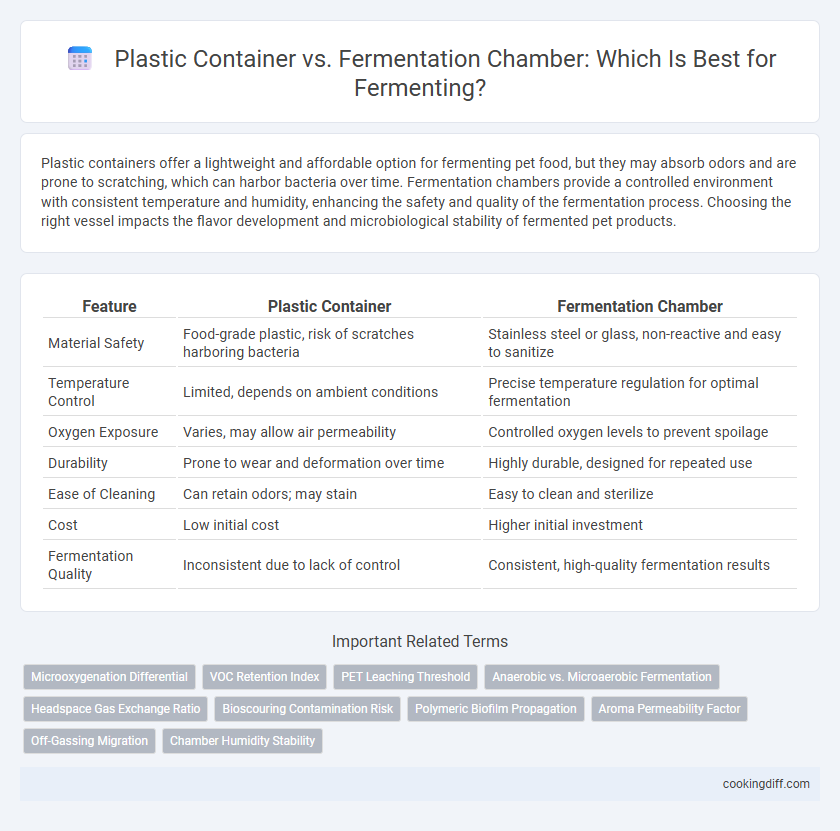
| Feature | Plastic Container | Fermentation Chamber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Safety | Food-grade plastic, risk of scratches harboring bacteria | Stainless steel or glass, non-reactive and easy to sanitize |
| Temperature Control | Limited, depends on ambient conditions | Precise temperature regulation for optimal fermentation |
| Oxygen Exposure | Varies, may allow air permeability | Controlled oxygen levels to prevent spoilage |
| Durability | Prone to wear and deformation over time | Highly durable, designed for repeated use |
| Ease of Cleaning | Can retain odors; may stain | Easy to clean and sterilize |
| Cost | Low initial cost | Higher initial investment |
| Fermentation Quality | Inconsistent due to lack of control | Consistent, high-quality fermentation results |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Fermentation Vessel
Plastic containers and fermentation chambers serve distinct purposes in the fermentation process, affecting flavor and safety. Selecting the optimal vessel depends on factors like material permeability, ease of cleaning, and temperature consistency.
Plastic containers are lightweight, affordable, and resist breakage but may absorb odors and harbor bacteria if scratched. Fermentation chambers offer precise temperature control and low oxygen permeability, essential for consistent fermentation quality. Proper vessel choice ensures optimal microbial activity and product safety during fermentation.
Plastic Containers: Overview and Popularity in Fermentation
Plastic containers are widely used in fermentation due to their lightweight, durable, and affordable nature, making them accessible for both home fermenters and commercial producers. Food-grade plastic containers with airtight seals reduce the risk of contamination and allow easy monitoring of the fermentation process.
Popular plastic materials for fermentation include high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene (PP), which resist chemical interactions and maintain structural integrity under acidic conditions. Despite some concerns about plastic leaching, properly certified fermentation-grade plastics provide a safe and practical environment for fermenting vegetables, kombucha, and other products.
Fermentation Chambers: Design and Functionality
Fermentation chambers offer precise temperature and humidity control essential for consistent fermenting outcomes, unlike plastic containers that lack such regulation. Their insulated design promotes an optimal anaerobic environment reducing contamination risks during fermentation.
- Temperature regulation - Fermentation chambers maintain stable temperatures critical for microbial activity and flavor development.
- Humidity control - These chambers provide adjustable humidity levels to prevent drying or sogginess of fermenting products.
- Material and sealing - High-quality insulation and airtight seals in fermentation chambers minimize oxygen exposure and contamination.
Airflow and Oxygen Control: Comparing Both Options
Plastic containers often offer limited airflow and insufficient oxygen control, which can impact the fermentation process by allowing unwanted air exposure or trapping excess gases. In contrast, fermentation chambers typically feature adjustable ventilation systems designed to maintain optimal oxygen levels and promote consistent airflow.
Effective oxygen control in fermentation chambers supports the growth of beneficial microorganisms while minimizing contamination risks. Plastic containers may require additional modifications to achieve similar airflow control, making them less ideal for precise fermentation environments.
Temperature Stability: Plastic Container vs Fermentation Chamber
| Container Type | Temperature Stability |
|---|---|
| Plastic Container | Plastic containers have limited insulation properties, causing greater temperature fluctuations that can affect fermentation consistency and microbial activity. |
| Fermentation Chamber | Fermentation chambers provide controlled temperature regulation with stable environments, optimizing yeast and bacterial growth for consistent fermentation results. |
Contamination Risks: Material and Sanitation Differences
Plastic containers pose higher contamination risks in fermentation due to their porous surfaces that harbor bacteria and are harder to sanitize effectively. Fermentation chambers, often made from stainless steel or glass, provide non-porous surfaces that resist microbial growth and allow thorough cleaning. Proper sanitation protocols are crucial for both materials, but fermentation chambers inherently offer better protection against contamination during the fermentation process.
Flavor Development: Impact of Vessel Choice
Choosing between a plastic container and a fermentation chamber significantly influences the flavor development during fermentation. Materials and environmental control affect microbial activity and flavor complexity.
- Plastic containers may impart off-flavors - Some plastics can leach chemicals or retain odors that alter the ferment's taste.
- Fermentation chambers provide stable conditions - Controlled temperature and humidity promote consistent microbial growth and richer flavor profiles.
- Surface interactions affect flavor - Non-porous plastic lacks the micro-oxygenation that wooden or specialized chambers offer, impacting fermentation depth.
Using a fermentation chamber generally results in more nuanced and desirable flavor development than standard plastic containers.
Durability and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Which lasts longer for fermenting: a plastic container or a fermentation chamber? Fermentation chambers, typically made from stainless steel or heavy-duty materials, offer superior durability and resist wear from acidic fermenting agents better than plastic containers. Plastic containers, while lightweight and affordable, tend to degrade, stain, and retain odors over time, reducing their longevity for repeated fermentation use.
Cost Efficiency: Budget Considerations for Fermenters
Plastic containers offer a lower initial investment compared to specialized fermentation chambers, making them accessible for beginners. However, fermentation chambers provide better temperature control, potentially reducing energy costs over time.
- Lower upfront cost - Plastic containers are inexpensive and widely available, ideal for tight budgets.
- Energy efficiency - Fermentation chambers maintain consistent temperatures, minimizing electricity usage.
- Long-term durability - Fermentation chambers tend to last longer, lowering replacement frequency and overall expenses.
Related Important Terms
Microoxygenation Differential
Plastic containers allow limited microoxygenation during fermentation, which can affect flavor development but risk oxidation if not properly sealed. Fermentation chambers offer more controlled microoxygenation, ensuring consistent anaerobic conditions that promote optimal microbial activity and prevent spoilage.
VOC Retention Index
Fermentation chambers made from food-grade plastic often exhibit variable VOC Retention Index values due to material porosity, which can absorb or release volatile organic compounds, affecting flavor profiles. In contrast, specialized fermentation chambers constructed from glass or stainless steel maintain a stable VOC Retention Index, preserving the integrity and consistency of aromatic compounds during fermentation.
PET Leaching Threshold
Plastic containers, especially those made from PET, pose a risk of leaching harmful chemicals into fermenting foods when exposed to acidic conditions and extended fermentation times, potentially exceeding safe PET leaching thresholds. Fermentation chambers made from food-grade stainless steel or glass offer safer alternatives that maintain product integrity by preventing plastic contaminant exposure.
Anaerobic vs. Microaerobic Fermentation
Plastic containers designed for fermentation create an anaerobic environment essential for lactic acid fermentation, effectively inhibiting oxygen exposure that could spoil the batch. Fermentation chambers with controlled airflow enable microaerobic conditions, facilitating processes like sourdough starter development where limited oxygen enhances yeast and bacterial activity.
Headspace Gas Exchange Ratio
Plastic containers typically offer limited gas permeability, resulting in a lower headspace gas exchange ratio that can trap carbon dioxide during fermentation, potentially causing off-flavors or fermentation stalls. Fermentation chambers, designed with controlled ventilation or gas exchange systems, optimize the headspace gas exchange ratio, promoting balanced oxygen and carbon dioxide levels essential for consistent microbial activity and improved fermentation quality.
Bioscouring Contamination Risk
Plastic containers often pose a higher bioscouring contamination risk during fermentation due to their porous surfaces that can harbor unwanted microbes, whereas fermentation chambers made from food-grade stainless steel or glass provide a more hygienic environment by minimizing microbial growth and ensuring better temperature control. Using fermentation chambers reduces contamination risks and enhances bioscouring efficiency in processes such as textile treatment or food fermentation.
Polymeric Biofilm Propagation
Plastic containers often hinder polymeric biofilm propagation due to their smooth, non-porous surfaces that limit microbial adhesion necessary for fermentation processes. Fermentation chambers made from porous or bio-compatible materials enhance microbial colonization, promoting robust polymeric biofilm development critical for efficient fermentation.
Aroma Permeability Factor
Plastic containers often have limited aroma permeability, which can trap unwanted odors and affect the fermentation environment. Fermentation chambers, designed with controlled ventilation and breathable materials, enhance aroma permeability, promoting optimal microbial activity and consistent flavor development.
Off-Gassing Migration
Plastic containers may release harmful chemicals through off-gassing and migration during fermentation, potentially contaminating the product and altering its flavor profile. Fermentation chambers made from inert materials such as glass or stainless steel minimize chemical migration, ensuring a safer and purer fermentation environment.
Plastic container vs fermentation camber for fermenting Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com