Rotisserie grilling offers even cooking by rotating the meat, resulting in juicy, tender cuts with a crispy exterior ideal for whole poultry. Parrilla grilling utilizes direct heat from a grill grate, providing a smoky flavor and distinct char marks, perfect for steaks and vegetables. Choosing between rotisserie and parrilla depends on the desired texture and flavor profile for your grilled pet meals.
Table of Comparison
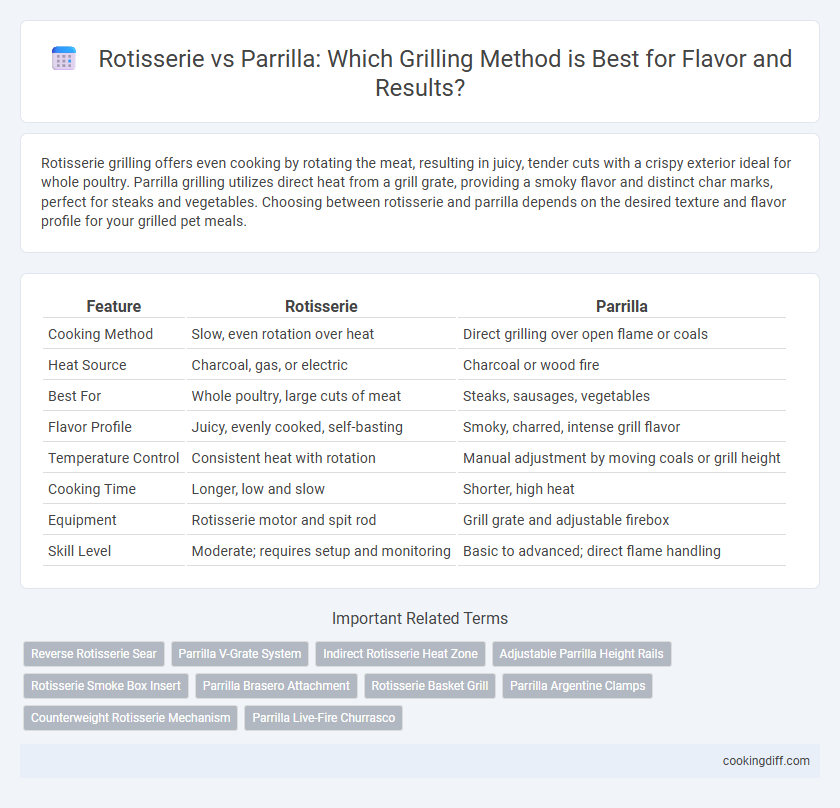
| Feature | Rotisserie | Parrilla |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Slow, even rotation over heat | Direct grilling over open flame or coals |
| Heat Source | Charcoal, gas, or electric | Charcoal or wood fire |
| Best For | Whole poultry, large cuts of meat | Steaks, sausages, vegetables |
| Flavor Profile | Juicy, evenly cooked, self-basting | Smoky, charred, intense grill flavor |
| Temperature Control | Consistent heat with rotation | Manual adjustment by moving coals or grill height |
| Cooking Time | Longer, low and slow | Shorter, high heat |
| Equipment | Rotisserie motor and spit rod | Grill grate and adjustable firebox |
| Skill Level | Moderate; requires setup and monitoring | Basic to advanced; direct flame handling |
Introduction to Rotisserie and Parrilla Grilling
Rotisserie grilling involves cooking meat on a rotating spit, ensuring even heat distribution and self-basting for tender, juicy results. It is ideal for whole chickens, roasts, and large cuts of meat that benefit from slow, consistent cooking.
Parrilla grilling, originating from Argentina, uses a flat or slatted grill over wood or charcoal, imparting smoky flavors with direct heat and flame. This method excels at grilling steaks, sausages, and vegetables with a distinct char and robust taste.
Key Differences Between Rotisserie and Parrilla
Rotisserie grilling uses a motorized spit to rotate meat evenly over heat, ensuring uniform cooking and self-basting. Parrilla involves grilling over an open flame with adjustable grates that allow direct control of heat intensity and smoky flavor infusion.
- Cooking Method - Rotisserie rotates food for even heat distribution, while Parrilla relies on static placement above coals or wood.
- Heat Control - Parrilla offers manual adjustment of grill height to manage temperature, unlike the fixed heat position in rotisserie setups.
- Flavor Profile - Parrilla imparts strong smoky notes due to open flame exposure, whereas rotisserie emphasizes juiciness through continuous rotation and self-basting.
Historical Origins of Rotisserie and Parrilla Methods
The rotisserie grilling method traces back to ancient civilizations such as the Greeks and Romans, who used spit-roasting to evenly cook meat over an open flame. The parrilla technique originates from South America, particularly Argentina and Uruguay, where it evolved as a social grilling tradition using a metal grate over wood embers.
- Rotisserie Technique - Utilizes a rotating spit to ensure uniform cooking and optimal flavor retention.
- Parrilla Method - Involves slow-cooking meat on a fixed grill grate to enhance smokiness and tenderness.
- Cultural Roots - Rotisserie reflects European culinary heritage while parrilla highlights South American communal grilling customs.
Both techniques exhibit unique cultural histories that influence modern grilling practices worldwide.
Flavor Profiles Achieved by Each Technique
Rotisserie grilling slowly cooks meat on a rotating spit, enabling even heat distribution and self-basting that enhances juiciness and develops a rich, savory flavor. Parrilla grilling uses direct high heat and wood or charcoal smoke to infuse a bold, smoky flavor with distinct charred notes.
- Rotisserie imparts tender, succulent texture - Slow rotation ensures meat remains juicy by allowing fats and juices to circulate continuously.
- Parrilla emphasizes smoky, robust taste - Open flames and smoke penetrate the meat surface, creating a characteristic grilled aroma.
- Flavor complexity differs by heat source - Rotisserie's indirect heat contrasts with Parrilla's direct flame, resulting in unique flavor profiles specific to each technique.
Equipment Needed for Rotisserie vs Parrilla Grilling
Rotisserie grilling requires a motorized spit, sturdy brackets to hold the spit in place, and a heat source that allows for even, consistent cooking. This equipment ensures the meat rotates slowly for uniform browning and self-basting effects.
Parrilla grilling, commonly used in Argentine barbecue, demands a grill grate with adjustable height over a bed of hot coals, often featuring a manual crank system to control temperature. Unlike the rotisserie's automated rotation, parrilla grilling relies on the grill master's skill to manage heat and placement. Essential tools include wood or charcoal fuel, a firebox or open grill frame, and metal tongs for handling food.
Cooking Techniques: How Rotisserie and Parrilla Work
| Rotisserie Cooking Technique | Rotisserie grilling involves skewering meat on a spit that rotates slowly over a heat source, allowing even cooking and self-basting through constant rotation, which locks in juices and flavors. |
| Parrilla Cooking Technique | Parrilla grilling uses a fixed grill grate positioned above charcoal or wood fire, where the controlled heat and proximity to flames create distinct grill marks and enhance smoky, charred flavors. |
Best Types of Meat for Rotisserie and Parrilla
Rotisserie grilling excels with large, evenly cooking cuts like whole chickens, pork roasts, and prime rib, ensuring tender, juicy results through slow, consistent rotation. Parrilla grilling is ideal for thinner, quick-cooking meats such as steaks, sausages, and vegetables, delivering robust smoky flavors with high direct heat.
Rotisserie's indirect heat method preserves moisture in fatty cuts, making it perfect for turkey legs and lamb shoulders. Parrilla's open grate allows excess fat to drip away, enhancing leaner meats like flank steak and skirt steak with a distinctive char.
Ease of Use and Maintenance Comparison
Rotisserie grills offer automated, even cooking with minimal attention, making them easier to use for beginners compared to parrillas that require manual control of heat and fuel. Maintenance for rotisserie systems involves cleaning motorized components and drip trays, while parrillas demand regular ash removal and grill grate scrubbing to prevent rust. Overall, rotisseries provide a more user-friendly grilling experience, whereas parrillas require hands-on effort but offer greater control and traditional flavor.
Popular Recipes for Rotisserie and Parrilla Grilling
Rotisserie grilling popular recipes include whole roasted chicken, slow-cooked pork shoulder, and herb-marinated lamb, which benefit from even heat distribution and self-basting. Parrilla grilling frequently features Argentine-style chimichurri steak, chorizo sausages, and grilled vegetables, showcasing direct flame cooking for robust smoky flavors. Both methods highlight regional ingredients and techniques that optimize flavor through either slow rotation or high-heat grilling.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Rotisserie Sear
Reverse rotisserie sear offers precise temperature control and even cooking by slowly roasting meat before finishing with a high-heat sear, enhancing flavor and texture. Parrilla grilling focuses on direct, open-flame cooking with adjustable grates, ideal for traditional smoky, charred results but lacks the slow-roasting precision of reverse rotisserie techniques.
Parrilla V-Grate System
The Parrilla V-Grate System enhances grilling by evenly distributing heat and allowing excess fat to drip away, producing juicier and healthier meats compared to traditional rotisserie methods. Its innovative V-shaped grates improve smoke circulation and create distinctive sear marks, optimizing flavor and texture for grilled dishes.
Indirect Rotisserie Heat Zone
The indirect rotisserie heat zone provides consistent, even cooking by slowly turning meat over a heat source, preventing flare-ups and ensuring juiciness and tenderness. In contrast, the parrilla grilling method relies on adjustable grate heights to create a controlled indirect heat area, allowing for versatile cooking but requiring more attention to temperature management.
Adjustable Parrilla Height Rails
Adjustable parrilla height rails allow precise control over cooking temperature by modifying the distance between the grill surface and heat source, essential for evenly grilling meats and vegetables. Unlike rotisseries that rely on constant rotation for even cooking, parrillas offer direct heat management, making them ideal for searing and traditional Argentine-style asado grilling.
Rotisserie Smoke Box Insert
The rotisserie smoke box insert enhances flavor by infusing slow-cooked meats with consistent smoky heat, ideal for even cooking over indirect flames. Compared to parrilla grills, rotisserie setups provide superior moisture retention and a self-basting effect, delivering tender, juicy results with less manual intervention.
Parrilla Brasero Attachment
The Parrilla Brasero attachment enhances traditional grilling by providing an adjustable grilling surface that allows precise control over heat intensity and cooking speed, ideal for achieving authentic Argentine-style barbecue flavors. Unlike a rotisserie, which relies on slow, consistent rotation, the Parrilla Brasero offers versatile direct and indirect heat zones, promoting even searing and the perfect char on meats and vegetables.
Rotisserie Basket Grill
Rotisserie basket grills offer even heat distribution and continuous rotation, ensuring perfectly cooked meats with a crispy exterior and juicy interior. Unlike parrilla grilling, which relies on stationary direct heat and manual flipping, the rotisserie basket grill automates the cooking process for consistent results and enhanced flavor infusion.
Parrilla Argentine Clamps
Parrilla Argentine clamps provide precise control over heat distribution and stability, essential for traditional Argentine grilling techniques that emphasize slow, even cooking of meats. Unlike rotisseries, parrillas allow direct contact with varying charcoal heat zones, enhancing flavor through natural smoke infusion and enabling versatile cooking adjustments.
Counterweight Rotisserie Mechanism
The counterweight rotisserie mechanism ensures even cooking by consistently rotating meat, making it ideal for juicy, evenly grilled results compared to the stationary setup of a parrilla. This system minimizes manual adjustments, enhancing temperature control and reducing flare-ups during grilling sessions.
Rotisserie vs Parrilla for grilling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com