Microwaving vegetables offers a quick and energy-efficient method that preserves nutrients by minimizing cooking time. Steam ovens provide even heat distribution and gentle cooking, enhancing texture and flavor while retaining vitamins more effectively. Choosing between the two depends on desired texture, nutrient retention, and kitchen convenience.
Table of Comparison
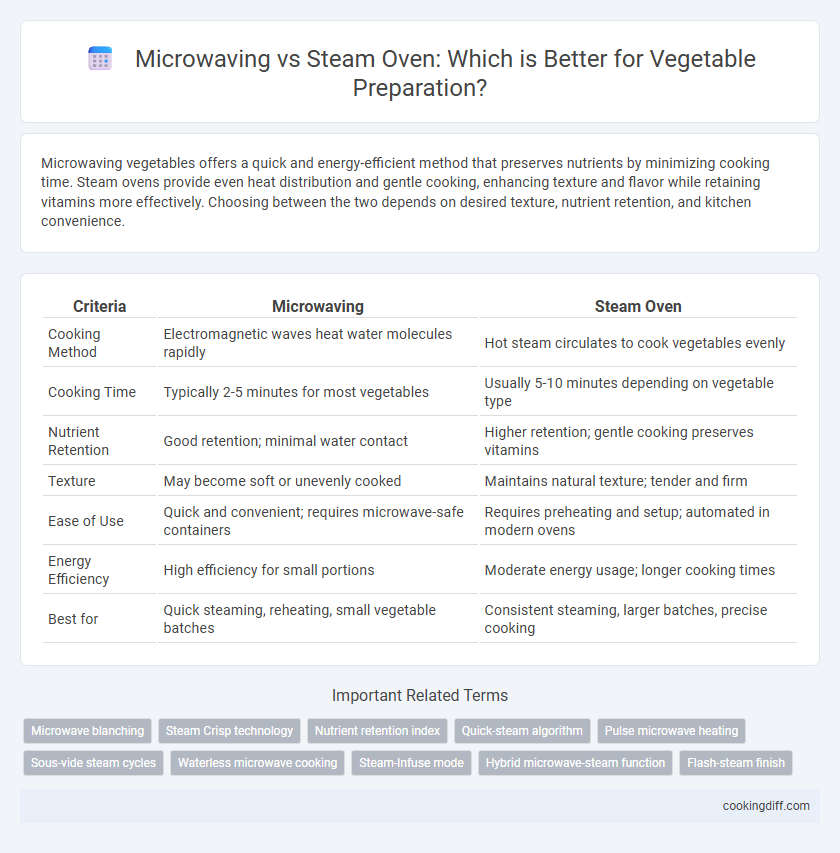
| Criteria | Microwaving | Steam Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Electromagnetic waves heat water molecules rapidly | Hot steam circulates to cook vegetables evenly |
| Cooking Time | Typically 2-5 minutes for most vegetables | Usually 5-10 minutes depending on vegetable type |
| Nutrient Retention | Good retention; minimal water contact | Higher retention; gentle cooking preserves vitamins |
| Texture | May become soft or unevenly cooked | Maintains natural texture; tender and firm |
| Ease of Use | Quick and convenient; requires microwave-safe containers | Requires preheating and setup; automated in modern ovens |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency for small portions | Moderate energy usage; longer cooking times |
| Best for | Quick steaming, reheating, small vegetable batches | Consistent steaming, larger batches, precise cooking |
Nutritional Retention: Microwaving vs Steam Oven
Microwaving vegetables generally retains more water-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin C and B-complex, due to shorter cooking times and minimal water use. Steam ovens preserve nutrients by cooking at lower temperatures and preventing direct contact with water, reducing nutrient leaching. Studies show both methods outperform boiling, but microwaving often leads to higher retention of heat-sensitive nutrients.
Flavor and Texture Differences in Vegetables
Microwaving vegetables often preserves their natural flavors by quickly heating them and minimizing nutrient loss, but it can sometimes lead to uneven texture and slight overcooking. The rapid heating can cause some parts to become mushy while others remain undercooked, affecting overall mouthfeel.
Steam ovens use gentle, moist heat that enhances vegetable texture, resulting in crisp-tender bites and vibrant colors. This method maintains the vegetable's structural integrity better, producing a more consistent and fresh flavor profile throughout.
Cooking Speed: Microwaving Compared to Steam Oven
| Cooking Speed | Microwaving heats vegetables significantly faster by directly exciting water molecules, typically reducing cooking time to 3-5 minutes. Steam ovens use indirect heat via steam circulation, which usually requires 10-15 minutes for similar vegetable preparation. Microwaving offers a time-efficient option without compromising nutrient retention compared to the slower steam oven method. |
Energy Efficiency: Which Method is Greener?
Microwaving vegetables consumes significantly less energy compared to steam ovens, making it a more energy-efficient option for quick cooking. The microwave uses electromagnetic waves that directly heat water molecules, reducing heat loss and overall cooking time.
Steam ovens require more electricity to generate and maintain steam, leading to higher energy consumption during vegetable preparation. Choosing microwaving over steam ovens can reduce your carbon footprint and lower utility costs while preserving vegetable nutrients.
Moisture Control in Vegetable Preparation
Microwaving retains moisture by rapidly heating water molecules inside vegetables, which can sometimes lead to uneven moisture distribution and occasional drying at the edges. Steam ovens provide consistent, gentle steam heat that preserves the natural moisture and texture of vegetables more effectively. For optimal moisture control, steam ovens are preferred due to their ability to maintain a humid environment, preventing dehydration during cooking.
Ease of Use and Convenience
Microwaving offers quick and straightforward vegetable preparation with minimal setup, making it highly convenient for busy households. Steam ovens require preheating and a more involved process but provide consistent results with enhanced flavor retention.
- Microwave Speed - Microwaves cook vegetables rapidly, often within minutes, reducing overall meal prep time.
- Steam Oven Complexity - Steam ovens demand time to preheat and monitor steaming cycles, adding steps to the cooking process.
- Cleanup Convenience - Microwaves generally involve easier cleanup due to simple containers, unlike steam ovens which may have multiple removable parts.
Equipment Cost and Kitchen Space
Microwaves typically cost between $50 and $300, making them a more budget-friendly option compared to steam ovens, which range from $400 to over $1,000. Compact in design, microwaves require minimal kitchen space, fitting easily on countertops or inside cabinets.
Steam ovens, while more expensive, offer multifunctional cooking capabilities that can justify their higher price for some households. These ovens are larger and need dedicated installation space, often built into kitchen cabinetry. Choosing between the two depends on budget constraints and available kitchen space for efficient vegetable preparation.
Versatility Beyond Vegetables
Microwaving offers rapid heating and defrosting capabilities suitable for diverse food types beyond vegetables. Steam ovens provide gentle, even cooking ideal for proteins, grains, and delicate dishes with moisture retention.
- Microwaving versatility - Efficient for reheating leftovers, melting ingredients, and quick defrosting tasks.
- Steam oven multifunctionality - Enables baking, roasting, and slow cooking with consistent steam infusion.
- Health benefits - Steam ovens preserve nutrients across various foods better than microwaves due to lower temperature cooking.
Choosing between these appliances depends on the desired cooking technique and food variety beyond vegetable preparation.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Which appliance demands less cleaning and maintenance for vegetable preparation, a microwave or a steam oven? Microwaves require minimal cleaning, as their interiors often feature smooth surfaces and removable turntables that are easy to wipe down. Steam ovens, while offering superior cooking quality, typically need more frequent descaling and careful maintenance of water reservoirs to prevent buildup and ensure optimal performance.
Related Important Terms
Microwave blanching
Microwave blanching preserves more nutrients and reduces cooking time compared to traditional steam ovens, making it an efficient method for vegetable preparation. This technique uses microwave energy to rapidly heat vegetables, ensuring even cooking and maintaining texture without water leaching essential vitamins.
Steam Crisp technology
Steam Crisp technology combines precise steam injection with convection heating, preserving the nutrients and natural texture of vegetables better than traditional microwaving. This method enhances flavor retention and delivers crispness without drying out produce, offering superior vegetable preparation compared to standard microwave cooking.
Nutrient retention index
Microwaving preserves up to 80-90% of nutrients in vegetables compared to traditional boiling, thanks to shorter cooking times and minimal water use, whereas steam ovens maintain nutrient retention slightly higher, often reaching 90-95%, by cooking food with moist heat that reduces nutrient loss. Studies highlight that steam ovens are particularly effective at preserving heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex, making them a superior choice for maximizing the Nutrient Retention Index (NRI) in vegetable preparation.
Quick-steam algorithm
The Quick-steam algorithm in steam ovens offers precise temperature and humidity control for optimal vegetable texture, preserving nutrients more effectively than traditional microwaving. Microwaving heats unevenly and risks nutrient loss due to variable power distribution, making steam ovens with Quick-steam a superior choice for consistent, healthy vegetable preparation.
Pulse microwave heating
Pulse microwave heating rapidly cooks vegetables by delivering controlled bursts of microwave energy, preserving nutrients and texture more effectively than continuous heating methods. Compared to steam ovens, pulse microwaving reduces cooking time while maintaining crispness and enhancing the retention of water-soluble vitamins.
Sous-vide steam cycles
Microwaving vegetables offers rapid heating but can lead to uneven cooking and nutrient loss, whereas steam ovens with sous-vide steam cycles provide precise temperature control and gentle, even cooking that preserves vitamins and texture. Sous-vide steam cycles optimize moisture retention and flavor development by maintaining low, consistent temperatures, enhancing the nutritional quality and sensory attributes of cooked vegetables compared to microwaving.
Waterless microwave cooking
Waterless microwave cooking preserves more nutrients in vegetables compared to steam ovens by using minimal or no added water, thus reducing nutrient leaching and enhancing flavor retention. Microwaves heat food quickly through dielectric heating, maintaining vegetable texture while steam ovens rely on steam, which can cause slight nutrient loss due to condensation and longer cooking times.
Steam-Infuse mode
Steam-Infuse mode in steam ovens ensures even heat distribution and preserves nutrients by cooking vegetables at precise steam temperatures, enhancing texture and flavor significantly more than microwaving. Unlike microwaving, which can cause uneven heating and nutrient loss, steam-infuse cooking maintains vegetable integrity and moisture content for superior quality.
Hybrid microwave-steam function
The hybrid microwave-steam function combines rapid cooking from microwaves with gentle steaming to preserve nutrients and texture in vegetables more effectively than traditional methods. This dual technology ensures even heat distribution and moisture retention, resulting in crisp-tender vegetables with enhanced flavor and higher vitamin content.
Microwaving vs Steam Oven for vegetable preparation Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com