Cheesecloth offers breathable coverage for pickling, allowing gases to escape while keeping out insects and debris, ideal for short-term or open-air fermentation. Fermentation lids provide an airtight seal with built-in airlocks to release carbon dioxide, ensuring controlled anaerobic conditions for consistent, long-term fermentation. Choosing between cheesecloth and a fermentation lid depends on the desired fermentation environment and the level of protection needed for pickling utensils.
Table of Comparison
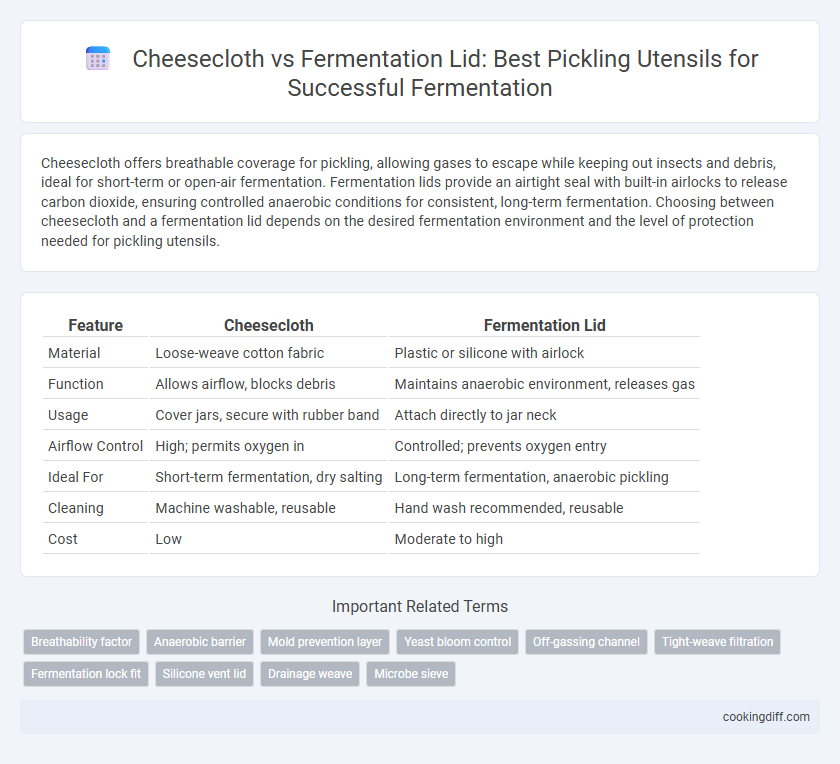
| Feature | Cheesecloth | Fermentation Lid |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Loose-weave cotton fabric | Plastic or silicone with airlock |
| Function | Allows airflow, blocks debris | Maintains anaerobic environment, releases gas |
| Usage | Cover jars, secure with rubber band | Attach directly to jar neck |
| Airflow Control | High; permits oxygen in | Controlled; prevents oxygen entry |
| Ideal For | Short-term fermentation, dry salting | Long-term fermentation, anaerobic pickling |
| Cleaning | Machine washable, reusable | Hand wash recommended, reusable |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to high |
Understanding Cheesecloth and Fermentation Lids
Cheesecloth is a loosely woven cotton fabric that allows air circulation while keeping out insects and debris during the pickling process. Fermentation lids are specially designed to create an anaerobic environment by releasing gas and preventing oxygen exposure, which is crucial for proper fermentation.
Cheesecloth is ideal for short-term pickling or brining when airflow is needed to prevent mold growth. Fermentation lids include an airlock system that maintains pressure balance and inhibits contamination, making them more effective for long-term fermentation projects. Understanding the differences between these utensils helps in selecting the best tool for successful pickling and fermentation outcomes.
Key Functions in Pickling: Cheesecloth vs Fermentation Lid
Cheesecloth serves as a breathable barrier allowing gases to escape while keeping contaminants out during the initial stages of pickling. Fermentation lids are designed with airlocks to maintain an anaerobic environment, crucial for preventing mold and harmful bacteria growth. Both utensils optimize fermentation by controlling airflow, but fermentation lids provide a more controlled and consistent environment ideal for long-term pickling processes.
Material Differences: Breathability and Durability
| Utensil | Material | Breathability | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cheesecloth | Loose-weave cotton fabric | High breathability allowing gases to escape during fermentation | Less durable; prone to tearing and requires frequent replacement |
| Fermentation Lid | Plastic or stainless steel with silicone seal | Controlled breathability via airlock preventing contamination | Highly durable and reusable over multiple fermentation cycles |
Ease of Use: Application in Pickling Jars
Cheesecloth offers a breathable, lightweight option for covering pickling jars, allowing gases to escape while keeping contaminants out, which simplifies the fermentation process. Its flexible nature makes it easy to secure with rubber bands, accommodating jars of various sizes without the need for specialized equipment.
Fermentation lids provide a more secure, airtight seal with built-in airlocks that vent gases automatically, reducing the risk of spoilage. These lids are designed for consistent use in fermentation, offering convenience and control over the pickling environment without frequent manual adjustments.
Impact on Fermentation Process
Cheesecloth allows airflow while protecting against contaminants, promoting natural fermentation by enabling beneficial aerobic bacteria growth. In contrast, a fermentation lid creates an anaerobic environment that helps prevent mold and unwanted bacteria, enhancing the control over fermentation conditions.
- Cheesecloth promotes oxygen exposure - This supports the growth of aerobic bacteria essential during early fermentation stages.
- Fermentation lids maintain anaerobic conditions - They reduce oxygen exposure, preventing mold and protecting lactic acid bacteria activity.
- Choice affects fermentation speed and flavor - Cheesecloth can lead to faster fermentation with complex flavors, while lids ensure consistent, controlled outcomes.
Preventing Contamination: Which Is Safer?
Cheesecloth allows airflow while providing a barrier against large contaminants, but it may not fully prevent airborne bacteria and mold during pickling. Fermentation lids create an airtight seal with an airlock system, minimizing exposure to oxygen and reducing the risk of contamination from harmful microorganisms.
The airtight environment produced by fermentation lids promotes anaerobic fermentation, which is essential for safe pickling processes. Cheesecloth's porous nature can lead to inconsistent fermentation by allowing unwanted microbes to enter, making fermentation lids a safer choice for preventing contamination.
Flavor and Texture: Effects of Each Utensil
Cheesecloth allows natural airflow during pickling, promoting a crisp texture and subtle tang by enabling wild fermentation bacteria to thrive. Fermentation lids create an anaerobic environment that enhances sour flavors and produces a softer texture through controlled carbon dioxide release. Choosing between cheesecloth or fermentation lid directly influences the balance of flavor complexity and texture firmness in the final pickled product.
Cleaning and Reusability Comparison
Cheesecloth is lightweight and easy to rinse but requires thorough drying to prevent mildew, making it less reusable over time. Fermentation lids are designed for easy cleaning and can be reused multiple times without degradation, offering greater durability for pickling processes.
- Cheesecloth Cleaning - Requires gentle washing and complete drying to avoid mold growth and maintain hygiene.
- Fermentation Lid Cleaning - Can be cleaned with soap and water or sanitized easily, ensuring consistent reuse without wear.
- Reusability Comparison - Fermentation lids provide longer-term usability, while cheesecloth often needs replacement after multiple uses.
Cost Analysis: Value for Home Picklers
Which pickling utensil offers better cost efficiency for home picklers, cheesecloth or a fermentation lid? Cheesecloth is an inexpensive, reusable option that requires minimal initial investment, making it ideal for those new to pickling. Fermentation lids, while costing more upfront, provide durable, airtight sealing that reduces the risk of contamination and spoilage, potentially saving money in the long term.
Related Important Terms
Breathability factor
Cheesecloth offers superior breathability during pickling, allowing gases to escape while preventing contaminants. Fermentation lids regulate airflow with built-in airlocks, providing controlled gas release but less natural ventilation.
Anaerobic barrier
Cheesecloth allows airflow during pickling, which can introduce oxygen and hinder anaerobic fermentation, while fermentation lids create a sealed environment that acts as an effective anaerobic barrier, preventing oxygen exposure and promoting optimal lactic acid bacteria growth. Using fermentation lids ensures a controlled anaerobic environment critical for successful pickling and preservation.
Mold prevention layer
Cheesecloth allows airflow that can lead to mold growth during pickling, while fermentation lids create an airtight seal that prevents mold by reducing oxygen exposure. Using fermentation lids as a mold prevention layer ensures a controlled anaerobic environment crucial for safe and effective fermentation.
Yeast bloom control
Cheesecloth allows airflow that promotes natural fermentation but may increase exposure to wild yeast, risking excessive yeast bloom and off-flavors in pickled products. Fermentation lids create a sealed environment with airlocks that effectively control yeast bloom by preventing oxygen ingress, ensuring consistent anaerobic conditions ideal for high-quality pickling.
Off-gassing channel
Cheesecloth allows airflow and acts as a basic off-gassing channel for pickling but lacks the airtight seal needed to prevent contamination, making it less effective for long-term fermentation. Fermentation lids are specifically designed with airlocks that provide controlled off-gassing while maintaining anaerobic conditions, crucial for preventing mold and ensuring consistent fermentation.
Tight-weave filtration
Cheesecloth offers a loose weave that allows airflow but may permit contaminants, whereas fermentation lids feature tight-weave filtration designed to prevent mold and bacteria while maintaining necessary gas exchange during pickling. The tight-weave filtration in fermentation lids ensures a controlled environment, enhancing safety and consistency in fermenting cucumbers and other vegetables.
Fermentation lock fit
A fermentation lid provides an airtight seal essential for optimal pickling by allowing gases to escape while preventing oxygen and contaminants from entering, ensuring a controlled anaerobic environment. Cheesecloth lacks a secure fit and barrier properties, making fermentation lids the superior choice for maintaining consistent fermentation conditions and reducing spoilage risk.
Silicone vent lid
Silicone vent lids offer precise airflow control and airtight sealing, enhancing pickling by preventing contamination while allowing gas release during fermentation. Compared to cheesecloth, silicone lids provide a reusable, durable, and mess-free solution that maintains consistent anaerobic conditions essential for optimal flavor and texture development.
Drainage weave
Cheesecloth offers a loose, breathable weave ideal for effective drainage and airflow during pickling, preventing moisture buildup and promoting fermentation. Fermentation lids provide a sealed environment but often lack the open drainage capability crucial for controlling brine levels and avoiding mold growth.
Cheesecloth vs fermentation lid for pickling utensils. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com