Microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly but can sometimes result in uneven heating or dryness. Steam microwaves combine microwave energy with steam, preserving moisture and enhancing texture while reheating. Choosing a steam microwave ensures juicier, more evenly heated meals compared to traditional microwave ovens.
Table of Comparison
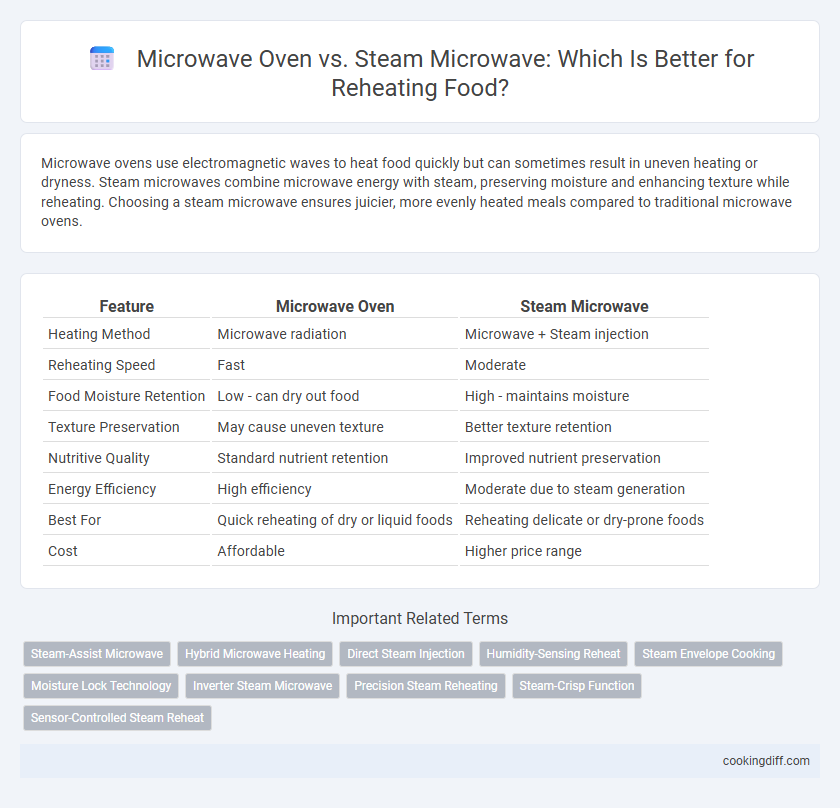
| Feature | Microwave Oven | Steam Microwave |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Microwave radiation | Microwave + Steam injection |
| Reheating Speed | Fast | Moderate |
| Food Moisture Retention | Low - can dry out food | High - maintains moisture |
| Texture Preservation | May cause uneven texture | Better texture retention |
| Nutritive Quality | Standard nutrient retention | Improved nutrient preservation |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency | Moderate due to steam generation |
| Best For | Quick reheating of dry or liquid foods | Reheating delicate or dry-prone foods |
| Cost | Affordable | Higher price range |
Introduction to Microwave Oven vs Steam Microwave
Microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to rapidly heat food by agitating water molecules, making them ideal for quick reheating. Steam microwaves combine traditional microwave heating with steam injection, enhancing moisture retention and reducing food dryness. This technology improves texture and flavor, offering a healthier alternative for reheating leftovers compared to conventional microwave ovens.
Key Differences Between Microwave and Steam Microwave
Microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly by agitating water molecules, resulting in fast reheating but sometimes uneven heating. In contrast, steam microwaves combine microwave energy with steam, providing more even heat distribution and retaining moisture in food during reheating.
Microwaves typically reheat food within minutes but may cause dryness or texture changes, whereas steam microwaves maintain food texture and prevent drying out due to the added moisture. The steam function also helps in killing bacteria more effectively, making steam microwaves a healthier option for reheating leftovers.
How Each Appliance Works for Reheating
| Microwave Oven | Uses electromagnetic waves to agitate water molecules in food, generating heat rapidly for reheating. The waves penetrate food unevenly, sometimes causing hot spots and cold centers. Best suited for quick reheating of homogeneous, moist foods. |
|---|---|
| Steam Microwave | Combines microwave radiation with steam injection, enhancing moisture retention and heating uniformity. Steam surrounds the food, preventing dryness and promoting even reheating. Ideal for delicate foods that require gentle heat and moisture preservation. |
Speed and Efficiency of Reheating
Microwave ovens reheat food rapidly by emitting electromagnetic waves that excite water molecules, achieving faster heating times compared to steam microwaves. Steam microwaves combine microwaving with steam injection, providing more even heating but typically requiring slightly longer reheating durations.
The speed advantage of traditional microwave ovens makes them ideal for quick reheating of small, dry, or solid foods. Steam microwaves enhance efficiency by retaining moisture and preventing food from drying out, which is especially beneficial for reheating vegetables and delicate dishes. While steam microwaves may take a few extra minutes, their balanced approach often results in better texture and flavor retention.
Food Quality and Texture After Reheating
Microwave ovens quickly reheat food but often cause dryness and uneven texture due to direct microwave radiation. Steam microwaves maintain moisture and tenderness by combining microwaves with steam, preserving food quality more effectively after reheating.
- Microwave Oven Texture - Food can become dry and rubbery because microwaves heat water molecules unevenly.
- Steam Microwave Moisture Retention - Steam adds humidity, preventing food from drying out and keeping it tender.
- Food Quality Preservation - Steam microwaves better preserve original flavors and mouthfeel during reheating.
Nutrient Retention in Reheated Food
Microwave ovens reheat food quickly but often cause nutrient loss due to uneven heating and high temperatures. Steam microwaves use moist heat, which better preserves vitamins and minerals during reheating.
- Microwave oven - Utilizes electromagnetic waves that can degrade heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C and folate.
- Steam microwave - Combines microwave energy with steam to maintain moisture and reduce nutrient degradation.
- Nutrient retention - Steam microwaving significantly enhances retention of antioxidants compared to conventional microwaving.
Steam microwaves offer a superior method for reheating while maintaining the nutritional quality of food.
Moisture Control: Dryness vs Steam
How does moisture control differ between a microwave oven and a steam microwave when reheating food? Standard microwave ovens tend to dry out food due to uneven heating and lack of moisture retention. Steam microwaves use controlled steam to maintain hydration, resulting in evenly reheated meals with significantly less dryness.
Versatility for Different Foods
Microwave ovens excel in reheating a wide variety of foods quickly, from leftovers to frozen meals, due to their powerful and consistent microwave radiation. Their straightforward heating method makes them ideal for dry or solid foods.
Steam microwaves offer enhanced versatility by incorporating steam technology that preserves moisture and texture, making them perfect for reheating delicate foods like vegetables, seafood, and baked goods. The steam function reduces dryness and uneven heating often experienced in conventional microwaves.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Microwave ovens generally consume less energy than steam microwaves due to their faster reheating times and direct electromagnetic wave heating method. Steam microwaves use additional energy to generate steam, increasing overall consumption during reheating processes.
- Microwave ovens energy efficiency - They consume approximately 0.6 kWh per hour of use by directly exciting water molecules in food.
- Steam microwave energy consumption - Incorporates a steam generation system that increases energy use to about 0.9 kWh per hour.
- Reheating duration impact - Faster reheating in standard microwaves results in lower total energy usage compared to longer steam microwave cycles.
Related Important Terms
Steam-Assist Microwave
Steam-assist microwaves enhance reheating by combining microwave energy with steam, preserving moisture and improving food texture compared to conventional microwave ovens. This technology ensures even heating, reduces drying out, and maintains the nutritional quality of leftovers, making it ideal for diverse meal types.
Hybrid Microwave Heating
Hybrid microwave heating combines microwave energy with steam technology, enhancing reheating by maintaining food moisture and ensuring uniform temperature distribution. Compared to conventional microwave ovens, steam microwaves reduce drying out and improve texture retention, making them ideal for reheating delicate dishes and preserving nutritional quality.
Direct Steam Injection
Microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly but can sometimes result in uneven reheating or drying out, whereas steam microwaves with Direct Steam Injection evenly distribute moisture and heat, preserving texture and preventing dryness. The Direct Steam Injection technology infuses steam directly into the cooking cavity, enhancing reheating efficiency and maintaining food quality by preventing surface dehydration.
Humidity-Sensing Reheat
Microwave ovens with humidity-sensing reheat technology adjust cooking time based on the moisture level of the food, preventing over-drying and ensuring even heating. Steam microwaves combine this sensor with steam injection, enhancing moisture retention and delivering juicier, more evenly reheated meals.
Steam Envelope Cooking
Steam envelope cooking in steam microwaves enhances reheating by infusing moisture, preserving texture and flavor unlike traditional microwave ovens that can cause dryness and uneven heating. The steam envelope creates a humid environment that accelerates heat transfer and prevents food from becoming tough, making it ideal for delicate dishes and leftovers.
Moisture Lock Technology
Microwave ovens use rapid electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly but can cause uneven moisture loss, resulting in dry or tough textures. Steam microwaves with Moisture Lock Technology infuse steam during reheating, preserving food's natural moisture and enhancing texture and flavor retention for superior reheated meals.
Inverter Steam Microwave
Inverter Steam Microwaves offer precise temperature control and evenly distributed steam for reheating, preserving moisture and texture better than traditional microwave ovens which rely solely on electromagnetic waves. This technology minimizes overheating and nutrient loss, making it ideal for efficiently warming food without drying or toughening.
Precision Steam Reheating
Microwave ovens utilize electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly but often result in uneven reheating and moisture loss, while steam microwaves employ precision steam reheating technology that ensures uniform temperature distribution and preserves food moisture. This method enhances texture and flavor by combining microwave energy with controlled steam injection, reducing the risk of overcooking and maintaining nutritional quality.
Steam-Crisp Function
The Steam-Crisp function in steam microwaves combines microwave heating with steam injection, delivering faster reheating times while maintaining food moisture and crispness compared to conventional microwave ovens. This technology prevents sogginess by creating a perfect balance of steam and heat, ensuring reheated meals retain fresh-like textures and enhanced flavor profiles.
Microwave Oven vs Steam Microwave for reheating Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com