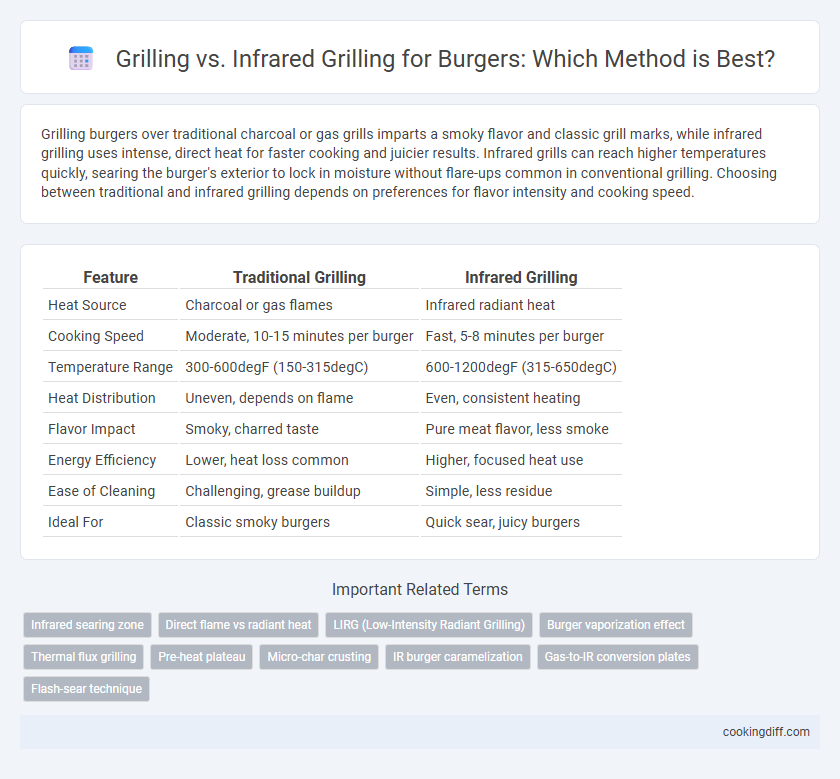
Grilling burgers over traditional charcoal or gas grills imparts a smoky flavor and classic grill marks, while infrared grilling uses intense, direct heat for faster cooking and juicier results. Infrared grills can reach higher temperatures quickly, searing the burger's exterior to lock in moisture without flare-ups common in conventional grilling. Choosing between traditional and infrared grilling depends on preferences for flavor intensity and cooking speed.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Grilling | Infrared Grilling |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Charcoal or gas flames | Infrared radiant heat |
| Cooking Speed | Moderate, 10-15 minutes per burger | Fast, 5-8 minutes per burger |
| Temperature Range | 300-600degF (150-315degC) | 600-1200degF (315-650degC) |
| Heat Distribution | Uneven, depends on flame | Even, consistent heating |
| Flavor Impact | Smoky, charred taste | Pure meat flavor, less smoke |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower, heat loss common | Higher, focused heat use |
| Ease of Cleaning | Challenging, grease buildup | Simple, less residue |
| Ideal For | Classic smoky burgers | Quick sear, juicy burgers |
Traditional Grilling Explained: How It Works
Traditional grilling cooks burgers by applying direct heat from charcoal or gas flames, creating a smoky flavor and charred texture. Heat transfers through convection and conduction, searing the meat and locking in juices for a classic grilled taste.
- Direct Flame Heat - The open flame directly contacts the grill grates, providing high temperatures to sear burgers quickly.
- Flavor Development - Dripping fats vaporize on hot coals or burners, producing characteristic smoky flavors unique to traditional grilling.
- Variable Heat Zones - Grillers can create zones with different heat intensities, allowing control over cooking speed and doneness levels.
The simplicity and flavor complexity of traditional grilling remain preferred by many burger enthusiasts over infrared grilling methods.
What Is Infrared Grilling? Key Features
Infrared grilling uses radiant heat generated by an infrared element to cook food quickly and evenly, often reaching higher temperatures than traditional grilling methods. This technique minimizes flare-ups and retains moisture in burgers, resulting in juicier and well-seared patties. Key features of infrared grilling include rapid heat transfer, precise temperature control, and energy efficiency, making it ideal for achieving restaurant-quality burger sears.
Heat Distribution: Conventional vs Infrared Methods
Conventional grilling uses direct flame to cook burgers, often resulting in uneven heat distribution that can cause hot spots and inconsistent cooking. Infrared grilling employs radiant heat that provides more even and intense heat, ensuring burgers cook uniformly with a crispy exterior.
- Conventional grilling heat distribution - relies on gas or charcoal flames that can create fluctuating temperatures and uneven cooking zones on the grill surface.
- Infrared grilling heat consistency - uses infrared panels to emit uniform radiant heat, reducing flare-ups and preserving juiciness by forming a quick sear.
- Cooking speed and control - infrared grills typically reach higher temperatures faster, offering better control over searing burgers compared to traditional grills.
Cooking Time: Which Grills Burgers Faster?
Infrared grilling cooks burgers significantly faster than traditional grilling due to its intense and direct heat. Infrared grills can sear a burger in as little as 2 to 3 minutes per side, reducing overall cooking time by up to 50% compared to conventional charcoal or gas grills.
Traditional grilling typically requires 5 to 7 minutes per side to achieve a properly cooked burger, depending on thickness and heat intensity. The quicker cooking time of infrared grilling helps retain juiciness and flavor by minimizing moisture loss during the grilling process.
Flavor Differences: Taste Test Comparison
Traditional grilling imparts a smoky, charred flavor to burgers thanks to direct contact with flames and smoke, enhancing the meat's natural taste. Infrared grilling produces a juicier burger with a more evenly cooked interior but lacks the distinct smoky notes typical of charcoal or gas grills.
- Smoky Flavor - Traditional grilling creates complex smoky flavors from combustion and smoke penetration.
- Juiciness Retention - Infrared grilling sears burgers quickly, locking in moisture for a tender bite.
- Flavor Intensity - Infrared's radiant heat yields a cleaner, less charred flavor profile compared to conventional grills.
Juiciness and Texture: Burger Results Reviewed
| Grilling Method | Juiciness | Texture | Results |
| Traditional Grilling | Moderate moisture retention due to indirect heat exposure | Firm exterior with slightly uneven cooking | Produces flavorful burgers but can risk dryness if overcooked |
| Infrared Grilling | Superior juiciness from rapid, high-temperature searing | Consistent outer crust with tender, evenly cooked interior | Delivers juicy, well-textured burgers with enhanced caramelization |
Energy Efficiency: Fuel Usage and Costs
Traditional grilling typically consumes more propane or charcoal due to longer cooking times and slower heat response, increasing overall fuel costs. Infrared grilling uses intense, direct heat that cooks burgers faster and more evenly, reducing fuel consumption significantly.
Infrared grills convert up to 90% of fuel energy into cooking heat, compared to about 60% for conventional grills, offering greater energy efficiency. This efficiency translates to lower operational costs over time, making infrared grilling a cost-effective choice for burger lovers seeking to optimize fuel usage.
Cleaning and Maintenance: Ease of Use
Which grilling method offers easier cleaning and maintenance for burgers? Traditional grilling often requires scrubbing grates and dealing with grease buildup, making cleanup time-consuming. Infrared grilling heats more evenly and reduces grease splatter, resulting in less residue and simpler maintenance.
Safety Considerations: Grilling vs Infrared
Infrared grilling for burgers offers faster cooking at higher temperatures, reducing flare-ups and minimizing the risk of charring harmful compounds compared to traditional grilling. Traditional grilling involves direct flame exposure, which can increase the chances of grease fires and uneven cooking safety hazards. Choosing infrared grills enhances temperature control and lowers the risk of foodborne illnesses by ensuring burgers are cooked thoroughly and evenly.
Related Important Terms
Infrared searing zone
Infrared grilling offers a searing zone that reaches temperatures above 1,800degF, creating a caramelized crust on burgers while locking in juices more effectively than traditional grilling at lower temperatures. This intense, focused heat reduces cooking time and enhances flavor by promoting Maillard reactions on the burger's surface.
Direct flame vs radiant heat
Grilling with direct flame sears burgers quickly, creating a smoky char and caramelized crust through intense, uneven heat, while infrared grilling uses radiant heat to cook burgers evenly and rapidly by emitting infrared energy that penetrates the meat. Infrared grills reach higher temperatures faster, reducing flare-ups and preserving juiciness compared to traditional direct flame grilling.
LIRG (Low-Intensity Radiant Grilling)
Low-Intensity Radiant Grilling (LIRG) offers precise heat control and even cooking, reducing flare-ups and retaining burger juiciness compared to traditional grilling methods. Infrared grilling emits intense, direct heat that sears the burger quickly, while LIRG provides a gentler, more uniform temperature, enhancing flavor depth and texture.
Burger vaporization effect
Infrared grilling sears burgers rapidly at high temperatures, enhancing the Maillard reaction while minimizing moisture loss and vaporization, which preserves juiciness. Traditional grilling exposes burgers to open flames, increasing vaporization and often drying out the patty due to prolonged cooking times and uneven heat distribution.
Thermal flux grilling
Grilling burgers with traditional methods relies on convective heat and direct flame contact, creating uneven thermal flux that can cause hot spots and flare-ups, affecting texture and flavor. Infrared grilling delivers a consistent and intense thermal flux by emitting radiant heat directly to the burger's surface, enabling faster searing, enhanced Maillard reaction, and juicier results.
Pre-heat plateau
Traditional grilling reaches a higher pre-heat plateau typically around 500degF, providing intense direct heat that sears burgers quickly and forms a flavorful crust. Infrared grilling achieves a more consistent and rapid pre-heat at approximately 700degF, enhancing caramelization and reducing cooking time for juicier, evenly cooked burgers.
Micro-char crusting
Infrared grilling produces higher, more consistent heat that intensifies the Maillard reaction, creating a superior micro-char crust on burgers compared to traditional grilling methods. This micro-char crust enhances flavor depth and juiciness by sealing in moisture while delivering a crispy, caramelized exterior.
IR burger caramelization
Infrared grilling delivers intense, even heat that enhances burger caramelization by reaching higher temperatures faster than traditional grilling methods. This rapid searing creates a flavorful crust through the Maillard reaction, locking in juices and producing a juicier, more flavorful burger.
Gas-to-IR conversion plates
Gas-to-infrared conversion plates enhance traditional gas grills by providing higher, more consistent heat ideal for searing burgers with a flavorful crust. These plates reduce flare-ups and improve temperature control compared to standard gas grilling, yielding juicier, evenly cooked patties.
Grilling vs Infrared Grilling for Burgers. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com