Pan frying delivers a rich flavor and crispy texture by cooking food directly in oil at high heat, creating a golden crust. Air frying uses rapid hot air circulation to cook food with minimal oil, resulting in a healthier alternative while still achieving a crispy exterior. Both methods offer distinct advantages depending on desired taste, texture, and nutritional preferences.
Table of Comparison
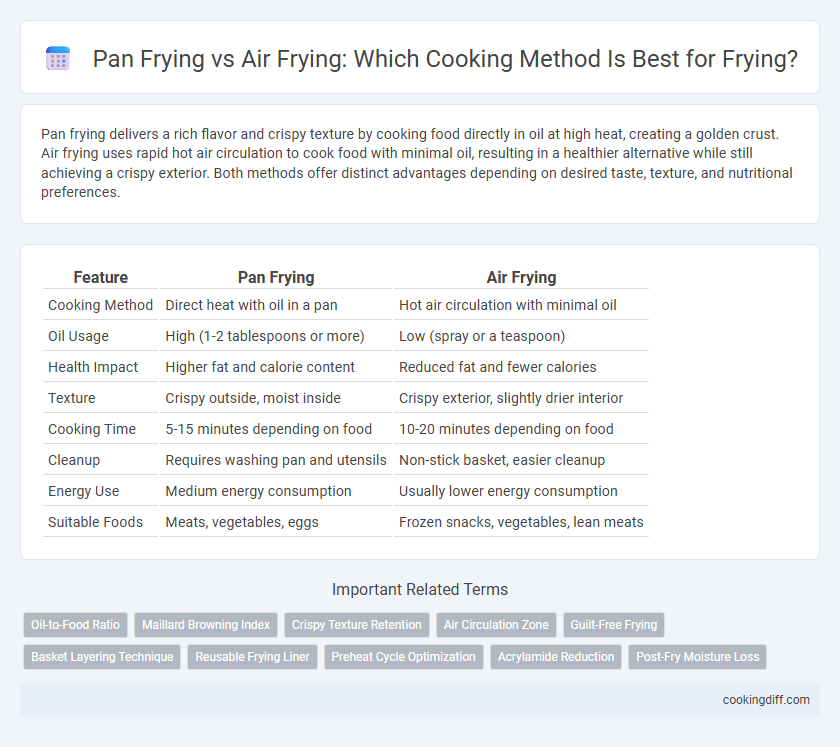
| Feature | Pan Frying | Air Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Direct heat with oil in a pan | Hot air circulation with minimal oil |
| Oil Usage | High (1-2 tablespoons or more) | Low (spray or a teaspoon) |
| Health Impact | Higher fat and calorie content | Reduced fat and fewer calories |
| Texture | Crispy outside, moist inside | Crispy exterior, slightly drier interior |
| Cooking Time | 5-15 minutes depending on food | 10-20 minutes depending on food |
| Cleanup | Requires washing pan and utensils | Non-stick basket, easier cleanup |
| Energy Use | Medium energy consumption | Usually lower energy consumption |
| Suitable Foods | Meats, vegetables, eggs | Frozen snacks, vegetables, lean meats |
Introduction: Understanding Pan Frying and Air Frying
Pan frying involves cooking food in a small amount of oil over direct heat, creating a crispy texture and rich flavor. This traditional method requires constant attention to avoid burning and ensures even browning on the food's surface.
Air frying uses hot air circulation to cook food with little to no oil, making it a healthier alternative to pan frying. It offers a convenient, less messy process while producing crispy results similar to deep frying but with significantly reduced fat content.
Cooking Techniques: How Pan Frying and Air Frying Work
Pan frying uses direct contact with a hot, oiled surface to cook food, creating a crispy exterior and moist interior. Air frying circulates hot air rapidly around the food, mimicking deep frying while using little to no oil for a healthier result.
- Heat Transfer Method - Pan frying relies on conduction from the skillet's surface, while air frying uses convection from circulating hot air.
- Oil Usage - Pan frying requires a moderate amount of oil to prevent sticking and enhance flavor, whereas air frying needs minimal to no added oil.
- Cooking Time and Texture - Pan frying typically cooks food faster with a more pronounced crust, while air frying offers a crisp texture with slightly longer cooking times.
Flavor and Texture Differences
| Pan frying often imparts a rich, crispy exterior with a golden-brown finish due to direct contact with hot oil, enhancing Maillard reactions and deep flavors. Air frying produces a lighter crispness with less oil absorption, resulting in a slightly drier texture and milder taste. Both methods offer distinct sensory experiences, with pan frying favoring intense savoriness and air frying prioritizing health-conscious crispiness. |
Health Considerations: Oil Usage and Nutrition
Pan frying typically requires more oil, which increases calorie content and may introduce unhealthy fats depending on the oil used. Air frying uses significantly less oil, reducing fat intake and promoting a lower-calorie meal.
Air frying preserves more nutrients due to shorter cooking times and less exposure to high heat compared to pan frying. The reduced oil absorption in air frying lowers the risk of heart disease and obesity-related health issues. Choosing air frying supports healthier cooking habits without sacrificing flavor or texture.
Cooking Speed and Efficiency
Pan frying typically cooks food faster due to direct contact with a hot surface, allowing efficient heat transfer and quicker browning. Foods usually take 3 to 7 minutes per side, depending on thickness and heat intensity.
Air frying uses convection to circulate hot air around the food, which may result in slightly longer cooking times, generally 10 to 20 minutes. However, air fryers use less oil and provide consistent heat distribution, enhancing overall cooking efficiency and reducing cleanup time.
Versatility and Recipe Adaptability
Pan frying offers greater versatility for cooking a wide range of ingredients with precise temperature control, enhancing flavor and texture. Air frying provides a healthier alternative with less oil, ideal for recipes requiring crispiness without deep frying.
- Pan frying versatility - Suitable for vegetables, meats, and delicate items due to adjustable heat and oil use.
- Air frying recipe adaptability - Works best for frozen foods and pre-breaded items, offering consistent results with minimal modification.
- Flavor and texture control - Pan frying allows for customization of seasoning and browning; air frying focuses on achieving crispiness with less fat.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Pan frying requires frequent scrubbing to remove oil residues and food particles, often demanding the use of oily water and degreasers to maintain non-stick surfaces. Air frying offers easier cleaning with removable, dishwasher-safe baskets and minimal oil usage, reducing grease buildup. Regular maintenance of both appliances ensures longevity, but air fryers typically demand less effort and time for thorough cleaning.
Cost and Kitchen Space Implications
Pan frying typically incurs lower initial costs because it requires only a stovetop and a quality pan, whereas air fryers involve a higher upfront investment but reduce ongoing oil expenses. Air fryers save considerable kitchen space as compact, multi-functional appliances, while pan frying demands more room for pots, pans, and oil storage.
- Cost Efficiency - Pan frying needs minimal equipment purchase, making it cost-effective in the short term.
- Space Utilization - Air fryers are designed to occupy less countertop area compared to multiple frying pans and oil containers.
- Maintenance Costs - Air frying reduces oil use, lowering recurring costs associated with purchasing and disposing of cooking oil.
Choosing between pan frying and air frying depends on balancing budget constraints with kitchen space availability and cooking preferences.
Environmental Impact and Energy Consumption
Which method between pan frying and air frying has a lower environmental impact? Pan frying typically consumes more energy due to longer cooking times and electric stove usage, leading to higher carbon emissions. Air frying uses rapid air technology to cook food efficiently, reducing energy consumption and minimizing environmental footprint.
Related Important Terms
Oil-to-Food Ratio
Pan frying typically uses a higher oil-to-food ratio, allowing food to cook in a thin layer of hot oil that promotes crispiness and even browning. Air frying significantly reduces oil usage by circulating hot air around the food, achieving a similar texture with 70-80% less oil compared to traditional pan frying methods.
Maillard Browning Index
Pan frying achieves a higher Maillard Browning Index due to direct contact with hot oil, promoting greater flavor development and crust formation. Air frying uses circulating hot air which produces a lighter browning effect, resulting in a lower Maillard reaction intensity but a healthier cooking profile.
Crispy Texture Retention
Pan frying delivers superior crispy texture retention due to direct oil contact that enhances browning and Maillard reactions, resulting in a more robust crunch and flavor. Air frying uses hot air circulation to crisp food with less oil, producing a lighter texture but often lacks the deep, consistent crispiness achieved through traditional pan frying methods.
Air Circulation Zone
Air frying utilizes a rapid air circulation zone to evenly cook food by surrounding it with hot air, reducing the need for oil while achieving a crispy texture; in contrast, pan frying relies on direct contact with hot oil or fat in a cooking surface, which can lead to uneven heat distribution and higher fat absorption. The air circulation zone in air fryers enhances heat transfer efficiency and promotes faster cooking times compared to traditional pan frying methods.
Guilt-Free Frying
Pan frying uses oil to achieve crispy textures but often increases calorie intake, while air frying circulates hot air to cook food with little to no oil, significantly reducing fat and calorie content for guilt-free frying. Air frying also preserves flavor and texture similar to pan frying, making it a healthier alternative without sacrificing taste.
Basket Layering Technique
Basket layering technique in air frying ensures even heat circulation around food items, resulting in uniform cooking with minimal oil, while pan frying relies on direct contact and frequent turning to prevent uneven cooking and achieve a crispy texture. Proper basket layering maximizes airflow efficiency in air fryers, reducing cooking time and oil absorption compared to pan frying's conventional surface cooking method.
Reusable Frying Liner
Reusable frying liners enhance both pan frying and air frying by preventing food from sticking and reducing cleanup time, making them an eco-friendly alternative to disposable liners. Their heat-resistant, non-stick surfaces improve cooking efficiency while maintaining the flavors and textures distinctive to each frying method.
Preheat Cycle Optimization
Pan frying requires precise preheat control to achieve optimal Maillard reaction and prevent oil degradation, ensuring even cooking and flavor development. Air frying benefits from rapid preheat cycles that stabilize temperature quickly, enhancing crispiness while reducing overall cooking time and energy consumption.
Acrylamide Reduction
Pan frying and air frying both offer crispy textures, but air frying significantly reduces acrylamide formation by using hot air circulation instead of submerging food in oil at high temperatures. Studies show air frying can lower acrylamide levels by up to 90% compared to traditional pan frying, making it a healthier cooking method for reducing this potential carcinogen.
Pan Frying vs Air Frying for Cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com