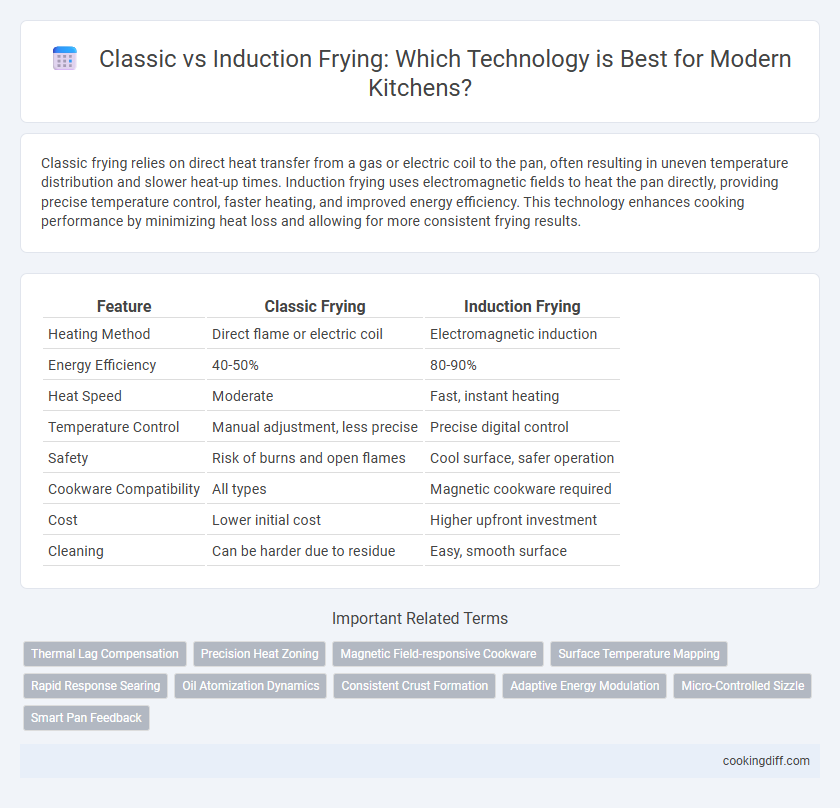
Classic frying relies on direct heat transfer from a gas or electric coil to the pan, often resulting in uneven temperature distribution and slower heat-up times. Induction frying uses electromagnetic fields to heat the pan directly, providing precise temperature control, faster heating, and improved energy efficiency. This technology enhances cooking performance by minimizing heat loss and allowing for more consistent frying results.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Classic Frying | Induction Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct flame or electric coil | Electromagnetic induction |
| Energy Efficiency | 40-50% | 80-90% |
| Heat Speed | Moderate | Fast, instant heating |
| Temperature Control | Manual adjustment, less precise | Precise digital control |
| Safety | Risk of burns and open flames | Cool surface, safer operation |
| Cookware Compatibility | All types | Magnetic cookware required |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Cleaning | Can be harder due to residue | Easy, smooth surface |
Introduction to Frying Technologies
Classic frying relies on direct heat transfer from a gas flame or electric coil to the cooking pan, which can lead to uneven temperature distribution and slower heat-up times. Induction frying uses electromagnetic fields to directly heat the pan, providing faster and more precise temperature control.
Induction technology improves energy efficiency by reducing heat loss and offers enhanced safety with cooler cooktop surfaces. Traditional frying methods, while simpler, often consume more energy and pose a higher risk of overheating and burns.
Classic Frying: Traditional Methods Explained
Classic frying relies on direct heat transfer from gas or electric stovetops to the pan, providing consistent high temperatures essential for browning and crisping foods. This traditional method allows precise control over heat levels, making it ideal for a variety of frying techniques like sauteing, deep-frying, and pan-frying.
Induction frying, in contrast, uses electromagnetic fields to heat the pan directly, resulting in faster heating and improved energy efficiency. However, classic frying remains preferred in many kitchens for its simplicity, compatibility with all cookware types, and tactile temperature management.
Induction Frying: Modern Approach Overview
Induction frying uses electromagnetic fields to heat cookware directly, offering faster and more efficient temperature control compared to classic frying methods that rely on gas or electric stovetops. This modern approach minimizes energy loss and provides precise heat adjustments, enhancing cooking performance and safety.
- Energy Efficiency - Induction frying transfers energy directly to the pan, reducing heat waste and lowering overall energy consumption.
- Temperature Precision - The electromagnetic control allows for rapid temperature changes, enabling more consistent frying results.
- Safety Features - Induction cooktops remain cool to the touch except under the cookware, reducing burn risks and enhancing kitchen safety.
Heat Control and Temperature Precision
Classic frying relies on direct heat transfer from a gas or electric burner, which often results in uneven heat distribution and slower response to temperature adjustments. Induction frying uses electromagnetic fields to heat the pan directly, offering superior heat control and rapid temperature precision adjustments. This technology enhances cooking accuracy, reduces energy waste, and minimizes the risk of overheating or burning food during frying.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Classic frying methods rely on gas or electric stovetops that often lose heat to the surrounding environment, resulting in lower energy efficiency. Induction frying technology uses electromagnetic fields to directly heat the cookware, achieving up to 90% energy efficiency compared to approximately 40-55% for traditional methods. Energy savings from induction frying reduce cooking time and electricity consumption, making it a more eco-friendly and cost-effective option for modern kitchens.
Safety Features and Considerations
Classic frying uses open flames or electric coils, which increases the risk of burns and fire hazards due to exposed heat sources. Induction frying provides a safer alternative by utilizing electromagnetic fields to directly heat the pan, reducing surface temperatures and minimizing accidental contact injuries.
- Heat Control Precision - Induction frying offers precise temperature adjustments, preventing overheating and reducing fire risks.
- Surface Temperature - Classic frying surfaces remain hot for longer periods, posing greater burn hazards compared to induction cooktops.
- Automatic Shutoff - Many induction frying systems feature automatic shutoff sensors that activate when pans are removed or overheating occurs, enhancing safety.
Cookware Compatibility: Classic vs Induction
How does cookware compatibility differ between classic frying and induction frying technologies? Classic frying pans work with almost any heat source, including gas and electric stoves, offering broad versatility. Induction frying requires magnetic cookware, such as cast iron or stainless steel with a ferrous base, to function efficiently and deliver precise temperature control.
Cooking Results: Taste, Texture, and Consistency
| Frying Method | Taste | Texture | Consistency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classic Frying | Produces rich, deep flavors due to prolonged oil heating and Maillard reactions. | Generates a crispy exterior but may result in uneven cooking with occasional sogginess. | Temperature fluctuations cause inconsistent results across batches. |
| Induction Frying | Enhances purity of taste by precise temperature control, reducing burnt flavors. | Delivers uniform crispiness and retains moisture effectively. | Maintains stable heat levels, ensuring consistent cooking outcomes every time. |
Environmental Impact of Frying Methods
Classic frying typically uses gas or electric stoves, which result in higher energy consumption and greater carbon emissions compared to induction frying. Induction frying employs electromagnetic fields to directly heat cookware, leading to improved energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
- Energy Efficiency - Induction frying transfers heat more effectively, reducing wasted energy.
- Carbon Emissions - Classic frying often relies on fossil fuels, increasing greenhouse gas output.
- Heat Waste - Induction frying minimizes ambient heat release, lowering overall kitchen energy usage.
Choosing induction frying technology supports sustainability goals by conserving energy and decreasing pollution.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Lag Compensation
Classic frying typically relies on gas or electric stovetops with slower temperature adjustments, resulting in higher thermal lag and uneven heat distribution, which may cause inconsistent cooking results. Induction frying technology incorporates thermal lag compensation by instantly adjusting power levels based on real-time temperature feedback, ensuring precise heat control and uniform frying performance.
Precision Heat Zoning
Classic frying relies on direct contact with gas or electric burners, often leading to uneven heat distribution and hot spots, while induction frying utilizes magnetic fields to precisely target and control heat zones for consistent cooking temperatures. Induction technology enables rapid adjustments and energy efficiency, enhancing precision heat zoning that minimizes food burning and ensures optimal frying results.
Magnetic Field-responsive Cookware
Classic frying relies on direct heat transfer through gas or electric coils, which often leads to uneven heating and longer preheating times. Induction frying uses magnetic field-responsive cookware that generates heat directly within the pan, resulting in precise temperature control, faster heating, and energy efficiency.
Surface Temperature Mapping
Classic frying typically involves uneven surface temperature distribution due to direct heat source variability, leading to hot spots and inconsistent cooking results. Induction frying provides precise surface temperature mapping through electromagnetic heating, ensuring uniform heat distribution and improved cooking efficiency.
Rapid Response Searing
Induction frying technology offers superior rapid response searing compared to classic frying methods, delivering precise temperature control that allows for immediate heat adjustments and consistent browning. Classic frying relies on slower heat transfer from the burner to the pan, resulting in delayed temperature changes and less efficient sear quality.
Oil Atomization Dynamics
Classic frying relies on direct heat transfer causing uneven oil atomization and localized hotspots, which can degrade oil quality and affect food texture. Induction frying employs electromagnetic fields to generate uniform heat distribution, enhancing oil atomization dynamics for consistent frying performance and improved energy efficiency.
Consistent Crust Formation
Classic frying relies on direct heat from gas or electric stoves, often causing uneven temperature distribution that leads to inconsistent crust formation on food. Induction frying utilizes electromagnetic fields for rapid, precise heating, ensuring uniform temperature control and consistently crispy, evenly browned crusts.
Adaptive Energy Modulation
Classic frying relies on direct heat transfer from a gas or electric burner, resulting in uneven temperature distribution, whereas induction frying uses adaptive energy modulation to precisely control the magnetic field, ensuring consistent and efficient heat application. This technology minimizes energy waste and enhances cooking precision by dynamically adjusting power based on pan temperature and cooking conditions.
Micro-Controlled Sizzle
Classic frying relies on direct heat transfer from gas or electric coils, often leading to uneven temperature distribution and less precise control over the cooking process. Induction frying utilizes electromagnetic fields to heat the pan directly, enabling micro-controlled sizzle that maintains consistent temperature for optimal texture and flavor development.
Classic frying vs induction frying for technology. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com