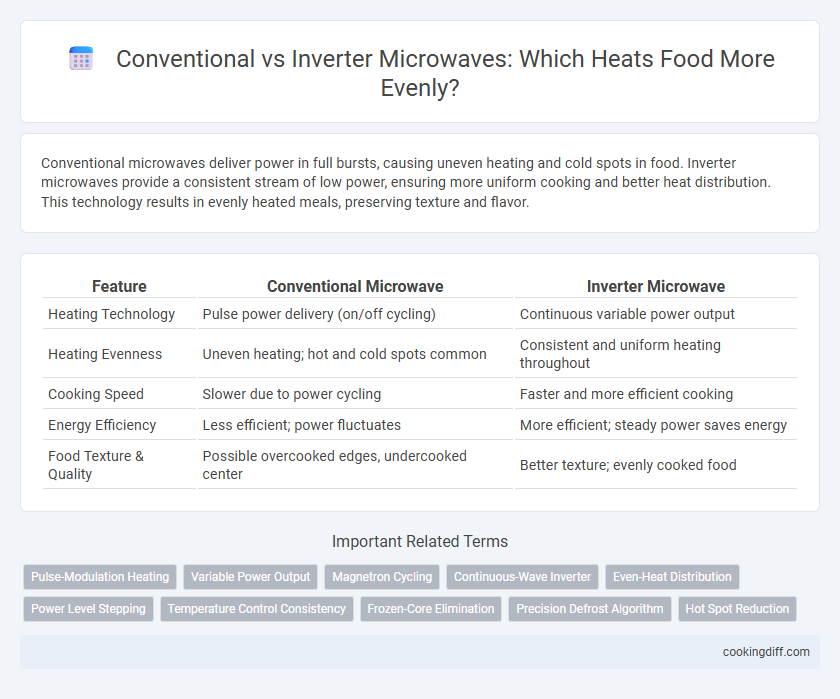
Conventional microwaves deliver power in full bursts, causing uneven heating and cold spots in food. Inverter microwaves provide a consistent stream of low power, ensuring more uniform cooking and better heat distribution. This technology results in evenly heated meals, preserving texture and flavor.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Conventional Microwave | Inverter Microwave |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Technology | Pulse power delivery (on/off cycling) | Continuous variable power output |
| Heating Evenness | Uneven heating; hot and cold spots common | Consistent and uniform heating throughout |
| Cooking Speed | Slower due to power cycling | Faster and more efficient cooking |
| Energy Efficiency | Less efficient; power fluctuates | More efficient; steady power saves energy |
| Food Texture & Quality | Possible overcooked edges, undercooked center | Better texture; evenly cooked food |
Introduction to Microwave Heating Technologies
| Conventional microwaves utilize a transformer to deliver full power in a pulsating manner, which can cause uneven heating and cold spots in food. Inverter microwaves use a microprocessor to provide continuous, variable power levels, resulting in more uniform heat distribution. This advanced technology improves cooking accuracy and preserves food texture by preventing overcooking or underheating. |
How Conventional Microwaves Work
Conventional microwaves operate by switching the magnetron on and off at full power, creating bursts of high energy. This method can result in uneven heating, as food sections alternate between cooking and resting phases.
- Fixed Power Output - The magnetron delivers full power in cycles, leading to temperature fluctuations in the food.
- Intermittent Cooking - The microwave alternates between cooking and pausing to control heat intensity.
- Uneven Heating Pattern - Hot and cold spots may develop due to the on/off power cycling effect.
Understanding Inverter Microwave Technology
Conventional microwaves use a transformer to switch the magnetron on and off, delivering full power intermittently, which can result in uneven heating or cold spots in food. Inverter microwave technology provides a consistent and precise power level by adjusting the voltage supplied to the magnetron continuously, enabling smoother and more even cooking.
Inverter microwaves excel at defrosting and reheating by applying low power consistently, preventing overcooked edges and undercooked centers common with traditional microwaves. Understanding inverter technology helps consumers choose appliances that offer better temperature control and improved food texture during microwave heating.
Key Differences: Conventional vs Inverter Microwaves
Conventional microwaves heat food using a fixed power cycle, switching the magnetron on and off, which can result in uneven cooking and hot spots. Inverter microwaves deliver a continuous, variable power output, allowing for more consistent and even heating throughout the food. This precise power control improves texture and flavor by preventing overcooking on the edges while thoroughly heating the center.
Heating Performance Comparison
Conventional microwaves heat food using a simple on-off cycling of power, which can cause uneven heating and cold spots. Inverter microwaves deliver consistent power levels, allowing for more uniform heat distribution and better texture in food. This precise control results in faster cooking times and improved heating performance compared to conventional models.
Evenness of Food Heating: Which Is Better?
Inverter microwaves provide more consistent and even heating by delivering a continuous power output, avoiding the temperature fluctuations common in conventional microwaves. Conventional microwaves operate with full power cycling on and off, which can lead to unevenly heated food and cold spots.
- Inverter Technology - Delivers precise and steady power for uniform heat distribution throughout the food.
- Conventional Microwave Operation - Uses fluctuating power levels that often cause inconsistent heating and uneven cooking results.
- Evenness of Heating - Inverter microwaves significantly reduce hot and cold spots, enhancing overall food texture and taste.
Power Levels and Cooking Control
How do power levels affect even heating in conventional and inverter microwaves? Conventional microwaves operate on fixed power cycles, which can cause uneven cooking due to intermittent full power bursts. Inverter microwaves provide consistent, adjustable power levels, offering precise cooking control and more uniform heating results.
Energy Efficiency and Cooking Times
Conventional microwaves operate at a fixed power level, causing intermittent heating cycles that can lead to uneven cooking and higher energy consumption. Inverter microwaves deliver continuous, precise power levels, ensuring consistent heat distribution and improved energy efficiency.
Energy efficiency in inverter microwaves reduces electricity usage by maintaining steady cooking power, which also shortens cooking times compared to conventional models. The ability to finely control the microwave power results in more uniform heating of food, preserving texture and flavor. Consequently, inverter technology offers significant advantages in both energy savings and meal preparation speed.
Impact on Food Texture and Nutrient Retention
Inverter microwaves provide more consistent and even heating by delivering a continuous power level, reducing hotspots that can cause uneven cooking and texture deterioration. Conventional microwaves use full power cycling, which can lead to overcooked edges and undercooked centers, negatively impacting food texture and nutrient retention.
- Even Heating - Inverter microwaves maintain a steady power output, ensuring uniform temperature distribution throughout the food.
- Food Texture - The gentle cooking process of inverter microwaves helps preserve the natural texture, avoiding dryness or rubberiness common with conventional models.
- Nutrient Retention - Consistent heating in inverter microwaves reduces nutrient loss by minimizing overheating and cooking time.
Inverter microwaves offer significant advantages over conventional microwaves in preserving both the texture and nutritional quality of foods.
Related Important Terms
Pulse-Modulation Heating
Conventional microwaves use pulse-modulation heating, cycling the magnetron on and off to regulate power, which often causes uneven heating and cold spots in food. Inverter microwaves provide continuous, variable power output, resulting in more consistent energy distribution and even heating throughout the cooking process.
Variable Power Output
Conventional microwaves operate using a fixed power output that cycles on and off, causing uneven heating and cold spots in food. Inverter microwaves deliver continuous, variable power output, ensuring more consistent heat distribution and better cooking results.
Magnetron Cycling
Conventional microwaves use magnetron cycling, turning the magnetron on and off to control power, which can cause uneven heating and cold spots. Inverter microwaves deliver a continuous, precise power level to the magnetron, resulting in more consistent and even heating throughout the food.
Continuous-Wave Inverter
Continuous-Wave Inverter microwaves provide consistent energy output that ensures more uniform heating compared to Conventional Microwave models, which rely on on/off cycling that can cause uneven cooking. The continuous energy flow of inverter technology allows precise temperature control, reducing cold spots and improving overall food quality.
Even-Heat Distribution
Conventional microwaves use fixed power levels that cycle on and off, often causing uneven heating with hot spots and cold areas in food. Inverter microwaves deliver continuous, precise power levels, ensuring more consistent and even heat distribution for thorough cooking.
Power Level Stepping
Conventional microwaves use fixed power level stepping by cycling the magnetron on and off, which can cause uneven heating and temperature fluctuations. Inverter microwaves provide continuous and precise power control, resulting in more consistent and even heating throughout the cooking process.
Temperature Control Consistency
Inverter microwaves provide precise temperature control through continuous power adjustment, ensuring consistent heating compared to conventional microwaves that rely on on-off cycling, often causing uneven temperature distribution. This consistent power delivery in inverter models results in evenly heated food, reducing hot spots and improving cooking quality.
Frozen-Core Elimination
Inverter microwaves deliver consistent and adjustable power levels, eliminating frozen cores by providing even heating throughout the food, unlike conventional microwaves that rely on simple on/off cycles causing uneven temperature distribution. This precise power control in inverter technology ensures frozen meals are thoroughly cooked without overcooked edges or cold spots.
Precision Defrost Algorithm
Conventional microwaves use a simple on/off power cycling method that can result in uneven heating and partially cooked edges during defrosting. Inverter microwaves employ a Precision Defrost Algorithm that delivers consistent, low power levels for uniform thawing and better texture retention in frozen foods.
Conventional Microwave vs Inverter Microwave for even heating Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com