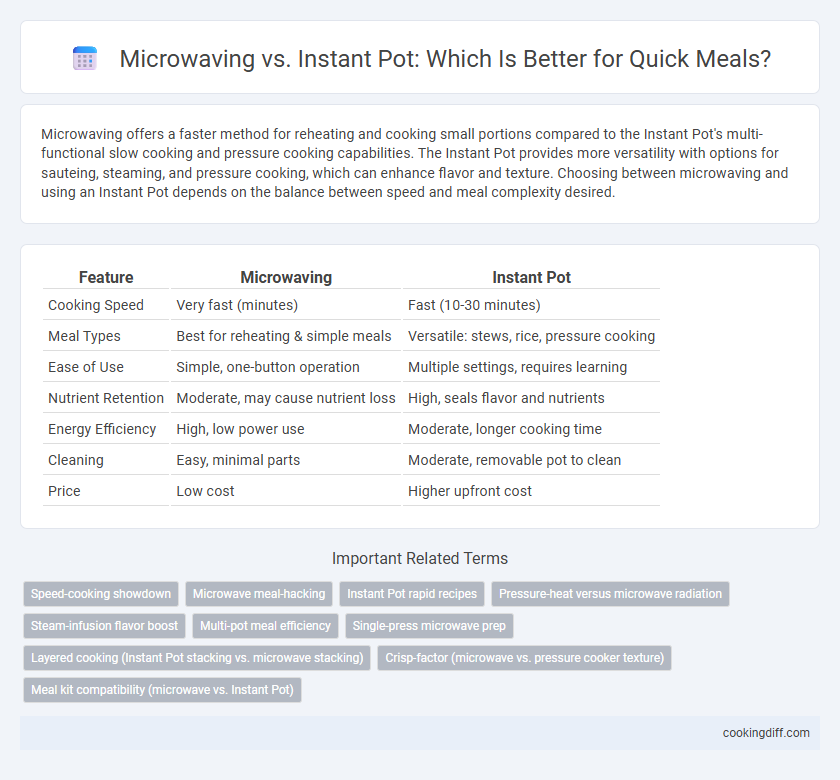
Microwaving offers a faster method for reheating and cooking small portions compared to the Instant Pot's multi-functional slow cooking and pressure cooking capabilities. The Instant Pot provides more versatility with options for sauteing, steaming, and pressure cooking, which can enhance flavor and texture. Choosing between microwaving and using an Instant Pot depends on the balance between speed and meal complexity desired.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Microwaving | Instant Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Speed | Very fast (minutes) | Fast (10-30 minutes) |
| Meal Types | Best for reheating & simple meals | Versatile: stews, rice, pressure cooking |
| Ease of Use | Simple, one-button operation | Multiple settings, requires learning |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate, may cause nutrient loss | High, seals flavor and nutrients |
| Energy Efficiency | High, low power use | Moderate, longer cooking time |
| Cleaning | Easy, minimal parts | Moderate, removable pot to clean |
| Price | Low cost | Higher upfront cost |
Speed Comparison: Microwaving vs Instant Pot
Microwaving generally cooks food faster than the Instant Pot, making it ideal for meals that require minimal prep and cooking time. The Instant Pot, while slower, offers more versatile cooking options and can prepare complex dishes quickly compared to traditional stovetop methods.
- Microwaving speed - Typically heats food within 1-5 minutes depending on quantity and wattage.
- Instant Pot speed - Requires 10-30 minutes including pressure build-up and release times, but speeds up slow cooking processes.
- Meal complexity - Microwaves excel at reheating or simple meals, while Instant Pots efficiently cook stews, rice, and meats from scratch faster than ovens or stovetops.
Taste and Texture Differences Between Methods
Microwaving often results in uneven heating, which can affect the texture by making some parts soggy while others remain cold, compromising the overall taste experience. In contrast, the Instant Pot uses pressure cooking to preserve moisture and enhance flavors, delivering a more consistent texture and richer taste. For quick meals, the Instant Pot generally offers superior texture and flavor retention compared to microwaving.
Nutritional Impact: Which Retains More Nutrients?
Which method retains more nutrients, microwaving or using an Instant Pot, when preparing quick meals? Microwaving often preserves more vitamins and minerals due to shorter cooking times and reduced water exposure. The Instant Pot, while efficient, may cause slight nutrient loss because of longer cooking durations and higher temperatures.
Versatility: What Can You Cook in Each?
Microwaving excels at reheating leftovers and cooking simple meals like steamed vegetables or microwaveable pasta with speed and convenience. Its limited cooking methods focus mainly on boiling, steaming, and defrosting, making it ideal for quick, straightforward dishes.
The Instant Pot offers versatility by combining pressure cooking, slow cooking, sauteing, and steaming, allowing you to prepare a wide range of meals including soups, stews, rice, yogurt, and even desserts. Its multifunctional features support complex recipes and one-pot meals that require varying cooking techniques and timings.
Energy Efficiency: Which Uses Less Power?
Microwaves typically use about 600 to 1200 watts of power, making them highly energy-efficient for reheating and cooking small portions quickly. Instant Pots consume around 700 to 1200 watts during pressure cooking but maintain heat for longer periods, which can increase overall power consumption.
For quick meals, microwaves generally use less energy due to their shorter cooking times and targeted heating technology. Instant Pots may be more energy-efficient for slow cooking or dishes requiring longer cooking times, but microwaving wins in terms of speed and minimal power usage.
Ease of Use: User-Friendly Features
| Microwaving | Offers straightforward operation with simple settings like power levels and timers, enabling quick meal preparation without complex programming. |
| Instant Pot | Boasts multiple preset cooking programs and digital displays that guide users through steps, combining pressure cooking and other functions in one device. |
| Ease of Use Comparison | Microwaves excel in immediate usability with minimal learning curve, while Instant Pots provide versatile features that require familiarization but deliver multifunctional convenience. |
Clean-Up: Which Appliance Is Easier to Maintain?
Microwaving typically involves fewer components, making it quicker to clean compared to the Instant Pot. Instant Pots have multiple parts like sealing rings and inner pots, which require thorough washing after each use.
- Microwave simplicity - Most microwaves have a smooth interior that can be wiped clean effortlessly with a damp cloth.
- Instant Pot parts - The lid, sealing ring, and inner pot of an Instant Pot must be cleaned separately, increasing maintenance time.
- Dishwasher compatibility - Many Instant Pot accessories are dishwasher safe, whereas microwaves generally need manual cleaning.
Safety Considerations for Quick Cooking
Microwaving uses electromagnetic waves to rapidly heat food, but uneven heating can cause hot spots, posing burn risks if not handled carefully. Instant Pots provide controlled pressure cooking with built-in safety mechanisms to prevent accidents like explosions or steam burns.
Microwaves eliminate the need for preheating, reducing exposure to heat-related hazards, though containers must be microwave-safe to avoid toxic leaching. Instant Pots lock securely during operation, minimizing the risk of lid removal under pressure, but improper sealing can lead to dangerous steam release. Both appliances require user caution, but Instant Pots generally offer more advanced safety features for quick meal preparation.
Cost Comparison: Appliance and Operating Expenses
Microwaves typically have a lower upfront cost compared to Instant Pots, making them a budget-friendly option for quick meals. Operating expenses for microwaves are generally lower due to shorter cooking times and less energy consumption.
- Initial Cost Advantage - Microwaves usually range from $50 to $150, while Instant Pots start around $80 and can exceed $200 depending on features.
- Energy Efficiency - Microwaves consume approximately 600-1200 watts during operation, often using less total energy for simple reheating tasks compared to Instant Pots' longer cooking cycles.
- Maintenance and Durability - Microwaves require minimal maintenance and have fewer components prone to failure, lowering long-term operating costs compared to pressure cookers.
Choosing a microwave is financially advantageous for those prioritizing low appliance and energy costs in quick meal preparation.
Related Important Terms
Speed-cooking showdown
Microwaving delivers rapid heat penetration using electromagnetic waves, cooking meals in minutes ideal for simple dishes or reheating leftovers. The Instant Pot combines pressure cooking and multiple functions, accelerating cooking times for complex meals while retaining moisture and flavor, making it a versatile choice for fast and flavorful dishes.
Microwave meal-hacking
Microwaving offers unparalleled speed by heating food in minutes through electromagnetic waves, ideal for quick meal hacks like steaming vegetables or reheating leftovers without flavor compromise. Utilizing microwave-safe containers and techniques such as layering ingredients or covering with a damp paper towel enhances moisture retention and evenly cooked results, making microwaving a convenient alternative to the longer cook times of Instant Pots.
Instant Pot rapid recipes
Instant Pot rapid recipes leverage pressure cooking technology, reducing meal preparation time to under 30 minutes while retaining flavors and nutrients better than microwaving. These recipes offer versatile options from stews to steamed vegetables, making the Instant Pot a preferred choice for quick, wholesome meals.
Pressure-heat versus microwave radiation
Pressure-heat in an Instant Pot cooks food by raising boiling points and rapidly breaking down fibers through high steam pressure, resulting in tender meals within minutes. Microwave radiation heats food by agitating water molecules at a molecular level, providing rapid cooking but often with uneven heat distribution and less tenderizing effect compared to pressure cooking.
Steam-infusion flavor boost
Microwaving retains essential nutrients rapidly but often lacks the depth of flavor that steam-infusion technology in Instant Pots enhances by circulating steam to intensify taste and moisture. The Instant Pot's steam-infusion method significantly boosts meal flavor profiles while maintaining speed, offering a superior quick-cooking solution over standard microwaving.
Multi-pot meal efficiency
Microwaving offers rapid heating but often lacks the multi-pot meal efficiency seen in Instant Pots, which combine pressure cooking, slow cooking, and sauteing in a single device. Instant Pots significantly reduce total cooking time for complex meals by integrating multiple functions, optimizing energy use, and minimizing cleanup.
Single-press microwave prep
Single-press microwave meals offer unmatched convenience with minimal prep time, making them ideal for quick snacks or simple dishes. Compared to Instant Pot cooking, microwaving provides faster results without the need for extensive setup or multiple steps, streamlining meal preparation in under five minutes.
Layered cooking (Instant Pot stacking vs. microwave stacking)
Microwaving allows quick reheating but struggles with effective layered cooking due to uneven heat distribution, whereas the Instant Pot's stacking trays enable simultaneous cooking of multiple ingredients with even heat application and flavor integration. The Instant Pot's pressure cooking enhances the taste and texture in layered dishes, offering a more efficient and gourmet approach compared to microwave stacking, which is limited to reheating convenience.
Crisp-factor (microwave vs. pressure cooker texture)
Microwaving preserves a crisp texture in foods like reheated pizza or roasted vegetables by using rapid, high-frequency electromagnetic waves that heat water molecules quickly without steaming. In contrast, the Instant Pot's pressure cooking method often softens or steams ingredients, resulting in tender but less crispy textures, making microwaves preferable for meals where crispness is desired.
Microwaving vs Instant Pot for quick meals Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com