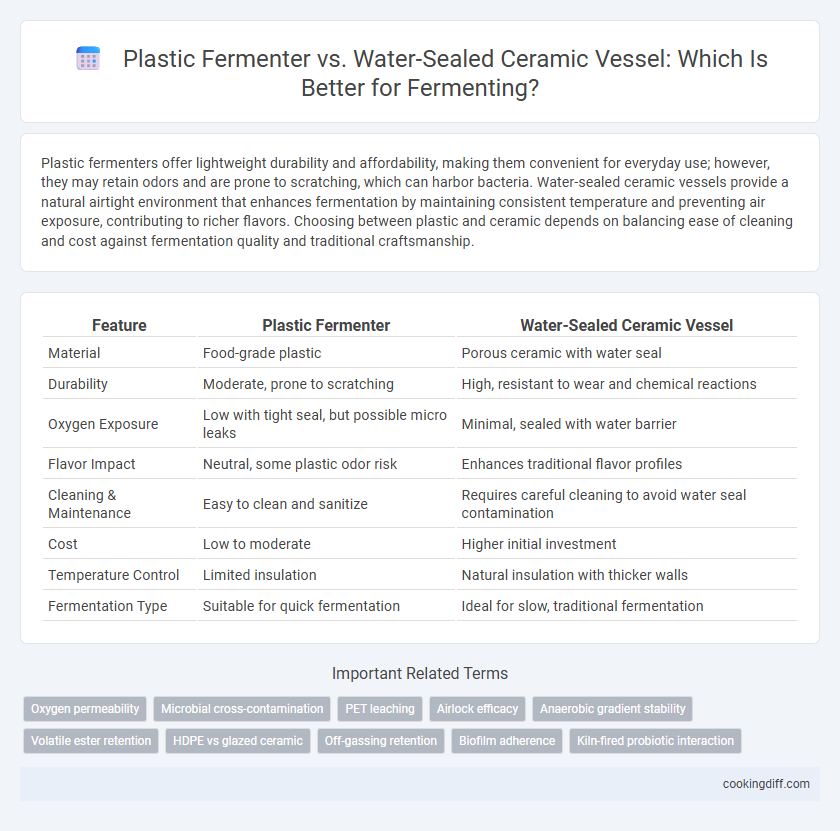
Plastic fermenters offer lightweight durability and affordability, making them convenient for everyday use; however, they may retain odors and are prone to scratching, which can harbor bacteria. Water-sealed ceramic vessels provide a natural airtight environment that enhances fermentation by maintaining consistent temperature and preventing air exposure, contributing to richer flavors. Choosing between plastic and ceramic depends on balancing ease of cleaning and cost against fermentation quality and traditional craftsmanship.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plastic Fermenter | Water-Sealed Ceramic Vessel |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Food-grade plastic | Porous ceramic with water seal |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to scratching | High, resistant to wear and chemical reactions |
| Oxygen Exposure | Low with tight seal, but possible micro leaks | Minimal, sealed with water barrier |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral, some plastic odor risk | Enhances traditional flavor profiles |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Easy to clean and sanitize | Requires careful cleaning to avoid water seal contamination |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Higher initial investment |
| Temperature Control | Limited insulation | Natural insulation with thicker walls |
| Fermentation Type | Suitable for quick fermentation | Ideal for slow, traditional fermentation |
Understanding Plastic Fermenters: Pros and Cons
| Plastic Fermenters Advantages | Lightweight, affordable, resistant to breakage, and often equipped with airlocks for effective fermentation control. |
| Plastic Fermenters Disadvantages | Prone to scratches that can harbor bacteria, possible chemical leaching, and less durable compared to ceramic vessels. |
| Comparison to Water-Sealed Ceramic Vessels | Plastic fermenters offer convenience and lower cost, while ceramic vessels provide natural temperature regulation and a neutral fermentation environment. |
Water-Sealed Ceramic Vessels: Traditional Fermentation Benefits
Why choose water-sealed ceramic vessels over plastic fermenters for fermentation? Water-sealed ceramic vessels provide a stable, oxygen-limiting environment that enhances microbial activity and preserves flavor integrity. Their natural porous composition supports consistent temperature regulation and reduces contamination risk compared to plastic fermenters.
Material Safety and Food-Grade Concerns
Plastic fermenters are often made from food-grade materials like HDPE or PET, but concerns about chemical leaching and microplastics can arise, especially with prolonged fermentation or high acidity levels. Water-sealed ceramic vessels offer a non-reactive, chemical-free environment that prevents contamination and preserves the natural flavor profile of fermented foods.
Food-grade certification and BPA-free labels are crucial when selecting plastic fermenters to ensure safety and compliance with health standards. Ceramic vessels, being naturally inert and durable, eliminate risks linked to plasticizers and provide better long-term food safety for fermentation processes.
Oxygen Exposure: How Each Fermenter Manages Airflow
Plastic fermenters typically allow more oxygen exposure due to their less airtight seals, affecting the fermentation process by increasing the risk of oxidation. Water-sealed ceramic vessels create a natural barrier against oxygen, maintaining an anaerobic environment crucial for controlled fermentation.
- Plastic fermenter oxygen exposure - Generally higher due to flexible lids and gasket seals that can allow micro-air leaks.
- Water-sealed ceramic vessel airflow - Uses a water lock system that effectively prevents oxygen from entering while allowing CO2 to escape.
- Impact on fermentation - Higher oxygen levels in plastic fermenters can lead to unwanted aerobic microbial growth, whereas ceramic vessels reduce this risk.
Flavor Development: Plastic vs Ceramic Impact
Plastic fermenters provide a neutral environment with minimal oxygen interaction, often preserving the raw flavors but potentially limiting complex flavor development during fermentation. Water-sealed ceramic vessels create a micro-oxygenation effect that enhances microbial activity and encourages deeper, richer flavor profiles through subtle oxidation. Ceramic's porous nature also allows for beneficial fermentation gases to interact with the brew, resulting in a more nuanced and aromatic final product compared to the inert qualities of plastic.
Cleaning and Maintenance Comparison
Plastic fermenters are lightweight and easy to handle, but they can retain odors and stains from previous batches, requiring thorough scrubbing and frequent replacement to ensure hygiene. Their surface can be prone to scratches, which may harbor bacteria if not cleaned properly.
Water-sealed ceramic vessels offer natural antimicrobial properties and do not absorb flavors, simplifying cleaning with just water and mild detergents. However, they are heavier and more fragile, necessitating careful handling and regular inspection for cracks to maintain a sanitary environment.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Plastic fermenters offer lightweight and impact-resistant advantages but tend to degrade faster due to chemical absorption and micro-scratches. Water-sealed ceramic vessels, while heavier and more fragile, provide superior longevity with their inert, non-porous surfaces that resist wear and contamination over decades.
- Resistance to Chemicals - Ceramic vessels resist acidic and fermenting chemicals better than plastic, preventing material breakdown.
- Physical Durability - Plastic fermenters withstand accidental drops without shattering, unlike ceramic which is prone to cracks and chips.
- Lifespan - Ceramic vessels can last for decades with proper care, whereas plastic fermenters generally require replacement after a few years.
The choice depends on balancing long-term durability with handling and maintenance preferences during fermentation processes.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Replacement
Plastic fermenters offer a lower initial investment compared to water-sealed ceramic vessels, making them attractive for beginners and small-scale fermenters. However, plastic vessels may require more frequent replacements due to wear and potential contamination compared to the durability of ceramic alternatives.
- Initial Cost Advantage - Plastic fermenters are typically cheaper upfront, often costing 30-50% less than ceramic vessels.
- Longevity and Replacement - Ceramic vessels have a longer lifespan, reducing the frequency and cost of replacements over time.
- Maintenance Considerations - Plastic fermenters can degrade with repeated use and cleaning, increasing replacement costs despite lower initial prices.
Suitability for Different Fermented Foods
Plastic fermenters offer durability and ease of cleaning, making them ideal for fermenting foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, and vegetables that require airtight environments. Water-sealed ceramic vessels provide natural temperature regulation and micro-oxygenation, which is beneficial for fermenting traditional foods such as sourdough starters, miso, and natto. The choice between these fermenters depends on the specific fermentation needs, with plastic suited for quicker, high-acid ferments and ceramic vessels preferred for long-term, slow fermentation processes.
Related Important Terms
Oxygen permeability
Plastic fermenters exhibit higher oxygen permeability compared to water-sealed ceramic vessels, increasing the risk of unwanted oxidation during fermentation. Water-sealed ceramic vessels create an anaerobic environment by minimizing oxygen exposure, which helps preserve flavor integrity and prevent spoilage.
Microbial cross-contamination
Plastic fermenters pose a higher risk of microbial cross-contamination due to their porous surfaces and potential for micro-scratches that harbor bacteria, whereas water-sealed ceramic vessels create an anaerobic environment with a natural barrier that significantly reduces contamination risks. Ceramic fermenters also offer superior chemical inertness and ease of sterilization, enhancing microbial purity during fermentation processes.
PET leaching
Plastic fermenters, especially those made from PET, pose a risk of chemical leaching during fermentation, potentially contaminating the product with harmful substances such as antimony and phthalates. Water-sealed ceramic vessels offer a safer alternative by providing an inert, non-toxic environment that prevents leaching and preserves the purity and flavor profile of the fermenting contents.
Airlock efficacy
Plastic fermenters feature integrated airlocks that provide consistent, reliable gas exchange and minimize contamination risk during fermentation. Water-sealed ceramic vessels rely on a liquid barrier airlock, which can be prone to evaporation and contamination, potentially compromising the anaerobic environment necessary for optimal fermentation.
Anaerobic gradient stability
Plastic fermenters often provide less anaerobic gradient stability due to their permeability to oxygen and potential for micro-leaks, which can disrupt the controlled fermentation environment. Water-sealed ceramic vessels maintain a more consistent anaerobic environment by creating a physical barrier with water traps, effectively preventing oxygen infiltration and ensuring stable fermentation conditions.
Volatile ester retention
Plastic fermenters often exhibit lower volatile ester retention due to their porous surfaces allowing ester evaporation, whereas water-sealed ceramic vessels provide a more airtight environment that preserves these aromatic compounds effectively. The ceramic's natural rigidity and impermeability create optimal fermentation conditions, enhancing ester concentration and overall flavor profile.
HDPE vs glazed ceramic
HDPE plastic fermenters offer lightweight durability and chemical resistance, making them ideal for consistent fermentation without risk of contamination, while glazed ceramic vessels provide natural breathability and temperature stability, enhancing flavor complexity during fermentation. The non-porous surface of glazed ceramic prevents microbial buildup unlike some plastics, but HDPE's resistance to cracking and impact makes it more practical for large-scale or mobile fermenting setups.
Off-gassing retention
Plastic fermenters often trap off-gassing byproducts like carbon dioxide due to limited permeability, which can lead to off-flavors and pressure build-up during fermentation. Water-sealed ceramic vessels enable controlled off-gassing through their porous material and water seal, reducing retention of undesired gases and enhancing flavor profiles.
Biofilm adherence
Plastic fermenters often promote greater biofilm adherence due to their porous surfaces, increasing the risk of contamination and affecting fermentation quality. Water-sealed ceramic vessels offer smoother, non-porous surfaces that inhibit biofilm formation, ensuring a cleaner environment for consistent fermentation results.
Plastic fermenter vs Water-sealed ceramic vessel for fermenting. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com