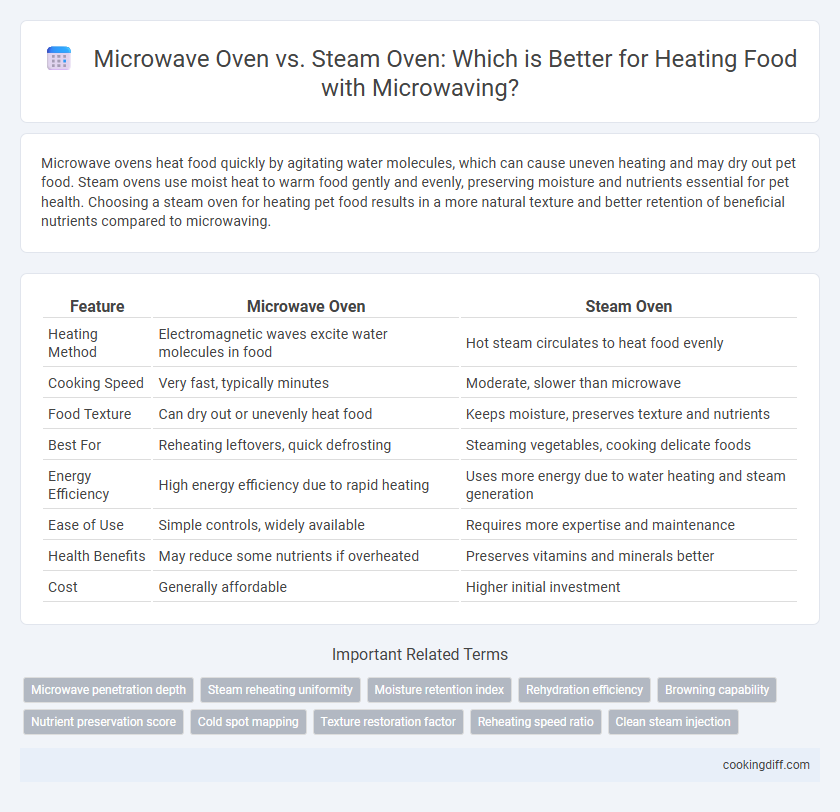
Microwave ovens heat food quickly by agitating water molecules, which can cause uneven heating and may dry out pet food. Steam ovens use moist heat to warm food gently and evenly, preserving moisture and nutrients essential for pet health. Choosing a steam oven for heating pet food results in a more natural texture and better retention of beneficial nutrients compared to microwaving.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Microwave Oven | Steam Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Electromagnetic waves excite water molecules in food | Hot steam circulates to heat food evenly |
| Cooking Speed | Very fast, typically minutes | Moderate, slower than microwave |
| Food Texture | Can dry out or unevenly heat food | Keeps moisture, preserves texture and nutrients |
| Best For | Reheating leftovers, quick defrosting | Steaming vegetables, cooking delicate foods |
| Energy Efficiency | High energy efficiency due to rapid heating | Uses more energy due to water heating and steam generation |
| Ease of Use | Simple controls, widely available | Requires more expertise and maintenance |
| Health Benefits | May reduce some nutrients if overheated | Preserves vitamins and minerals better |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Higher initial investment |
Introduction: Comparing Microwave and Steam Ovens
Microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to rapidly heat food by agitating water molecules, offering quick and convenient reheating. Steam ovens utilize moist heat to warm food gently, preserving texture and nutrients more effectively than microwaves.
- Speed - Microwave ovens heat food faster, typically within minutes, ideal for quick meals.
- Food Quality - Steam ovens maintain moisture and enhance flavor retention during heating.
- Energy Efficiency - Microwaves generally consume less energy compared to steam ovens for similar tasks.
Choosing between a microwave and steam oven depends on priorities such as speed, food texture, and nutritional preservation.
How Microwave Ovens Heat Food
Microwave ovens heat food by emitting electromagnetic waves that excite water molecules, causing them to vibrate and generate heat rapidly. This process allows food to warm evenly and quickly without heating the surrounding air.
Unlike steam ovens, which heat food through moist hot air and require more time for temperature transfer, microwave ovens penetrate food at a molecular level, resulting in faster heating. The microwaves specifically target polar molecules such as water, fats, and sugars, enabling efficient internal heating. This precise mechanism makes microwave ovens ideal for quick reheating and defrosting tasks.
How Steam Ovens Work for Reheating
| Steam ovens use moist heat generated by boiling water to evenly reheat food, preserving moisture and texture better than microwave ovens. |
| Unlike microwave ovens, which heat food unevenly by agitating water molecules, steam ovens envelop food in steam that penetrates and warms food uniformly. |
| Steam reheating reduces the risk of drying out or overcooking, making it ideal for delicate dishes and retaining nutrients effectively. |
Speed and Efficiency: Which Heats Faster?
Microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to excite water molecules in food, resulting in rapid heating that typically takes minutes. This direct energy transfer makes microwaves extremely efficient for heating or reheating meals quickly.
Steam ovens rely on convection of hot steam to transfer heat, which takes longer but provides more even temperature distribution and better moisture retention. While slower in speed, steam ovens enhance food texture and reduce drying compared to microwaves.
Food Texture and Quality After Heating
Microwave ovens heat food rapidly but can often result in uneven textures and moisture loss, leading to dry or rubbery spots. Steam ovens preserve food's moisture and texture better by gently heating through steam, maintaining a more natural and tender quality.
- Microwave ovens speed up heating - They use electromagnetic waves that excite water molecules, causing rapid internal heating but sometimes uneven cooking.
- Steam ovens maintain moisture - Steam gently penetrates food, preventing drying out and preserving delicate textures and flavors.
- Food quality retention - Steam ovens generally yield higher food quality with tender, juicy results compared to the often tougher or patchy textures from microwaving.
Nutrient Retention: Microwave vs Steam Oven
Microwave ovens preserve nutrients efficiently by using rapid, high-frequency waves that heat food quickly, minimizing nutrient loss. Steam ovens maintain nutrient content by cooking food with moist heat, which reduces the leaching of water-soluble vitamins compared to boiling. Both methods offer superior nutrient retention compared to conventional ovens, with steam ovens being particularly effective for delicate vegetables and microwave ovens excelling in speed.
Usability and Convenience in Everyday Cooking
Microwave ovens offer rapid heating and easy operation, making them ideal for quick meal preparation and reheating leftovers with minimal effort. Their compact design and preset functions enhance usability, especially in busy households.
Steam ovens excel in evenly heating food while preserving moisture and nutrients, providing a more gentle cooking process suitable for delicate dishes. They require longer heating times and more attention, which can be less convenient for everyday quick use.
Energy Consumption: Which is More Efficient?
Microwave ovens typically consume less energy for heating food quickly by targeting water molecules directly, resulting in faster cooking times with lower power usage. Steam ovens use more energy due to the need to generate steam and maintain temperature for thorough heating, making them less efficient for quick reheat tasks.
- Microwave ovens use 50-65% less energy - They heat food rapidly by exciting water molecules, minimizing energy waste.
- Steam ovens require more power - Energy consumption increases due to water heating and steam generation processes.
- Efficiency depends on cooking duration - Longer heating cycles in steam ovens reduce overall energy efficiency compared to microwaves.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Microwave ovens require minimal maintenance with easy-to-clean interiors made from smooth materials that resist stains and odors, making them ideal for quick daily use. Steam ovens demand more thorough cleaning to prevent mineral buildup and mold due to their high humidity environment, often requiring descaling and regular water reservoir care. Both appliances benefit from routine wiping, but steam ovens typically involve more complex cleaning protocols to maintain optimal performance and hygiene.
Related Important Terms
Microwave penetration depth
Microwave ovens utilize electromagnetic waves with a penetration depth typically ranging from 1 to 3 centimeters, allowing rapid internal heating by exciting water molecules within food. Steam ovens rely on convective heat transfer with steam, heating food more evenly on the surface but with limited penetration, resulting in slower internal heating compared to microwaves.
Steam reheating uniformity
Steam ovens provide superior reheating uniformity compared to microwave ovens by using moist heat that evenly penetrates food, preventing hot and cold spots commonly experienced in microwaving. This consistent steam heat preserves texture and flavor while ensuring thorough warming throughout the dish.
Moisture retention index
Microwave ovens typically have a lower moisture retention index due to rapid heating that can cause water evaporation, while steam ovens excel in preserving moisture by surrounding food with hot steam, maintaining juiciness and texture. Studies show steam ovens retain up to 30% more moisture compared to microwave ovens, enhancing flavor and nutritional value.
Rehydration efficiency
Microwave ovens use dielectric heating to rapidly excite water molecules, offering fast reheating but often resulting in uneven moisture distribution and partial dehydration of food. Steam ovens maintain a moist environment by injecting steam during the heating process, enhancing rehydration efficiency, preserving texture, and preventing food from drying out.
Browning capability
Microwave ovens heat food rapidly using electromagnetic waves but typically lack browning capability, resulting in steamed or soggy textures. Steam ovens use moist heat to cook food evenly and can achieve slight caramelization, though they generally do not produce the crisp, browned surfaces characteristic of convection ovens.
Nutrient preservation score
Microwave ovens heat food rapidly by agitating water molecules, often preserving more water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex compared to steam ovens, which use moist heat and can cause nutrient leaching. Steam ovens excel in retaining minerals and antioxidants due to gentle cooking temperatures, resulting in a higher overall nutrient preservation score for delicate vegetables and fruits.
Cold spot mapping
Microwave ovens often create uneven heating due to microwave interference patterns causing cold spots, whereas steam ovens provide more uniform heat distribution, minimizing cold spot formation by enveloping food in moist, consistent steam. Cold spot mapping in microwave ovens reveals these inconsistent hot and cold zones, critical for ensuring food safety and thorough reheating.
Texture restoration factor
Microwave ovens rapidly heat food through dielectric heating, often causing uneven texture restoration and moisture loss, leading to a rubbery or dry mouthfeel. Steam ovens utilize moist heat to gently reheat food, preserving and improving texture by maintaining moisture, resulting in a more tender and evenly heated meal.
Reheating speed ratio
Microwave ovens reheat food significantly faster, with average times reducing up to 70% compared to steam ovens due to their electromagnetic waves directly agitating water molecules. Steam ovens, while slower by 30-50% in reheating speed, excel in preserving moisture and texture through gentle, uniform heat distribution.
Microwave oven vs Steam oven for heating food. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com