Nonstick pans offer easy food release and require less oil, making them ideal for frying delicate items like eggs or fish. Carbon steel pans provide excellent heat retention and develop a natural seasoning over time, which enhances flavor and allows for high-temperature frying. Choosing between the two depends on your cooking style, with nonstick prioritizing convenience and carbon steel delivering durability and superior searing capabilities.
Table of Comparison
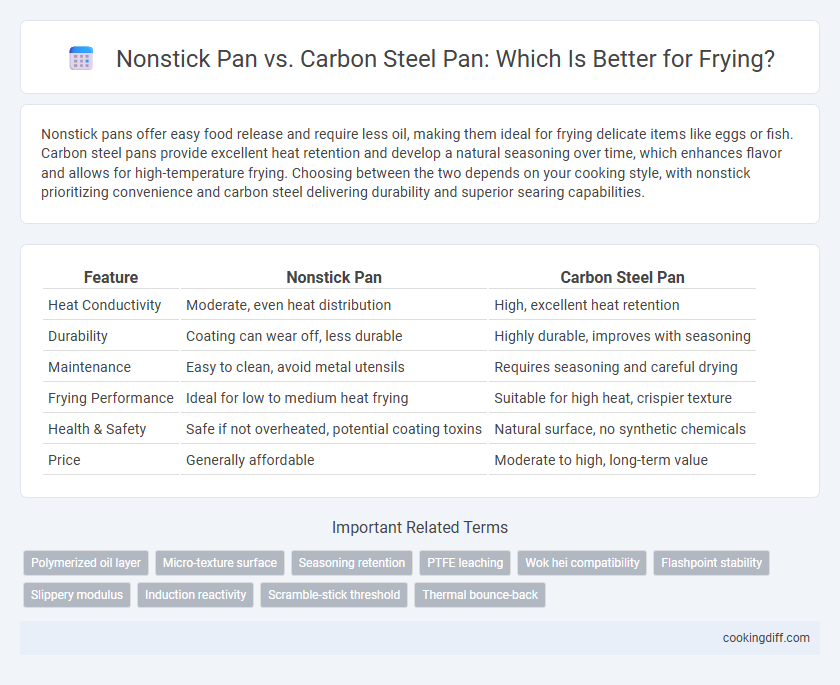
| Feature | Nonstick Pan | Carbon Steel Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Conductivity | Moderate, even heat distribution | High, excellent heat retention |
| Durability | Coating can wear off, less durable | Highly durable, improves with seasoning |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, avoid metal utensils | Requires seasoning and careful drying |
| Frying Performance | Ideal for low to medium heat frying | Suitable for high heat, crispier texture |
| Health & Safety | Safe if not overheated, potential coating toxins | Natural surface, no synthetic chemicals |
| Price | Generally affordable | Moderate to high, long-term value |
Introduction: Nonstick vs Carbon Steel Pans for Frying
Which frying pan offers better cooking performance: nonstick or carbon steel? Nonstick pans provide easy food release and simple cleanup, ideal for delicate items like eggs and pancakes. Carbon steel pans develop a natural seasoning over time, enhancing heat retention and searing capabilities for a versatile frying experience.
Key Differences Between Nonstick and Carbon Steel Pans
Nonstick pans feature a synthetic coating that provides superior food release and requires less oil, making them ideal for cooking delicate items like eggs and pancakes. Carbon steel pans, composed of durable metal, offer excellent heat retention and develop a natural nonstick patina over time but need seasoning and careful maintenance. Choosing between them depends on cooking style, with nonstick pans favoring convenience and carbon steel pans suited for high-heat searing and long-term durability.
Heat Conductivity and Distribution Comparison
Nonstick pans typically have an aluminum base, providing excellent heat conductivity for quick and even heating. Carbon steel pans, while slower to heat, offer superior heat retention and gradually distribute heat across the surface.
Aluminum's high thermal conductivity in nonstick pans allows for precise temperature control, ideal for delicate frying tasks. Carbon steel's ability to maintain consistent heat helps achieve an even sear and browning, especially useful for high-heat frying. The durability of carbon steel also supports long-term performance without hotspot formation common in lower-quality nonstick coatings.
Nonstick Coating Advantages and Limitations
| Nonstick Coating Advantages | Nonstick pans require less oil for frying, promoting healthier meals and easy food release for delicate items like eggs and fish. The smooth surface reduces food sticking, making cleaning faster and less labor-intensive. Heat distribution is consistent, minimizing hot spots and preventing burning during frying. |
| Nonstick Coating Limitations | Nonstick coatings can degrade at high temperatures, limiting their use for high-heat frying or searing. Scratches from metal utensils can damage the coating, reducing durability and safety. Nonstick surfaces may release toxic fumes if overheated beyond recommended limits. |
Carbon Steel Pan’s Natural Nonstick Properties
Carbon steel pans develop a natural nonstick surface through seasoning, which enhances with use and heat exposure, making them ideal for frying. Their ability to withstand high temperatures allows for better caramelization and browning compared to conventional nonstick pans. Unlike synthetic coatings, the seasoned carbon steel surface releases food easily, improving cooking performance while avoiding harmful chemicals.
Durability and Longevity for Frying Applications
Carbon steel pans offer superior durability and can withstand high heat and frequent use without degrading, making them ideal for long-term frying applications. Nonstick pans, while convenient, tend to have a shorter lifespan due to coating wear and are more prone to scratches that reduce their frying efficiency over time.
- Carbon steel robustness - Maintains structural integrity and performance after years of frying at high temperatures.
- Nonstick coating wear - Coatings degrade with use and cleaning, limiting the pan's effective frying life.
- Heat tolerance - Carbon steel can tolerate higher heat levels without damage, extending usability for frying.
For reliable longevity in frying, carbon steel pans outperform nonstick options in durability and resilience.
Frying Performance: Crispy Results and Browning
Nonstick pans excel at preventing food from sticking, allowing for easy frying and cleaning, but they often produce less browning compared to carbon steel pans. Carbon steel pans offer superior heat retention and distribution, resulting in crispier textures and more pronounced browning ideal for searing and frying.
- Nonstick coating reduces sticking - Helps achieve even cooking without food tearing or sticking to the surface.
- Carbon steel promotes Maillard reaction - Higher heat capacity encourages browning and formation of crispy crusts on fried foods.
- Heat retention differences impact texture - Carbon steel retains heat better, maintaining consistent frying temperatures for superior crispiness.
Maintenance and Care: Cleaning and Seasoning
Nonstick pans require gentle cleaning with mild detergents and avoid abrasive scrubbers to maintain the coating, while carbon steel pans need regular seasoning to develop a natural nonstick surface. Proper care for carbon steel includes drying immediately after washing to prevent rust and applying a thin layer of oil after each use.
- Nonstick pans - Clean with soft sponges and mild soap to preserve the nonstick coating and avoid damage.
- Carbon steel pans - Require seasoning by applying oil and heating to maintain nonstick properties and protect against rust.
- Maintenance routine - Carbon steel pans must be dried thoroughly and lightly oiled after cleaning to ensure longevity and performance.
Safety Considerations for High-Heat Frying
Nonstick pans are popular for frying due to their easy release and minimal oil requirements, but they can degrade and release toxic fumes if overheated above 500degF (260degC), posing health risks. Carbon steel pans withstand high temperatures safely, making them ideal for searing and frying at temperatures exceeding 600degF (315degC) without harmful chemical emissions.
For high-heat frying, carbon steel pans offer superior durability and safety, as their natural seasoning prevents food from sticking without the risk of toxic fumes. Proper maintenance of carbon steel pans, including regular seasoning, ensures a nonstick surface and enhances safety during frequent high-temperature cooking.
Related Important Terms
Polymerized oil layer
Nonstick pans rely on a synthetic polymerized oil layer that creates a smooth, friction-resistant surface ideal for frying delicate foods without sticking. Carbon steel pans develop a natural polymerized oil layer over time through seasoning, providing a durable, nonstick surface that improves with use and high-heat cooking.
Micro-texture surface
Nonstick pans feature a smooth micro-texture surface that minimizes food adhesion, enabling easy frying and quick cleanup, while carbon steel pans develop a naturally seasoned micro-texture over time that enhances nonstick properties and promotes superior browning. The evolving patina on carbon steel provides a durable, heat-responsive surface ideal for high-temperature frying, contrasting with the consistent but less heat-tolerant coating of nonstick pans.
Seasoning retention
Nonstick pans offer excellent initial release properties but often lose seasoning effectiveness quickly due to their synthetic coatings, while carbon steel pans develop and retain a natural, durable seasoning layer over time that enhances nonstick performance with repeated use. Carbon steel's ability to maintain and improve its seasoning makes it superior for frying applications requiring high heat and consistent surface texture.
PTFE leaching
Nonstick pans coated with PTFE can release toxic fumes when overheated above 260degC (500degF), posing health risks during frying, whereas carbon steel pans, free from synthetic coatings, avoid PTFE leaching and withstand high frying temperatures safely. Carbon steel's seasoning layer provides natural nonstick properties without chemical leaching, making it a safer option for high-heat frying applications.
Wok hei compatibility
Nonstick pans provide effortless release and easy cleanup but lack the high heat tolerance required to achieve authentic wok hei, whereas carbon steel pans excel in retaining and distributing intense heat, making them ideal for developing the characteristic smoky flavor and sear of traditional stir-frying. Carbon steel's rapid heat response and ability to withstand open flames enable the creation of wok hei, a key element in Chinese stir-fry cooking, which nonstick coatings cannot replicate without damage.
Flashpoint stability
Nonstick pans offer superior flashpoint stability due to their smooth, coated surface that prevents food from sticking and overheating, reducing the risk of burning oils. Carbon steel pans have a higher heat tolerance but require seasoning and careful temperature control to avoid flare-ups and maintain stable flashpoints during frying.
Slippery modulus
Nonstick pans offer a superior slippery modulus compared to carbon steel pans, significantly reducing food adhesion and enabling easier frying with minimal oil. Carbon steel pans require proper seasoning to develop a natural nonstick surface but generally exhibit a lower slippery modulus, leading to increased likelihood of food sticking during frying.
Induction reactivity
Nonstick pans generally exhibit poor induction reactivity due to their aluminum or non-ferrous metal bases, requiring additional magnetic layers to function, whereas carbon steel pans are highly compatible with induction cooktops because of their ferromagnetic properties, ensuring rapid and even heating. The superior induction responsiveness of carbon steel enhances frying performance by providing better temperature control and energy efficiency compared to most nonstick counterparts.
Scramble-stick threshold
Nonstick pans offer a lower scramble-stick threshold due to their PTFE coating that prevents food adhesion, making them ideal for delicate eggs and quick frying tasks. Carbon steel pans require proper seasoning to create a natural nonstick surface but provide superior heat retention and durability for higher-heat frying applications.
Nonstick pan vs carbon steel pan for frying. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com